|
Dieric Bouts The Elder
Dieric Bouts (born c. 1415 – 6 May 1475) was an Early Netherlandish painter. Bouts may have studied under Rogier van der Weyden, and his work was influenced by van der Weyden and Jan van Eyck. He worked in Leuven from 1457 (or possibly earlier) until his death in 1475. Bouts was among the first northern painters to demonstrate the use of a single vanishing point (as illustrated in his ''Last Supper''). Works Early works (before 1464) Bouts's earliest work is the ''Triptych of the Virgin's Life (Bouts), Triptych of the Virgin's Life'' in the Prado (Madrid), dated to about 1445. The ''Deposition Altarpiece'' in Granada (Capilla Real) probably also dates to this period, around 1450–1460. A dismembered canvas altarpiece—now in the Royal Museums of Fine Arts of Belgium (Brussels), the J. Paul Getty Museum (Los Angeles), National Gallery (London), Norton Simon Museum (Pasadena), and a Swiss private collection—with the same dimensions as the ''Altarpiece of the Holy Sacrament' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
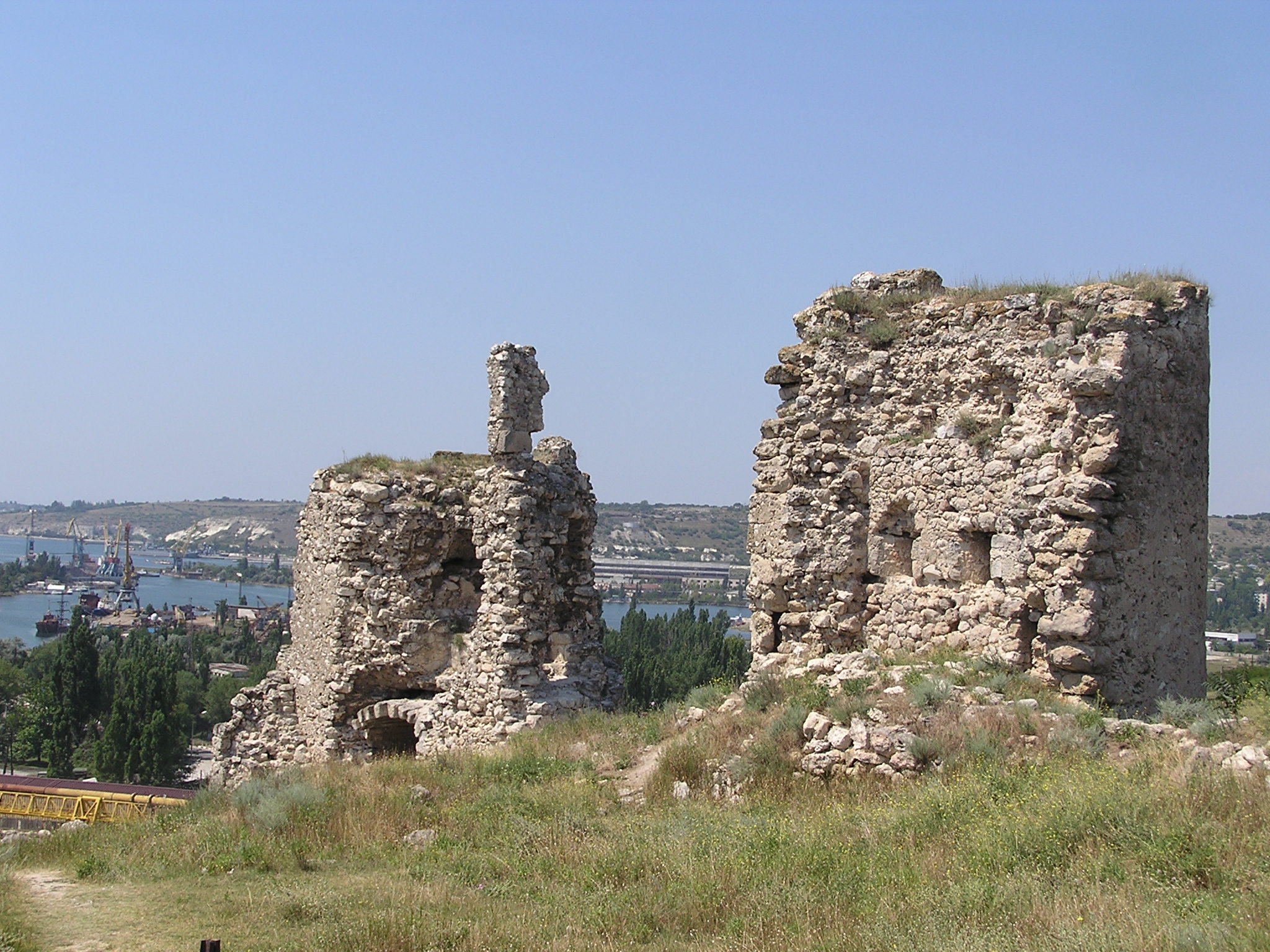
Theodoro Harlemio
The Principality of Theodoro ( el, Αὐθεντία πόλεως Θεοδωροῦς καὶ παραθαλασσίας), also known as Gothia ( el, Γοτθία) or the Principality of Theodoro-Mangup, was a Greek principality in the southern part of Crimea, specifically on the foothills of the Crimean Mountains. It represented one of the final rump states of the Eastern Roman Empire and the last territorial vestige of the Crimean Goths until its conquest by the Ottoman Empire by the Ottoman Albanian Gedik Ahmed Pasha in 1475. Its capital was Doros, also sometimes called Theodoro and now known as Mangup. The state was closely allied with the Empire of Trebizond. History In the late 12th century, the Crimean peninsula had seceded from the Byzantine Empire, but soon after the sack of Constantinople in 1204 parts of it were included in the Trapezuntine '' Gazarian Perateia''. This dependence was never very strong and was eventually replaced by the invading Mongols, who i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
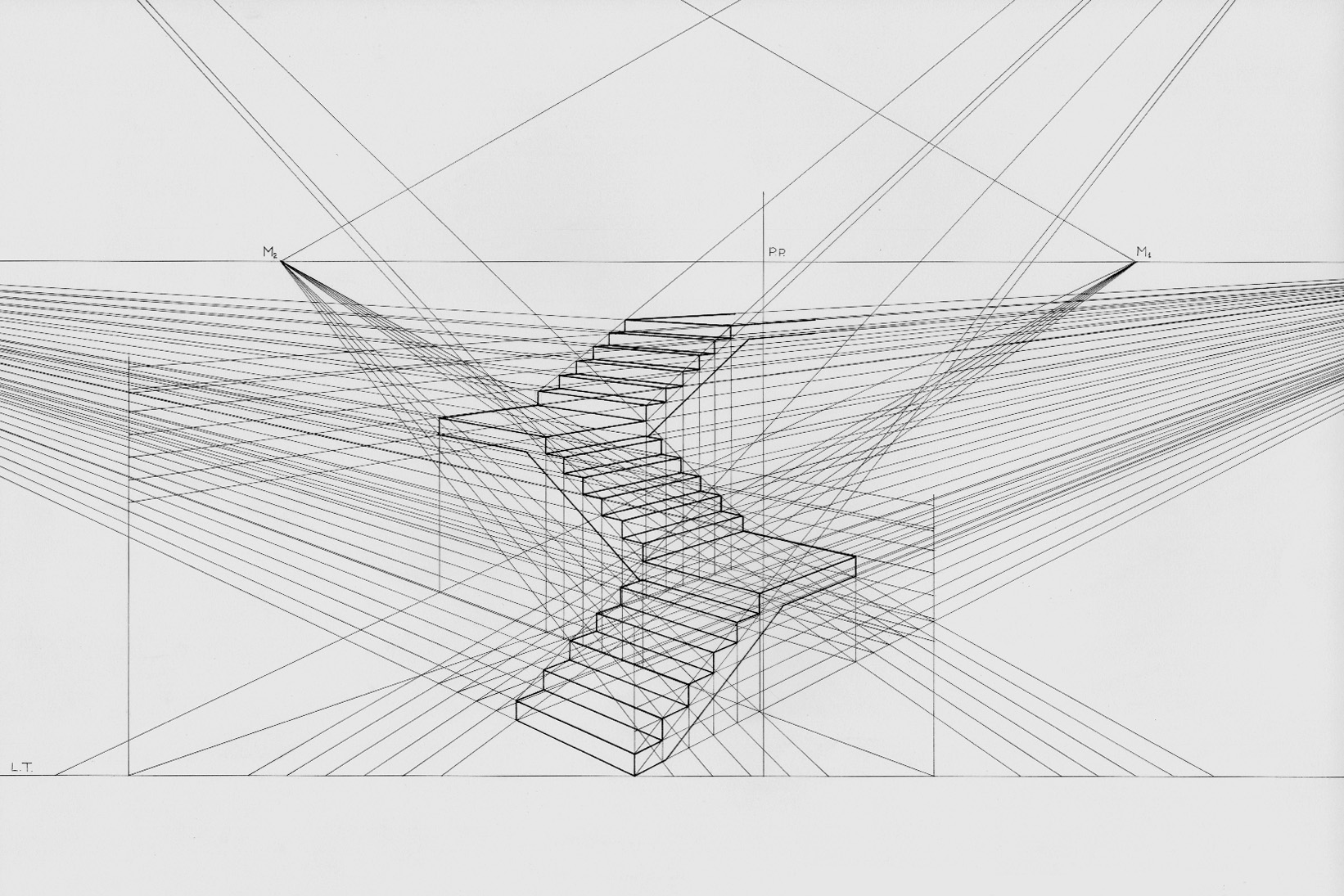
Perspective (graphical)
Linear or point-projection perspective (from la, perspicere 'to see through') is one of two types of 3D projection, graphical projection perspective in the graphic arts; the other is parallel projection. Linear perspective is an approximate representation, generally on a flat surface, of an image as it is seen by the eye. Perspective drawing is useful for representing a three-dimensional scene in a two-dimensional medium, like paper. The most characteristic features of linear perspective are that objects appear smaller as their distance from the observer increases, and that they are subject to ''foreshortening'', meaning that an object's dimensions along the line of sight appear shorter than its dimensions across the line of sight. All objects will recede to points in the distance, usually along the horizon line, but also above and below the horizon line depending on the view used. Italian Renaissance painters and architects including Masaccio, Paolo Uccello, Piero della Fran ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Fall Of The Damned (Bouts)
''The Fall of the Damned'' is a c. 1470 oil on panel painting by Dirk Bouts, originally produced as part of a triptych of the Last Judgement commissioned by the town of Louvain in 1468. The central panel is lost but the other side panel, ''The Ascension of the Elect ''The Ascension of the Elect'' is a c. 1470 oil on panel painting by the Early Netherlandish painter Dieric Bouts, originally produced as part of a triptych of the Last Judgment commissioned by the town of Louvain in 1468. The central panel is los ...'', survives. They draw on Genesis 2:10, Book of Revelation and '' The Purgatory of St Patrick'', a 14th-century Irish manuscript by Berol telling of Sir Owein's legendary trip to Purgatory. ''Ascension'' is now in the palais des Beaux-Arts de Lille. Michel Butor, ''Dirk Bouts – L'ascension des élus et la chute des damnés'', Editions Invenit, 2011 References Paintings by Dieric Bouts 1470s paintings Paintings based on the Book of Revelation Paintings i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leuven Town Hall
The Town Hall (Dutch: ) of Leuven, Belgium, is a landmark building on that city's ''Grote Markt'' (Main Market) square, across from the monumental St. Peter's Church. Built in a Brabantine Late Gothic style between 1448 and 1469, it is famous for its ornate architecture, crafted in lace-like detail. The building The Town Hall has three main stories, lined with pointed Gothic windows on the three sides visible from the Markt. Above is a gallery parapet A parapet is a barrier that is an extension of the wall at the edge of a roof, terrace, balcony, walkway or other structure. The word comes ultimately from the Italian ''parapetto'' (''parare'' 'to cover/defend' and ''petto'' 'chest/breast'). Whe ..., behind which rises a steep roof studded with four tiers of dormers. At the angles of the roof are octagonal Turret (architecture), turrets pierced with slits allowing for the passage of light. Statues in canopied niche (architecture), niches are distributed all over the buildi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Typology (theology)
Typology in Christian theology and biblical exegesis is a doctrine or theory concerning the relationship of the Old Testament to the New Testament. Events, persons, or statements in the Old Testament are seen as types prefiguring or superseded by antitypes, events or aspects of Christ or his revelation described in the New Testament. For example, Jonah may be seen as the ''type'' of Christ in that he emerged from the fish's belly and thus appeared to rise from death. In the fullest version of the theory of typology, the whole purpose of the Old Testament is viewed as merely the provision of types for Christ, the antitype or fulfillment. The theory began in the Early Church, was at its most influential in the High Middle Ages, and continued to be popular, especially in Calvinism, after the Protestant Reformation, but in subsequent periods has been given less emphasis. In 19th century German protestantism, typological interpretation was distinguished from rectilinear inte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Altarpiece
An altarpiece is an artwork such as a painting, sculpture or relief representing a religious subject made for placing at the back of or behind the altar of a Christian church. Though most commonly used for a single work of art such as a painting or sculpture, or a set of them, the word can also be used of the whole ensemble behind an altar, otherwise known as a reredos, including what is often an elaborate frame for the central image or images. Altarpieces were one of the most important products of Christian art especially from the late Middle Ages to the era of the Counter-Reformation. Many altarpieces have been removed from their church settings, and often from their elaborate sculpted frameworks, and are displayed as more simply framed paintings in museums and elsewhere. History Origins and early development Altarpieces seem to have begun to be used during the 11th century, with the possible exception of a few earlier examples. The reasons and forces that led to the developme ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
James Snyder (art Historian)
James Snyder (James E. Snyder) (1928–1990) was an American art historian, specializing in northern Renaissance art. His ''Northern Renaissance Art'' of 1985 was a standard textbook on the subject for several decades, with a posthumous revised edition in 2005, revised by Larry Silver and Henry Luttikhuizen, being somewhat replaced by Jeffrey Chipps Smith's ''The Northern Renaissance'' of 2004. Snyder taught at Bryn Mawr College from 1964 until his retirement in 1989. He died of liver disease in August 1990, aged 62. He is not to be confused with the American museum director and art historian, James S. Snyder (born 1952). Career Born in Peoria, Illinois, Snyder graduated with a B.A. from the University of Colorado in 1952, continuing to Princeton University for an M.F.A.in 1955. There he studied under Kurt Weitzmann and it was Erwin Panofsky who suggested the Early Netherlandish painter Early Netherlandish painting, traditionally known as the Flemish Primitives, refers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Judas Iscariot
Judas Iscariot (; grc-x-biblical, Ἰούδας Ἰσκαριώτης; syc, ܝܗܘܕܐ ܣܟܪܝܘܛܐ; died AD) was a disciple and one of the original Twelve Apostles of Jesus Christ. According to all four canonical gospels, Judas betrayed Jesus to the Sanhedrin in the Garden of Gethsemane by kissing him on the cheek and addressing him as "master" to reveal his identity in the darkness to the crowd who had come to arrest him. His name is often used synonymously with betrayal or treason. The Gospel of Mark gives no motive for Judas's betrayal, but does present Jesus predicting it at the Last Supper, an event also described in all the other gospels. The Gospel of Matthew states that Judas committed the betrayal in exchange for thirty pieces of silver. The Gospel of Luke and the Gospel of John suggest that he was possessed by Satan. According to , after learning that Jesus was to be crucified, Judas attempted to return the money he had been paid for his betrayal to th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Catholic Mass
The Mass is the central liturgical service of the Eucharist in the Catholic Church, in which bread and wine are consecrated and become the body and blood of Christ. As defined by the Church at the Council of Trent, in the Mass, "the same Christ who offered himself once in a bloody manner on the altar of the cross, is present and offered in an unbloody manner". The Church describes the Mass as the "source and summit of the Christian life". Thus the Church teaches that the Mass is a sacrifice. It teaches that the sacramental bread and wine, through consecration by an ordained priest, become the sacrificial body, blood, soul, and divinity of Christ as the sacrifice on Calvary made truly present once again on the altar. The Catholic Church permits only baptised members in the state of grace (Catholics who are not in a state of mortal sin) to receive Christ in the Eucharist. Many of the other sacraments of the Catholic Church, such as confirmation, holy orders, and holy matrimony, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sacramental Bread
Sacramental bread, also called Communion bread, Eucharistic bread, the Lamb or simply the host ( la, hostia, lit=sacrificial victim), is the bread used in the Christian ritual of the Eucharist. Along with sacramental wine, it is one of two elements of the Eucharist. The bread may be either leavened or unleavened, depending on tradition. Catholic theology generally teaches that at the Words of Institution the bread's substance is changed into the Body of Christ (transubstantiation), whereas Eastern Christian theology generally views the epiclesis as the point at which the change occurs. Bread was also used in Jewish Temple ritual as well as in the religious rituals of Mandaeism, Mithraism, and other pagan cultures like that of ancient Egypt. Christianity Etymology of ''host'' The word ''host'' is derived from the Latin , which means 'sacrificial victim'. The term can be used to describe the bread both before and after consecration, although it is more correct to use it a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eucharist In The Catholic Church
Eucharist ( grc-gre, εὐχαριστία, eucharistía, thanksgiving) here refers to Holy Communion or the Body and Blood of Christ, which is consumed during the Catholic Mass or Eucharistic Celebration. "At the Last Supper, on the night he was betrayed, our Savior instituted the Eucharistic sacrifice of his Body and Blood, … a memorial of his death and resurrection: a sacrament of love, a sign of unity, a bond of charity, a Paschal banquet 'in which Christ is consumed, the mind is filled with grace, and a pledge of future glory is given to us. As such, Eucharist is "an action of thanksgiving to God" derived from "the Jewish blessings that proclaim – especially during a meal – God's works: creation, redemption, and sanctification." ''Blessed Sacrament'' is a devotional term used in the Catholic Church to refer to the Eucharistic species (consecrated sacramental bread and wine) . Consecrated hosts are kept in a tabernacle after Mass, so that the Blessed Sacrament can b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |