|
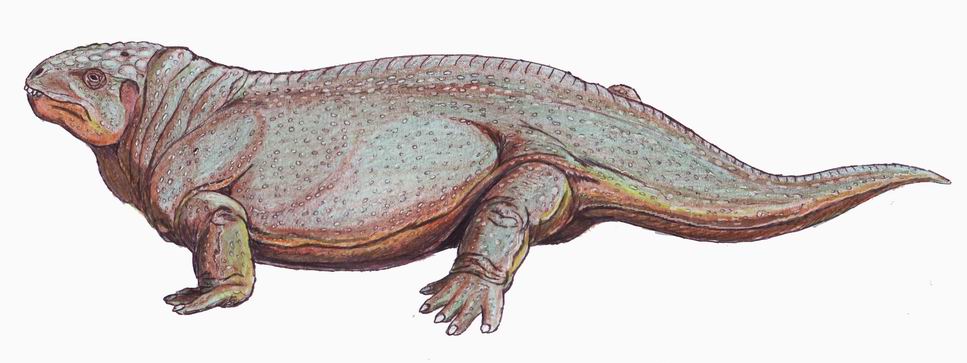
Dimetropus
''Dimetropus'' is a reptile ichnogenus commonly found in assemblages of ichnofossils dating to the Permian to Triassic in Europe and North America. Analysis of trackways of ''Dimetropus'' provides evidence that the tracks were left by diadectids or non-therapsid synapsids ("pelycosaurs"). References {{Trace-fossil-stub Reptile trace fossils ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Permian
The Permian ( ) is a geologic period and stratigraphic system which spans 47 million years from the end of the Carboniferous Period million years ago (Mya), to the beginning of the Triassic Period 251.9 Mya. It is the last period of the Paleozoic Era; the following Triassic Period belongs to the Mesozoic Era. The concept of the Permian was introduced in 1841 by geologist Sir Roderick Murchison, who named it after the region of Perm in Russia. The Permian witnessed the diversification of the two groups of amniotes, the synapsids and the sauropsids ( reptiles). The world at the time was dominated by the supercontinent Pangaea, which had formed due to the collision of Euramerica and Gondwana during the Carboniferous. Pangaea was surrounded by the superocean Panthalassa. The Carboniferous rainforest collapse left behind vast regions of desert within the continental interior. Amniotes, which could better cope with these drier conditions, rose to dominance in place of their am ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Triassic
The Triassic ( ) is a geologic period and system which spans 50.6 million years from the end of the Permian Period 251.902 million years ago ( Mya), to the beginning of the Jurassic Period 201.36 Mya. The Triassic is the first and shortest period of the Mesozoic Era. Both the start and end of the period are marked by major extinction events. The Triassic Period is subdivided into three epochs: Early Triassic, Middle Triassic and Late Triassic. The Triassic began in the wake of the Permian–Triassic extinction event, which left the Earth's biosphere impoverished; it was well into the middle of the Triassic before life recovered its former diversity. Three categories of organisms can be distinguished in the Triassic record: survivors from the extinction event, new groups that flourished briefly, and other new groups that went on to dominate the Mesozoic Era. Reptiles, especially archosaurs, were the chief terrestrial vertebrates during this time. A specialized subgroup of archo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ichnogenus
An ichnotaxon (plural ichnotaxa) is "a taxon based on the fossilized work of an organism", i.e. the non-human equivalent of an artifact. ''Ichnotaxa'' comes from the Greek ίχνος, ''ichnos'' meaning ''track'' and ταξις, ''taxis'' meaning ''ordering''.Definition o'ichno'at dictionary.com. Ichnotaxa are names used to identify and distinguish morphologically distinctive ichnofossils, more commonly known as trace fossils. They are assigned genus and species ranks by ichnologists, much like organisms in Linnaean taxonomy. These are known as ichnogenera and ichnospecies, respectively. "Ichnogenus" and "ichnospecies" are commonly abbreviated as "igen." and "isp.". The binomial names of ichnospecies and their genera are to be written in italics. Most researchers classify trace fossils only as far as the ichnogenus rank, based upon trace fossils that resemble each other in morphology but have subtle differences. Some authors have constructed detailed hierarchies up to ichnosupe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ichnofossil
A trace fossil, also known as an ichnofossil (; from el, ἴχνος ''ikhnos'' "trace, track"), is a fossil record of biological activity but not the preserved remains of the plant or animal itself. Trace fossils contrast with body fossils, which are the fossilized remains of parts of organisms' bodies, usually altered by later chemical activity or mineralization. The study of such trace fossils is ichnology and is the work of ichnologists. Trace fossils may consist of impressions made on or in the substrate by an organism. For example, burrows, borings ( bioerosion), urolites (erosion caused by evacuation of liquid wastes), footprints and feeding marks and root cavities may all be trace fossils. The term in its broadest sense also includes the remains of other organic material produced by an organism; for example coprolites (fossilized droppings) or chemical markers (sedimentological structures produced by biological means; for example, the formation of stromatolites). ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diadectids
Diadectidae is an extinct family (biology), family of early tetrapods that lived in what is now North America and Europe during the Late Carboniferous and Early Permian in Asia during the Late Permian. They were the first herbivore, herbivorous tetrapods, and also the first fully terrestrial animals to attain large sizes. Footprints indicate that diadectids walked with an erect posture. They were the first to exploit plant material in terrestrial food chains, making their appearance an important stage in both vertebrate evolution and the development of terrestrial ecosystems. The best known and largest representative of the family is ''Diadectes'', a heavily built animal that attained a maximum length of several metres. Several other genera and various fragmentary fossil remains are also known. Although well known genera like ''Diadectes'' first appear in the Late Pennsylvanian, fragmentary remains of possible diadectids are known from much earlier deposits, including a piece of l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Therapsid
Therapsida is a major group of eupelycosaurian synapsids that includes mammals, their ancestors and relatives. Many of the traits today seen as unique to mammals had their origin within early therapsids, including limbs that were oriented more underneath the body, as opposed to the sprawling posture of many reptiles and salamanders. Therapsids evolved from "pelycosaurs", specifically within the Sphenacodontia, more than 279.5 million years ago. They replaced the "pelycosaurs" as the dominant large land animals in the Middle Permian through to the Early Triassic. In the aftermath of the Permian–Triassic extinction event, therapsids declined in relative importance to the rapidly diversifying reptiles during the Middle Triassic. The therapsids include the cynodonts, the group that gave rise to mammals ( Mammaliaformes) in the Late Triassic, around 225 million years ago. Of the non-mammalian therapsids, only cynodonts survived beyond the end of the Triassic, with the only other ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Synapsids
Synapsids + (, 'arch') > () "having a fused arch"; synonymous with ''theropsids'' (Greek, "beast-face") are one of the two major groups of animals that evolved from basal amniotes, the other being the Sauropsida, sauropsids, the group that includes Reptile, reptiles and birds. The group includes mammals and every animal more closely related to mammals than to sauropsids. Unlike other amniotes, synapsids have a single temporal fenestra, an opening low in the skull roof behind each eye orbit (anatomy), orbit, leaving a Zygomatic arch, bony arch beneath each; this accounts for their name. The distinctive temporal fenestra developed about 318 million years ago during the Late Carboniferous period, when synapsids and sauropsids diverged, but was subsequently merged with the orbit in early mammals. Traditionally, non-mammalian synapsids were believed to have evolved from reptiles, and therefore described as mammal-like reptiles in classical systematics, and primitive synapsids w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pelycosaurs
Pelycosaur ( ) is an older term for basal or primitive Late Paleozoic synapsids, excluding the therapsids and their descendants. Previously, the term ''mammal-like reptile'' had been used, and pelycosaur was considered an order, but this is now thought to be incorrect, and seen as outdated. Because it excludes the advanced synapsid group Therapsida, the term is paraphyletic and contrary to modern formal naming practice. Thus the name ''pelycosaurs'', similar to the term ''mammal-like reptiles'', had fallen out of favor among scientists by the 21st century, and is only used informally, if at all, in the modern scientific literature. The terms stem mammals, protomammals, and basal or primitive synapsids are used where needed, instead. Etymology The term ''pelycosaur'' has been fairly well abandoned by paleontologists because it no longer matches the features that distinguish a clade. The modern word was created from Greek meaning 'wooden bowl' or 'axe' and meaning 'lizard ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orléans - MOBE 12
Orléans (;"Orleans" (US) and , ) is a city in north-central France, about 120 kilometres (74 miles) southwest of Paris. It is the prefecture of the of Loiret and of the region of . Orléans is located on the river [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.jpg)