|
Differentiated Service (design Pattern)
{{for, the network traffic classification system, Differentiated services Differentiated service is a design pattern for business services and software, in which the service varies automatically according to the identity of the consumer and/or the context in which the service is used. Sometimes known as smart service or context-aware service. Concept Differentiated service is extensively covered in a few narrow technical areas, such as telecoms networks and internet (see Differentiated services). It is also mentioned in some marketing sources, with reference to customer segmentation. But the general principle of service differentiation extends far beyond these domains, and it is one of the mechanisms for implementing flexibility in a service-oriented architecture (SOA). Various dimensions of the service can be differentiated, including: *Information quality. For example, an information service providing stock prices may offer real-time prices to selected users, and 15-minute-delay ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Design Pattern (computer Science)
In software engineering, a software design pattern is a general, reusable solution to a commonly occurring problem within a given context in software design. It is not a finished design that can be transformed directly into source or machine code. Rather, it is a description or template for how to solve a problem that can be used in many different situations. Design patterns are formalized best practices that the programmer can use to solve common problems when designing an application or system. Object-oriented design patterns typically show relationships and interactions between classes or objects, without specifying the final application classes or objects that are involved. Patterns that imply mutable state may be unsuited for functional programming languages. Some patterns can be rendered unnecessary in languages that have built-in support for solving the problem they are trying to solve, and object-oriented patterns are not necessarily suitable for non-object-oriented lan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Context-aware
Context awareness refers, in information and communication technologies, to a capability to take into account the ''situation'' of ''entities'', which may be users or devices, but are not limited to those. ''Location'' is only the most obvious element of this ''situation''. Narrowly defined for mobile devices, context awareness does thus generalize location awareness. Whereas location may determine how certain processes around a contributing device operate, context may be applied more flexibly with mobile users, especially with users of smart phones. Context awareness originated as a term from ubiquitous computing or as so-called pervasive computing which sought to deal with linking changes in the environment with computer systems, which are otherwise static. The term has also been applied to business theory in relation to contextual application design and business process management issues. Qualities of context Various categorizations of context have been proposed in the past. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Differentiated Services
Differentiated services or DiffServ is a computer networking architecture that specifies a mechanism for classifying and managing network traffic and providing quality of service (QoS) on modern IP networks. DiffServ can, for example, be used to provide low-latency to critical network traffic such as voice or streaming media while providing best-effort service to non-critical services such as web traffic or file transfers. DiffServ uses a 6-bit differentiated services code point (DSCP) in the 8-bit differentiated services field (DS field) in the IP header for packet classification purposes. The DS field replaces the outdated IPv4 TOS field. Background Modern data networks carry many different types of services, including voice, video, streaming music, web pages and email. Many of the proposed QoS mechanisms that allowed these services to co-exist were both complex and failed to scale to meet the demands of the public Internet. In December 1998, the IETF published - ''Def ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Service-oriented Architecture
In software engineering, service-oriented architecture (SOA) is an architectural style that focuses on discrete services instead of a monolithic design. By consequence, it is also applied in the field of software design where services are provided to the other components by application components, through a communication protocol over a network. A service is a discrete unit of functionality that can be accessed remotely and acted upon and updated independently, such as retrieving a credit card statement online. SOA is also intended to be independent of vendors, products and technologies. Service orientation is a way of thinking in terms of services and service-based development and the outcomes of services. A service has four properties according to one of many definitions of SOA: # It logically represents a repeatable business activity with a specified outcome. # It is self-contained. # It is a black box for its consumers, meaning the consumer does not have to be aware of the ser ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Personalization
Personalization (broadly known as customization) consists of tailoring a service or a product to accommodate specific individuals, sometimes tied to groups or segments of individuals. A wide variety of organizations use personalization to improve customer satisfaction, digital sales conversion, marketing results, branding, and improved website metrics as well as for advertising. Personalization is a key element in social media and recommender systems. Personalization is affecting every sector of society -- work, leisure, and citizenship. History of Personalization The idea of personalization is rooted in ancient rhetoric as part of the practice of an agent or communicator being responsive to the needs of the audience. When industrialization led to the rise of mass communication, the practice of message personalization diminished for a time. But the significant increase in the number of mass media outlets that use advertising as a primary revenue stream, and as they sought to a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
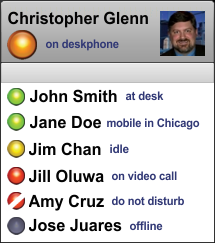
Presence Information
In computer and telecommunications networks, presence information is a status indicator that conveys ability and willingness of a potential communication partner—for example a user—to communicate. A user's client provides presence information (presence state) via a network connection to a presence service, which is stored in what constitutes his personal availability record (called a presentity) and can be made available for distribution to other users (called ''watchers'') to convey their availability for communication. Presence information has wide application in many communication services and is one of the innovations driving the popularity of instant messaging or recent implementations of voice over IP clients. Presence state A user client may publish a presence state to indicate its current communication status. This published state informs others that wish to contact the user of his availability and willingness to communicate. The most common use of presence today is t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PAYD
Usage-based insurance (UBI), also known as pay as you drive (PAYD), pay how you drive (PHYD) and mile-based auto insurance, is a type of vehicle insurance whereby the costs are dependent upon type of vehicle used, measured against time, distance, behavior and place. This differs from traditional insurance, which attempts to differentiate and reward "safe" drivers, giving them lower premiums and/or a no-claims bonus. However, conventional differentiation is a reflection of history rather than present patterns of behaviour. This means that it may take a long time before safer (or more reckless) patterns of driving and changes in lifestyle feed through into premiums. Concept The simplest form of usage-based insurance bases the insurance costs simply on distance driven. However, the general concept of ''pay as you drive'' includes any scheme where the insurance costs may depend not just on how much you drive but how, where, and when one drives. Pay as you drive (PAYD) means that the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Telematics 2
Telematics is an interdisciplinary field encompassing telecommunications, vehicular technologies (road transport, road safety, etc.), electrical engineering (sensors, instrumentation, wireless communications, etc.), and computer science (multimedia, Internet, etc.). Telematics can involve any of the following: * The technology of sending, receiving, and storing information using telecommunication devices to control remote objects * The integrated use of telecommunications and informatics for application in vehicles and to control vehicles on the move * Global navigation satellite system technology integrated with computers and mobile communications technology in automotive navigation systems * (Most narrowly) The use of such systems within road vehicles (also called vehicle telematics) History Telematics is a translation of the French word ''télématique,'' which was first coined by Simon Nora and Alain Minc in a 1978 report to the French government on the computerization o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Context-aware Pervasive Systems
Context-aware computing refers to a general class of mobile systems that can sense their physical environment, and adapt their behavior accordingly. Three important aspects of context are: where you are; who you are with; and what resources are nearby. Although location is a primary capability, location-aware does not necessarily capture things of interest that are mobile or changing. Context-aware in contrast is used more generally to include nearby people, devices, lighting, noise level, network availability, and even the social situation, e.g., whether you are with your family or a friend from school. History The concept emerged from ubiquitous computing research at Xerox PARC and elsewhere in the early 1990s. The term 'context-aware' was first used by Schilit and Theimer in their 1994 paper ''Disseminating Active Map Information to Mobile Hosts'' where they describe a model of computing ''in which users interact with many different mobile and stationary computers'' and clas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Differentiated Security
Differentiated security is a form of computer security that deploys a range of different security policies and mechanisms according to the identity and context of a user or transaction. This makes it much more difficult to scale or replicate attacks, since each cluster/individual has a different security profile and there should be no common weaknesses. One way of achieving this is by subdividing the population into small differentiated clusters. At the extreme, each individual belongs to a different class. See also * Differentiated service (design pattern) *Separation of protection and security In computer sciences, the separation of protection and security is a design choice. Wulf et al. identified protection as a mechanism and security as a policy,Wulf 74 pp.337-345 therefore making the protection-security distinction a particular case ... External linksDifferentiated security in wireless networksAndreas Johnsson, 2002. Computer security procedures ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Software Design Patterns
In software engineering, a software design pattern is a general, reusable solution to a commonly occurring problem within a given context in software design. It is not a finished design that can be transformed directly into source or machine code. Rather, it is a description or template for how to solve a problem that can be used in many different situations. Design patterns are formalized best practices that the programmer can use to solve common problems when designing an application or system. Object-oriented design patterns typically show relationships and interactions between classes or objects, without specifying the final application classes or objects that are involved. Patterns that imply mutable state may be unsuited for functional programming languages. Some patterns can be rendered unnecessary in languages that have built-in support for solving the problem they are trying to solve, and object-oriented patterns are not necessarily suitable for non-object-oriented ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |