|
Dihydrochandonium
Dihydrochandonium is an aminosteroid non-depolarizing neuromuscular blocking agent Neuromuscular-blocking drugs block neuromuscular transmission at the neuromuscular junction, causing paralysis of the affected skeletal muscles. This is accomplished via their action on the post-synaptic acetylcholine (Nm) receptors. In clin .... References Muscle relaxants Nicotinic antagonists Quaternary ammonium compounds Steroids Neuromuscular blockers {{musculoskeletal-drug-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
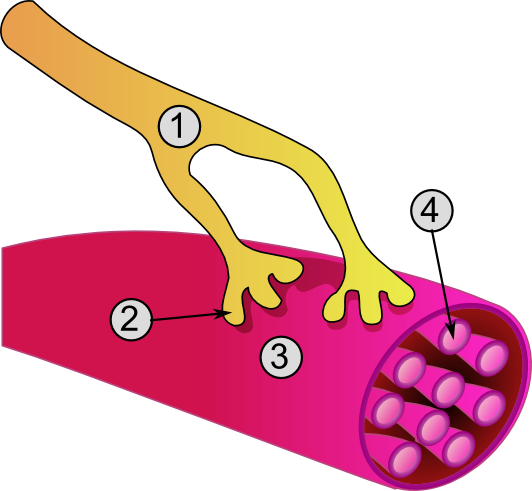
Neuromuscular Blocking Agent
Neuromuscular-blocking drugs block neuromuscular transmission at the neuromuscular junction, causing paralysis of the affected skeletal muscles. This is accomplished via their action on the post-synaptic acetylcholine (Nm) receptors. In clinical use, neuromuscular block is used adjunctively to anesthesia to produce paralysis, firstly to paralyze the vocal cords, and permit intubation of the trachea, and secondly to optimize the surgical field by inhibiting spontaneous ventilation, and causing relaxation of skeletal muscles. Because the appropriate dose of neuromuscular-blocking drug may paralyze muscles required for breathing (i.e., the diaphragm), mechanical ventilation should be available to maintain adequate respiration. Patients are still aware of pain even after full conduction block has occurred; hence, general anesthetics and/or analgesics must also be given to prevent anesthesia awareness. Nomenclature Neuromuscular blocking drugs are often classified into two broad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aminosteroid
Aminosteroids are a group of steroids with a similar structure based on an amino- substituted steroid nucleus. They are neuromuscular blocking agents, acting as competitive antagonists of the nicotinic acetylcholine receptor (nAChR), and block the signaling of acetylcholine in the nervous system. These drugs include candocuronium iodide (chandonium iodide), dacuronium bromide, dihydrochandonium, dipyrandium, malouetine, pancuronium bromide, pipecuronium bromide, rapacuronium bromide, rocuronium bromide, stercuronium iodide, and vecuronium bromide. See also * Benzylisoquinolines, such as atracurium and tubocurarine Tubocurarine (also known as ''d''-tubocurarine or DTC) is a toxic alkaloid historically known for its use as an arrow poison. In the mid-1900s, it was used in conjunction with an anesthetic to provide skeletal muscle relaxation during surgery or ..., the other major group of neuromuscular blocking agents References Muscle relaxants Nicotinic antagonists ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Muscle Relaxants
A muscle relaxant is a drug that affects skeletal muscle function and decreases the muscle tone. It may be used to alleviate symptoms such as muscle spasms, pain, and hyperreflexia. The term "muscle relaxant" is used to refer to two major therapeutic groups: neuromuscular blockers and spasmolytics. Neuromuscular blockers act by interfering with transmission at the neuromuscular end plate and have no central nervous system (CNS) activity. They are often used during surgical procedures and in intensive care and emergency medicine to cause temporary paralysis. Spasmolytics, also known as "centrally acting" muscle relaxant, are used to alleviate musculoskeletal pain and spasms and to reduce spasticity in a variety of neurological conditions. While both neuromuscular blockers and spasmolytics are often grouped together as muscle relaxant, [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nicotinic Antagonists
A nicotinic antagonist is a type of anticholinergic drug that inhibits the action of acetylcholine (ACh) at nicotinic acetylcholine receptors. These compounds are mainly used for peripheral muscle paralysis in surgery, the classical agent of this type being tubocurarine,P. Taylor (1990). In ''Goodman and Gilman's The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics, 8th Ed.'', (A. G. Gilman et al., Eds.), pp. 166-186, New York: Pergamon Press. but some centrally acting compounds such as bupropion, mecamylamine, and 18-methoxycoronaridine block nicotinic acetylcholine receptors in the brain and have been proposed for treating nicotine addiction. *Note: Succinylcholine is a nicotinic agonist. See neuromuscular blocking agents page for details on the mechanism of action. See also * Nicotinic acetylcholine receptor * Nicotinic agonist * Muscarinic acetylcholine receptor * Muscarinic agonist * Muscarinic antagonist A muscarinic receptor antagonist (MRA) is a type of anticholinergic agent t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quaternary Ammonium Compounds
In chemistry, quaternary ammonium cations, also known as quats, are positively charged polyatomic ions of the structure , R being an alkyl group or an aryl group. Unlike the ammonium ion () and the primary, secondary, or tertiary ammonium cations, the quaternary ammonium cations are permanently charged, independent of the pH of their solution. Quaternary ammonium salts or quaternary ammonium compounds (called quaternary amines in oilfield parlance) are salts of quaternary ammonium cations. Polyquats are a variety of engineered polymer forms which provide multiple quat molecules within a larger molecule. Quats are used in consumer applications including as antimicrobials (such as detergents and disinfectants), fabric softeners, and hair conditioners. As an antimicrobial, they are able to inactivate enveloped viruses (such as SARS-CoV-2). Quats tend to be gentler on surfaces than bleach-based disinfectants, and are generally fabric-safe. Synthesis Quaternary ammonium compou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Steroids
A steroid is a biologically active organic compound with four rings arranged in a specific molecular configuration. Steroids have two principal biological functions: as important components of cell membranes that alter membrane fluidity; and as signaling molecules. Hundreds of steroids are found in plants, animals and fungi. All steroids are manufactured in cells from the sterols lanosterol (opisthokonts) or cycloartenol (plants). Lanosterol and cycloartenol are derived from the cyclization of the triterpene squalene. The steroid core structure is typically composed of seventeen carbon atoms, bonded in four " fused" rings: three six-member cyclohexane rings (rings A, B and C in the first illustration) and one five-member cyclopentane ring (the D ring). Steroids vary by the functional groups attached to this four-ring core and by the oxidation state of the rings. Sterols are forms of steroids with a hydroxy group at position three and a skeleton derived from cholestane. '' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |