|
Diceratias Bispinosus
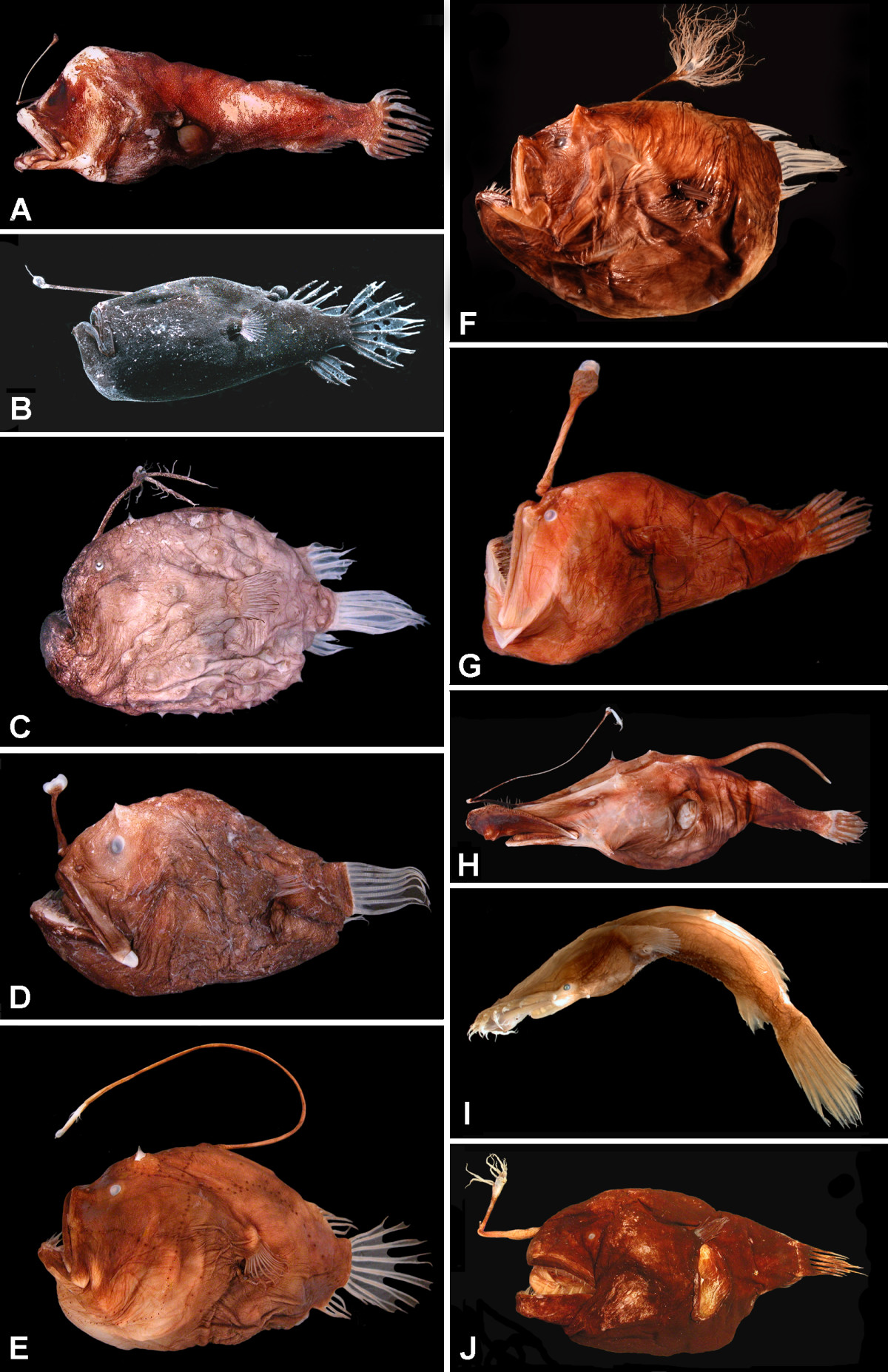
''Diceratias bispinosus'', commonly known as the two-rod angler, is a species of double angler, a type of anglerfish. The fish is bathypelagic The bathypelagic zone or bathyal zone (from Greek βαθύς (bathýs), deep) is the part of the open ocean that extends from a depth of below the ocean surface. It lies between the mesopelagic above, and the abyssopelagic below. The bathypelagic ... and has been found at depths ranging from . It is endemic to the Indian and Pacific Oceans. References Diceratiidae Deep sea fish Fish described in 1887 Taxa named by Albert Günther {{Lophiiformes-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Albert Günther
Albert Karl Ludwig Gotthilf Günther FRS, also Albert Charles Lewis Gotthilf Günther (3 October 1830 – 1 February 1914), was a German-born British zoologist, ichthyologist, and herpetologist. Günther is ranked the second-most productive reptile taxonomist (after George Albert Boulenger) with more than 340 reptile species described. Early life and career Günther was born in Esslingen in Swabia (Württemberg). His father was a ''Stiftungs-Commissar'' in Esslingen and his mother was Eleonora Nagel. He initially schooled at the Stuttgart Gymnasium. His family wished him to train for the ministry of the Lutheran Church for which he moved to the University of Tübingen. A brother shifted from theology to medicine, and he, too, turned to science and medicine at Tübingen in 1852. His first work was "''Ueber den Puppenzustand eines Distoma''". He graduated in medicine with an M.D. from Tübingen in 1858, the same year in which he published a handbook of zoology for students of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Double Angler
Double anglers are a family, Diceratiidae, of anglerfishes. They are found in deep, lightless waters of the Atlantic, Indian and western Pacific Oceans. They are easily distinguished from other anglerfishes by their possession of a second light-bearing dorsal fin spine immediately behind the illicium (the bioluminescent lure present in other anglerfishes). As in other anglerfishes, the male is very much smaller than the female, and after a larval and adolescent free-living stage, spends the rest of his life parasitically attached to a female. Species in this family are known almost entirely from adolescent females; only two larvae, one adult female, and one adult male have been found. One of the first specimens of the two-rod anglerfish (first called ''Ceratias bispinosus'') was collected during the expedition of during 1873–1876. It was first described by Albert Günther in 1887 in volume 22 of "Report on the deep-sea fishes collected by H. M. S. Challenger during th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anglerfish
The anglerfish are fish of the teleost order Lophiiformes (). They are bony fish named for their characteristic mode of predation, in which a modified luminescent fin ray (the esca or illicium) acts as a lure for other fish. The luminescence comes from symbiotic bacteria, which are thought to be acquired from seawater, that dwell in and around the sea. Some anglerfish are notable for extreme sexual dimorphism and sexual symbiosis of the small male with the much larger female, seen in the suborder Ceratioidei, the deep sea anglerfish. In these species, males may be several orders of magnitude smaller than females. Anglerfish occur worldwide. Some are pelagic (dwelling away from the sea floor), while others are benthic (dwelling close to the sea floor). Some live in the deep sea (such as the Ceratiidae), while others on the continental shelf, such as the frogfishes and the Lophiidae (monkfish or goosefish). Pelagic forms are most often laterally compressed, whereas the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bathypelagic
The bathypelagic zone or bathyal zone (from Greek βαθύς (bathýs), deep) is the part of the open ocean that extends from a depth of below the ocean surface. It lies between the mesopelagic above, and the abyssopelagic below. The bathypelagic is known as the midnight zone because of the lack of sunlight; this feature does not allow for photosynthesis-driven primary production, preventing growth of phytoplankton or aquatic plants. Although larger by volume than the photic zone, our knowledge of the bathypelagic zone remains limited by our ability to explore the deep ocean. Physical characteristics The bathypelagic zone is characterized by a nearly constant temperature of approximately and a salinity range of 33-35 g/kg. This region has little to no light, because sunlight does not reach this deep in the ocean and bioluminescence is limited. The hydrostatic pressure in this zone ranges 100-400 atmospheres (atm), due to the increase of 1 atm for every 10 m depth. It is belie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indian Ocean
The Indian Ocean is the third-largest of the world's five oceanic divisions, covering or ~19.8% of the water on Earth's surface. It is bounded by Asia to the north, Africa to the west and Australia to the east. To the south it is bounded by the Southern Ocean or Antarctica, depending on the definition in use. Along its core, the Indian Ocean has some large marginal or regional seas such as the Arabian Sea, Laccadive Sea, Bay of Bengal, and Andaman Sea. Etymology The Indian Ocean has been known by its present name since at least 1515 when the Latin form ''Oceanus Orientalis Indicus'' ("Indian Eastern Ocean") is attested, named after Indian subcontinent, India, which projects into it. It was earlier known as the ''Eastern Ocean'', a term that was still in use during the mid-18th century (see map), as opposed to the ''Western Ocean'' (Atlantic Ocean, Atlantic) before the Pacific Ocean, Pacific was surmised. Conversely, Ming treasure voyages, Chinese explorers in the Indian Oce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pacific Ocean
The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of Earth's five oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean (or, depending on definition, to Antarctica) in the south, and is bounded by the continents of Asia and Oceania in the west and the Americas in the east. At in area (as defined with a southern Antarctic border), this largest division of the World Ocean—and, in turn, the hydrosphere—covers about 46% of Earth's water surface and about 32% of its total surface area, larger than Earth's entire land area combined .Pacific Ocean . '' Britannica Concise.'' 2008: Encyclopædia Britannica, Inc. The centers of both the |
Deep Sea Fish
Deep-sea fish are fish that live in the darkness below the sunlit surface waters, that is below the epipelagic or photic zone of the sea. The lanternfish is, by far, the most common deep-sea fish. Other deep sea fishes include the flashlight fish, cookiecutter shark, bristlemouths, anglerfish, viperfish, and some species of eelpout. Only about 2% of known marine species inhabit the pelagic environment. This means that they live in the water column as opposed to the benthic organisms that live in or on the sea floor. Deep-sea organisms generally inhabit bathypelagic (1000–4000m deep) and abyssopelagic (4000–6000m deep) zones. However, characteristics of deep-sea organisms, such as bioluminescence can be seen in the mesopelagic (200–1000m deep) zone as well. The mesopelagic zone is the disphotic zone, meaning light there is minimal but still measurable. The oxygen minimum layer exists somewhere between a depth of 700m and 1000m deep depending on the place in the ocean. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fish Described In 1887
Fish are Aquatic animal, aquatic, craniate, gill-bearing animals that lack Limb (anatomy), limbs with Digit (anatomy), digits. Included in this definition are the living hagfish, lampreys, and Chondrichthyes, cartilaginous and bony fish as well as various extinct related groups. Approximately 95% of living fish species are ray-finned fish, belonging to the class Actinopterygii, with around 99% of those being teleosts. The earliest organisms that can be classified as fish were soft-bodied chordates that first appeared during the Cambrian period. Although they lacked a vertebrate, true spine, they possessed notochords which allowed them to be more agile than their invertebrate counterparts. Fish would continue to evolve through the Paleozoic era, diversifying into a wide variety of forms. Many fish of the Paleozoic developed placodermi, external armor that protected them from predators. The first fish with jaws appeared in the Silurian period, after which many (such as sharks) b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)

