|
Digit Symbol Substitution Test
Digit symbol substitution test (DSST) is a neuropsychological test sensitive to brain damage, dementia, age and depression. The test is not sensitive to the location of brain-damage (except for damage comprising part of the visual field). It consists of (e.g. nine) digit-symbol pairs (e.g. 1/-,2/┴ ... 7/Λ,8/X,9/=) followed by a list of digits. Under each digit the subject should write down the corresponding symbol as fast as possible. The number of correct symbols within the allowed time (e.g. 90 or 120 sec) is measured. The DSST contained in the Wechsler Adult Intelligence Scale is called 'Digit Symbol' (WAIS-R), 'Digit-Symbol-Coding' (WAIS-III), or most recently, 'Coding' (WAIS-IV). Based on The Boston Process Approach to assessment, in order to examine the role of memory in Digit-Symbol-Coding performance, WAIS-III (but not WAIS-IV) contains an optional implicit learning test: after the Digit Symbol-Coding test paired and free recall of the symbols is assessed. The National ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neuropsychological Test
Neuropsychological tests are specifically designed tasks that are used to measure a psychological function known to be linked to a particular brain structure or pathway. Tests are used for research into brain function and in a clinical setting for the diagnosis of deficits. They usually involve the systematic administration of clearly defined procedures in a formal environment. Neuropsychological tests are typically administered to a single person working with an examiner in a quiet office environment, free from distractions. As such, it can be argued that neuropsychological tests at times offer an estimate of a person's peak level of cognitive performance. Neuropsychological tests are a core component of the process of conducting neuropsychological assessment, along with personal, interpersonal and contextual factors. Most neuropsychological tests in current use are based on traditional psychometric theory. In this model, a person's raw score on a test is compared to a large gen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dementia
Dementia is a disorder which manifests as a set of related symptoms, which usually surfaces when the brain is damaged by injury or disease. The symptoms involve progressive impairments in memory, thinking, and behavior, which negatively affects a person's ability to function and carry out everyday activities. Aside from memory impairment and a disruption in thought patterns, the most common symptoms include emotional problems, difficulties with language, and decreased motivation. The symptoms may be described as occurring in a continuum over several stages. Consciousness is not affected. Dementia ultimately has a significant effect on the individual, caregivers, and on social relationships in general. A diagnosis of dementia requires the observation of a change from a person's usual mental functioning, and a greater cognitive decline than what is caused by normal aging. Several diseases and injuries to the brain, such as a stroke, can give rise to dementia. However, th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
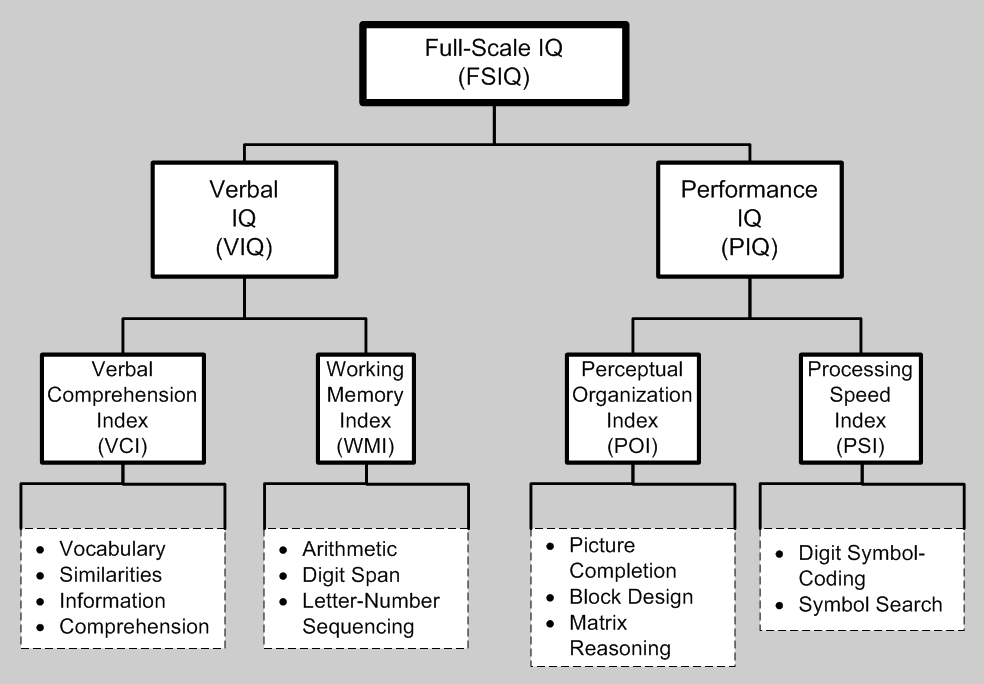
Wechsler Adult Intelligence Scale
The Wechsler Adult Intelligence Scale (WAIS) is an IQ test designed to measure intelligence and cognitive ability in adults and older adolescents. The original WAIS (Form I) was published in February 1955 by David Wechsler, as a revision of the Wechsler–Bellevue Intelligence Scale, released in 1939. It is currently in its fourth edition (''WAIS-IV'') released in 2008 by Pearson, and is the most widely used IQ test, for both adults and older adolescents, in the world. History The WAIS is founded on Wechsler's definition of intelligence, which he defined as "... the global capacity of a person to act purposefully, to think rationally, and to deal effectively with his environment." He believed that intelligence was made up of specific elements that could be isolated, defined, and subsequently measured. However, these individual elements were not entirely independent, but were all interrelated. His argument, in other words, is that general intelligence is composed of various speci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Health And Nutrition Examination Survey
The National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) is a survey research program conducted by the National Center for Health Statistics (NCHS) to assess the health and nutritional status of adults and children in the United States, and to track changes over time. The survey combines interviews, physical examinations and laboratory tests. The NHANES interview includes demographic, socioeconomic, dietary, and health-related questions. The examination component consists of medical, dental, and physiological measurements, as well as laboratory tests administered by medical personnel. The first NHANES was conducted in 1971, and in 1999 the surveys became an annual event; the first report on the topic was published in 2001. NHANES findings are used to determine the prevalence of major diseases and risk factors for diseases. Information is used to assess nutritional status and its association with health promotion and disease prevention. NHANES findings are also the basis for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NHANES
The National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) is a survey research program conducted by the National Center for Health Statistics (NCHS) to assess the health and nutritional status of adults and children in the United States, and to track changes over time. The survey combines interviews, physical examinations and laboratory tests. The NHANES interview includes demographic, socioeconomic, dietary, and health-related questions. The examination component consists of medical, dental, and physiological measurements, as well as laboratory tests administered by medical personnel. The first NHANES was conducted in 1971, and in 1999 the surveys became an annual event; the first report on the topic was published in 2001. NHANES findings are used to determine the prevalence of major diseases and risk factors for diseases. Information is used to assess nutritional status and its association with health promotion and disease prevention. NHANES findings are also the basis for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Four Boxes Test
The four boxes test is a computer-based test used to measure reaction times. In the test, a black circle appears in one of four boxes on the screen, and the patient presses the corresponding key on the keyboard as quickly as possible. The next circle appears after 500 ms, until 52 circles have been exposed. The computer measures the time the subject takes to complete the test and the number of errors they make. The test has been used to measure long-term cognitive dysfunction in elderly people who have undergone an operation. When subjects had undergone anesthesia with different drugs, and were then tested using the Stroop Colour and Word Interference Test, the digit symbol substitution test and the four boxes test, recovery times varied both by anesthetic and by type of test. Other studies have shown that there is an association between postoperative cognitive dysfunction Postoperative cognitive dysfunction (POCD) is a decline in cognition, cognitive function (especially i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |