|
Dibamidae
Dibamidae or blind skinks is a family of lizards characterized by their elongated cylindrical body and an apparent lack of limbs. Female dibamids are entirely limbless and the males retain small flap-like hind limbs, which they use to grip their partner during mating. They have a rigidly fused skull, lack pterygoid teeth and external ears. Their eyes are greatly reduced, and covered with a scale. They are small insectivorous lizards, with long, slender bodies, adapted for burrowing into the soil. They usually lay one egg with a hard, calcified shell, rather than the leathery shells typical of many other reptile groups. The family Dibamidae has two genera, ''Dibamus'' with 23 species native to Southeast Asia, Indonesia, the Philippines, and western New Guinea and the monotypic '' Anelytropsis'' native to Mexico. Recent phylogenetic analyses place the dibamids as the sister clade to all the other lizards and snakes or classify them as sharing a common ancestor with the infraorder ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Squamata
Squamata (, Latin ''squamatus'', 'scaly, having scales') is the largest order of reptiles, comprising lizards, snakes, and amphisbaenians (worm lizards), which are collectively known as squamates or scaled reptiles. With over 10,900 species, it is also the second-largest order of extant (living) vertebrates, after the perciform fish. Members of the order are distinguished by their skins, which bear horny scales or shields, and must periodically engage in molting. They also possess movable quadrate bones, making possible movement of the upper jaw relative to the neurocranium. This is particularly visible in snakes, which are able to open their mouths very wide to accommodate comparatively large prey. Squamata is the most variably sized order of reptiles, ranging from the dwarf gecko (''Sphaerodactylus ariasae'') to the Reticulated python (''Malayopython reticulatus'') and the now- extinct mosasaurs, which reached lengths over . Among other reptiles, squamates are most ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
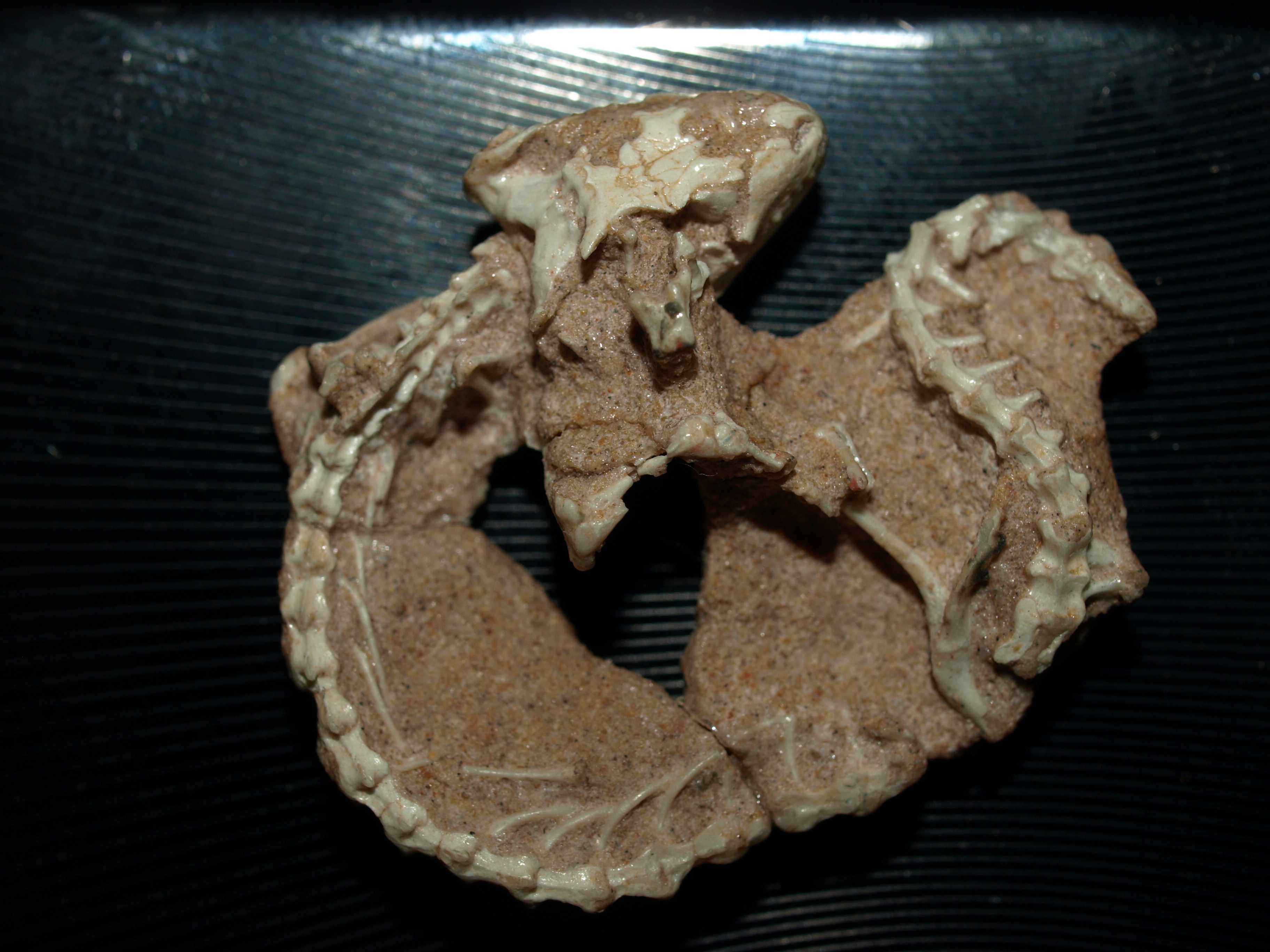
Hoeckosaurus
''Hoeckosaurus'' is an extinct genus of lizard from the Oligocene of Mongolia. It contains a single species, ''H. mongoliensis''. The genus name commemorates Austrian paleontologist Gudrun Höck, who collected the type material. ''Hoeckosaurus'' was a member of the Dibamidae (a family of primitive legless squamates), and represents the only known fossil record of the Dibamidae, despite the presumed ancient origins of the group. Despite the close resemblance of the fossils to extant dibamids in the genera ''Dibamus'' and '' Anelytropsis'', some distinguishing features such as an open Meckelian groove suggests that ''Hoeckosaurus'' is basal to both. The remains of ''Hoeckosaurus'' consist of some jawbones, and were collected in 1995-1997 from the Valley of the Lakes in central Mongolia. The sediments they were collected from are thought to be Early Oligocene in age. Previous studies postulated the jaws as belonging to an arretosaurid (an extinct family of Asian iguanians) or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mexican Blind Lizard
The Mexican blind lizard (''Anelytropsis papillosus'') is a species of legless lizard in the family Dibamidae, and the only species in the genus ''Anelytropsis''. It is endemic to Mexico. They look like Amphisbaenia, but are in fact, only distantly related. Etymology Although early authors did not discuss the etymology, the generic name, ''Anelytropsis'', is presumed to be based on the Greek words: ''ana'' = up opon; ''elytron'' = shield; ''ops'' = eye, in reference to the eyes which are concealed by ocular scales. The trivial name or specific epithet, ''papillosus'', is Latin and refers to the minute papillae present on the scales in the anterior areas of the mouth and nose (rostral scale, first labial scale, and loreal).Campbell, Howard W. 1974. ''Catalogue of American Amphibians and Reptiles: Anelytropsis, A. papillosus.'' Society for the Study of Amphibians and Reptiles. 156:1–2. Description The Mexican blind lizard is a limbless lizard, adapted for burrowing. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dibamus
''Dibamus'' is a genus of legless lizards in the family Dibamidae. Neang T, Holden J, Eastoe T, Seng R, Ith S, Grismer LL (2011). "A new species of ''Dibamus'' (Squamata: Dibamidae) from Phnom Samkos Wildlife Sanctuary, southwestern Cardamom Mountains, Cambodia". ''Zootaxa'' 2828: 58-68. Etymology Greek διβαμος ''dibamos'' "two-footed, on two legs". Species The following 24 species are recognized as being valid. *'' Dibamus alfredi'' – Alfred's blind skink, Alfred's dibamid lizard, Alfred's limbless skink *''Dibamus bogadeki'' *'' Dibamus booliati'' – Boo Liat's blind lizard *'' Dibamus bourreti'' – Bourret's blind skink *'' Dibamus celebensis'' *'' Dibamus dalaiensis'' *'' Dibamus deharvengi'' *'' Dibamus dezwaani'' *'' Dibamus floweri'' – Flowers's blind lizard *'' Dibamus greeri'' – Greer's blind skink *'' Dibamus ingeri'' *'' Dibamus kondaoensis'' *'' Dibamus leucurus'' – white blind skink *'' Dibamus manadotuaensis'' *'' Dibamus monta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gekkota
Geckos are small, mostly carnivorous lizards that have a wide distribution, found on every continent except Antarctica. Belonging to the infraorder Gekkota, geckos are found in warm climates throughout the world. They range from . Geckos are unique among lizards for their vocalisations, which differ from species to species. Most geckos in the family Gekkonidae use chirping or clicking sounds in their social interactions. Tokay geckos (''Gekko gecko'') are known for their loud mating calls, and some other species are capable of making hissing noises when alarmed or threatened. They are the most species-rich group of lizards, with about 1,500 different species worldwide. All geckos, except species in the family Eublepharidae lack eyelids; instead, the outer surface of the eyeball has a transparent membrane, the cornea. They have a fixed lens within each iris that enlarges in darkness to let in more light. Since they cannot blink, species without eyelids generally lick t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lamella (surface Anatomy)
Lamellae on a gecko's foot. In surface anatomy, a lamella is a thin plate-like structure, often one amongst many lamellae very close to one another, with open space between. Aside from respiratory organs, they appear in other biological roles including filter feeding and the traction surfaces of geckos. In fish, gill lamellae are used to increase the surface area in contact with the environment to maximize gas exchange (both to attain oxygen and to expel carbon dioxide) between the water and the blood. In fish gills there are two types of lamellae, primary and secondary. The primary gill lamellae (also called gill filament) extends from the gill arch, and the secondary gill lamellae extends from the primary gill lamellae. Gas exchange primarily occurs at the secondary gill lamellae, where the tissue is notably only one cell layer thick. Furthermore, countercurrent gas exchange at the secondary gill lamellae further maximizes oxygen uptake and carbon dioxide release. See al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maxilla
The maxilla (plural: ''maxillae'' ) in vertebrates is the upper fixed (not fixed in Neopterygii) bone of the jaw formed from the fusion of two maxillary bones. In humans, the upper jaw includes the hard palate in the front of the mouth. The two maxillary bones are fused at the intermaxillary suture, forming the anterior nasal spine. This is similar to the mandible (lower jaw), which is also a fusion of two mandibular bones at the mandibular symphysis. The mandible is the movable part of the jaw. Structure In humans, the maxilla consists of: * The body of the maxilla * Four processes ** the zygomatic process ** the frontal process of maxilla ** the alveolar process ** the palatine process * three surfaces – anterior, posterior, medial * the Infraorbital foramen * the maxillary sinus * the incisive foramen Articulations Each maxilla articulates with nine bones: * two of the cranium: the frontal and ethmoid * seven of the face: the nasal, zygomatic, lacrimal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pineal Foramen
A parietal eye, also known as a third eye or pineal eye, is a part of the epithalamus present in some vertebrates. The eye is located at the top of the head, is photoreceptive and is associated with the pineal gland, regulating circadian rhythmicity and hormone production for thermoregulation. The hole in the head which contains the eye is known as a pineal foramen or parietal foramen, since it is often enclosed by the parietal bones. Presence in various animals The parietal eye is found in the tuatara, most lizards, frogs, salamanders, certain bony fish, sharks, and lampreys. It is absent in mammals, but was present in their closest extinct relatives, the therapsids, suggesting it was lost during the course of the mammalian evolution due to it being useless in endothermic animals. It is also absent in the ancestrally endothermic ("warm-blooded") archosaurs such as birds. The parietal eye is also lost in ectothermic ("cold-blooded") archosaurs like crocodilians, and in turtles, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quadrate Bone
The quadrate bone is a skull bone in most tetrapods, including amphibians, sauropsids (reptiles, birds), and early synapsids. In most tetrapods, the quadrate bone connects to the quadratojugal and squamosal bones in the skull, and forms upper part of the jaw joint. The lower jaw articulates at the articular bone, located at the rear end of the lower jaw. The quadrate bone forms the lower jaw articulation in all classes except mammals. Evolutionarily, it is derived from the hindmost part of the primitive cartilaginous upper jaw. Function in reptiles In certain extinct reptiles, the variation and stability of the morphology of the quadrate bone has helped paleontologists in the species-level taxonomy and identification of mosasaur squamates and spinosaurine dinosaurs. In some lizards and dinosaurs, the quadrate is articulated at both ends and movable. In snakes, the quadrate bone has become elongated and very mobile, and contributes greatly to their ability to swallow very l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
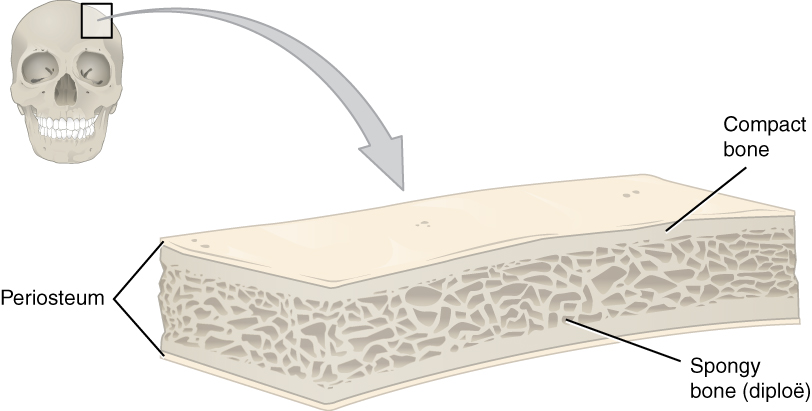
Neurocranium
In human anatomy, the neurocranium, also known as the braincase, brainpan, or brain-pan is the upper and back part of the skull, which forms a protective case around the brain. In the human skull, the neurocranium includes the calvaria or skullcap. The remainder of the skull is the facial skeleton. In comparative anatomy, neurocranium is sometimes used synonymously with endocranium or chondrocranium. Structure The neurocranium is divided into two portions: * the membranous part, consisting of flat bones, which surround the brain; and * the cartilaginous part, or chondrocranium, which forms bones of the base of the skull. In humans, the neurocranium is usually considered to include the following eight bones: * 1 ethmoid bone * 1 frontal bone * 1 occipital bone * 2 parietal bones * 1 sphenoid bone * 2 temporal bones The ossicles (three on each side) are usually not included as bones of the neurocranium. There may variably also be extra sutural bones present. Below the neuroc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Post-temporal Fenestra
The skull is a bone protective cavity for the brain. The skull is composed of four types of bone i.e., cranial bones, facial bones, ear ossicles and hyoid bone. However two parts are more prominent: the cranium and the mandible. In humans, these two parts are the neurocranium and the viscerocranium ( facial skeleton) that includes the mandible as its largest bone. The skull forms the anterior-most portion of the skeleton and is a product of cephalisation—housing the brain, and several sensory structures such as the eyes, ears, nose, and mouth. In humans these sensory structures are part of the facial skeleton. Functions of the skull include protection of the brain, fixing the distance between the eyes to allow stereoscopic vision, and fixing the position of the ears to enable sound localisation of the direction and distance of sounds. In some animals, such as horned ungulates (mammals with hooves), the skull also has a defensive function by providing the mount (on the fro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Supratemporal Fenestra
The skull is a bone protective cavity for the brain. The skull is composed of four types of bone i.e., cranial bones, facial bones, ear ossicles and hyoid bone. However two parts are more prominent: the cranium and the mandible. In humans, these two parts are the neurocranium and the viscerocranium (facial skeleton) that includes the mandible as its largest bone. The skull forms the anterior-most portion of the skeleton and is a product of cephalisation—housing the brain, and several sensory structures such as the eyes, ears, nose, and mouth. In humans these sensory structures are part of the facial skeleton. Functions of the skull include protection of the brain, fixing the distance between the eyes to allow stereoscopic vision, and fixing the position of the ears to enable sound localisation of the direction and distance of sounds. In some animals, such as horned ungulates (mammals with hooves), the skull also has a defensive function by providing the mount (on the front ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |