|
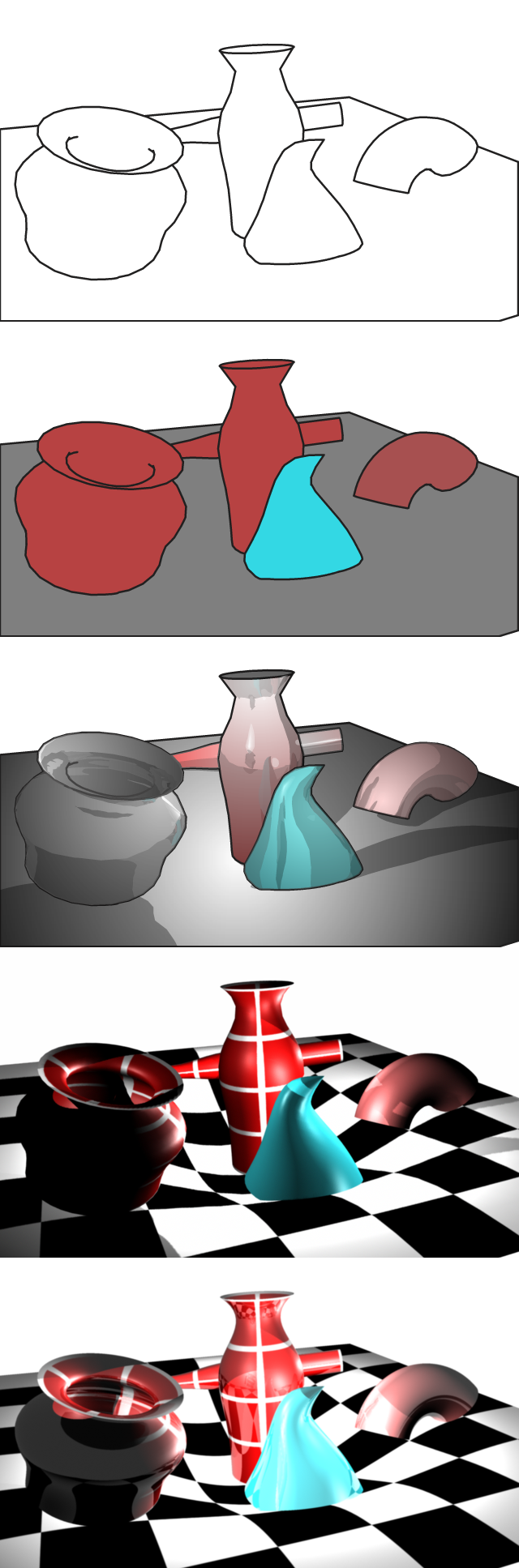
Dielectric Shader
The Dielectric Physical Phenomenon Shader is a shader used by the LightWave and Mental Ray 3D rendering engines. It is based on a dielectric model of physics, which describes how electromagnetic fields behave inside materials. The dielectric shader is able to realistically render the behavior of light rays passing through materials with differing refractive indices, as well as attenuation of the ray as it passes through a material. The shader uses Fresnel equations to simulate reflectance and transmittance of light passing through the dielectric interface, as well as using Snell's law Snell's law (also known as Snell–Descartes law and ibn-Sahl law and the law of refraction) is a formula used to describe the relationship between the angles of incidence and refraction, when referring to light or other waves passing through ... to determine the angle of refraction. In addition Beer's law is used to determine absorption of rays passing through dielectric materials. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glass Is Liquide
Glass is a non- crystalline, often transparent, amorphous solid that has widespread practical, technological, and decorative use in, for example, window panes, tableware, and optics. Glass is most often formed by rapid cooling ( quenching) of the molten form; some glasses such as volcanic glass are naturally occurring. The most familiar, and historically the oldest, types of manufactured glass are "silicate glasses" based on the chemical compound silica (silicon dioxide, or quartz), the primary constituent of sand. Soda–lime glass, containing around 70% silica, accounts for around 90% of manufactured glass. The term ''glass'', in popular usage, is often used to refer only to this type of material, although silica-free glasses often have desirable properties for applications in modern communications technology. Some objects, such as drinking glasses and eyeglasses, are so commonly made of silicate-based glass that they are simply called by the name of the material. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seduce Me By DonBertone
Seduction has multiple meanings. Platonically, it can mean "to persuade to disobedience or disloyalty", or "to lead astray, usually by persuasion or false promises". Strategies of seduction include conversation and sexual scripts, paralingual features, non-verbal communication, and short-term behavioural strategies. The word ''seduction'' stems from Latin and means literally "leading astray." As a result, the term may have a positive or negative connotation. Famous seducers from history or legend include Lilith, Giacomo Casanova, and the fictional character Don Juan. The emergence of the Internet and technology has supported the availability and the existence of a seduction community, which is based on discourse about seduction. This is predominately by "pickup artists" (PUA). Seduction is also used within marketing to increase compliance and willingness. Seduction, seen negatively, involves temptation and enticement, often sexual in nature, to lead someone astray into ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shader
In computer graphics, a shader is a computer program that calculates the appropriate levels of light, darkness, and color during the rendering of a 3D scene - a process known as ''shading''. Shaders have evolved to perform a variety of specialized functions in computer graphics special effects and video post-processing, as well as general-purpose computing on graphics processing units. Traditional shaders calculate rendering effects on graphics hardware with a high degree of flexibility. Most shaders are coded for (and run on) a graphics processing unit (GPU), though this is not a strict requirement. ''Shading languages'' are used to program the GPU's rendering pipeline, which has mostly superseded the fixed-function pipeline of the past that only allowed for common geometry transforming and pixel-shading functions; with shaders, customized effects can be used. The position and color (hue, saturation, brightness, and contrast) of all pixels, vertices, and/or textures us ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
LightWave
LightWave 3D is a 3D computer graphics program developed by NewTek. It has been used in films, television, motion graphics, digital matte painting, visual effects, video game development, product design, architectural visualizations, virtual production, music videos, pre-visualizations and advertising. Overview LightWave is a software package used for rendering 3D images, both animated and static. It includes a fast rendering engine that supports such advanced features as realistic reflection, radiosity, caustics, and 999 render nodes. The 3D modeling component supports both polygon modeling and subdivision surfaces. The animation component has features such as inverse and forward kinematics for character animation, particle systems and dynamics. Programmers can expand LightWave's capabilities using an included SDK which offers Python, LScript (a proprietary scripting language) scripting and C language interfaces. History In 1988, Allen Hastings created a rendering an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rendering (computer Graphics)
Rendering or image synthesis is the process of generating a photorealistic or non-photorealistic image from a 2D or 3D model by means of a computer program. The resulting image is referred to as the render. Multiple models can be defined in a ''scene file'' containing objects in a strictly defined language or data structure. The scene file contains geometry, viewpoint, texture, lighting, and shading information describing the virtual scene. The data contained in the scene file is then passed to a rendering program to be processed and output to a digital image or raster graphics image file. The term "rendering" is analogous to the concept of an artist's impression of a scene. The term "rendering" is also used to describe the process of calculating effects in a video editing program to produce the final video output. Rendering is one of the major sub-topics of 3D computer graphics, and in practice it is always connected to the others. It is the last major step in the gr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dielectric
In electromagnetism, a dielectric (or dielectric medium) is an electrical insulator that can be polarised by an applied electric field. When a dielectric material is placed in an electric field, electric charges do not flow through the material as they do in an electrical conductor, because they have no loosely bound, or free, electrons that may drift through the material, but instead they shift, only slightly, from their average equilibrium positions, causing dielectric polarisation. Because of dielectric polarisation, positive charges are displaced in the direction of the field and negative charges shift in the direction opposite to the field (for example, if the field is moving parallel to the positive ''x'' axis, the negative charges will shift in the negative ''x'' direction). This creates an internal electric field that reduces the overall field within the dielectric itself. If a dielectric is composed of weakly bonded molecules, those molecules not only become polaris ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electromagnetic Fields
An electromagnetic field (also EM field or EMF) is a classical (i.e. non-quantum) field produced by (stationary or moving) electric charges. It is the field described by classical electrodynamics (a classical field theory) and is the classical counterpart to the quantized electromagnetic field tensor in quantum electrodynamics (a quantum field theory). The electromagnetic field propagates at the speed of light (in fact, this field can be identified ''as'' light) and interacts with charges and currents. Its quantum counterpart is one of the four fundamental forces of nature (the others are gravitation, weak interaction and strong interaction.) The field can be viewed as the combination of an electric field and a magnetic field. The electric field is produced by stationary charges, and the magnetic field by moving charges (currents); these two are often described as the sources of the field. The way in which charges and currents interact with the electromagnetic field is described ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Refractive Index
In optics, the refractive index (or refraction index) of an optical medium is a dimensionless number that gives the indication of the light bending ability of that medium. The refractive index determines how much the path of light is bent, or refracted, when entering a material. This is described by Snell's law of refraction, , where ''θ''1 and ''θ''2 are the angle of incidence and angle of refraction, respectively, of a ray crossing the interface between two media with refractive indices ''n''1 and ''n''2. The refractive indices also determine the amount of light that is reflected when reaching the interface, as well as the critical angle for total internal reflection, their intensity ( Fresnel's equations) and Brewster's angle. The refractive index can be seen as the factor by which the speed and the wavelength of the radiation are reduced with respect to their vacuum values: the speed of light in a medium is , and similarly the wavelength in that medium is , where ''� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fresnel Equations
The Fresnel equations (or Fresnel coefficients) describe the reflection and transmission of light (or electromagnetic radiation in general) when incident on an interface between different optical media. They were deduced by Augustin-Jean Fresnel () who was the first to understand that light is a transverse wave, even though no one realized that the "vibrations" of the wave were electric and magnetic fields. For the first time, polarization could be understood quantitatively, as Fresnel's equations correctly predicted the differing behaviour of waves of the ''s'' and ''p'' polarizations incident upon a material interface. Overview When light strikes the interface between a medium with refractive index ''n''1 and a second medium with refractive index ''n''2, both reflection and refraction of the light may occur. The Fresnel equations give the ratio of the ''reflected'' wave's electric field to the incident wave's electric field, and the ratio of the ''transmitted'' wave's electri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Snell's Law
Snell's law (also known as Snell–Descartes law and ibn-Sahl law and the law of refraction) is a formula used to describe the relationship between the angles of incidence and refraction, when referring to light or other waves passing through a boundary between two different isotropic media, such as water, glass, or air. This law was named after the Dutch astronomer and mathematician Willebrord Snellius (also called Snell). In optics, the law is used in ray tracing to compute the angles of incidence or refraction, and in experimental optics to find the refractive index of a material. The law is also satisfied in meta-materials, which allow light to be bent "backward" at a negative angle of refraction with a negative refractive index. Snell's law states that, for a given pair of media, the ratio of the sines of angle of incidence (\theta_1 ) and angle of refraction (\theta_2 ) is equal to the refractive index of the second medium w.r.t the first (n21) which is equal to the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)