|
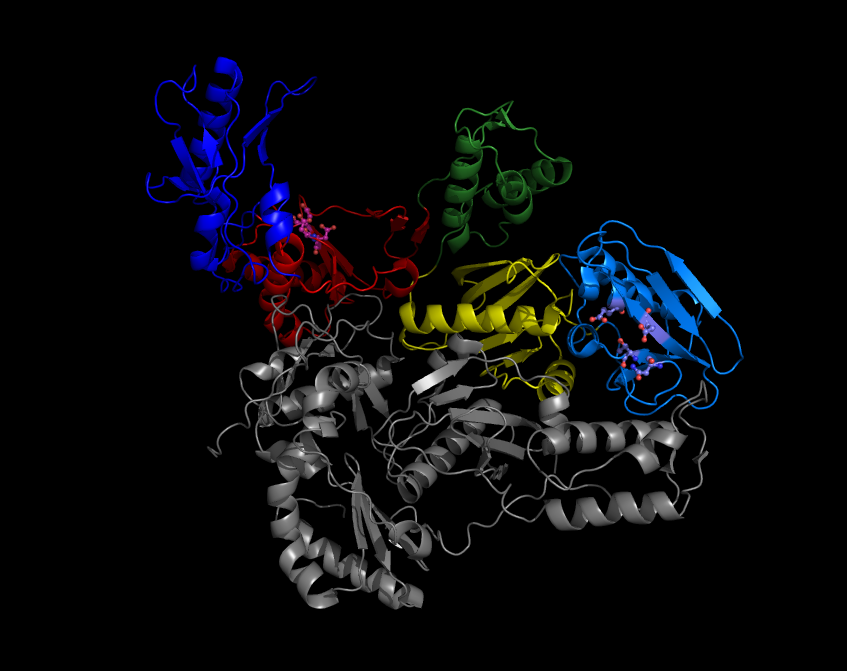
Diarylpyrimidine
Diarylpyrimidines (DAPY) and diaryltriazines (DATA) are two closely related classes of molecules resembling the pyrimidine nucleotides found in DNA. They show great potency in inhibiting the activity of HIV reverse transcriptase. Several compounds in this class are non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors used clinically in the treatment of HIV/AIDS, notably etravirine and rilpivirine Rilpivirine, sold under the brand names Edurant and Rekambys, is a medication, developed by Tibotec, used for the treatment of HIV/AIDS. It is a second-generation non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor (NNRTI) with higher potency (pharmac ....Steve MitchellHIV Market To Top 10 Billion Dollars United Press International. April 11, 2007. References Antiretroviral drugs Pyrimidines {{heterocyclic-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Etravirine
Etravirine (ETR, brand name Intelence, formerly known as TMC125) is a drug used for the treatment of HIV. Etravirine is a non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor (NNRTI). Unlike the currently available agents in the class, resistance to other NNRTIs does not seem to confer resistance to etravirine. Etravirine is marketed by Janssen, a subsidiary of Johnson & Johnson. In January 2008, the Food and Drug Administration approved its use for patients with established resistance to other drugs, making it the 30th anti-HIV drug approved in the United States and the first to be approved in 2008. It was also approved for use in Canada on April 1, 2008. Etravirine is licensed in the United States, Canada, Israel, Russia, Australia and the European Union, and is under regulatory review in Switzerland. Indications and dosage Etravirine, in combination with other anti-retrovirals, is indicated for the treatment of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) infection in antiretrovir ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Etravirine
Etravirine (ETR, brand name Intelence, formerly known as TMC125) is a drug used for the treatment of HIV. Etravirine is a non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor (NNRTI). Unlike the currently available agents in the class, resistance to other NNRTIs does not seem to confer resistance to etravirine. Etravirine is marketed by Janssen, a subsidiary of Johnson & Johnson. In January 2008, the Food and Drug Administration approved its use for patients with established resistance to other drugs, making it the 30th anti-HIV drug approved in the United States and the first to be approved in 2008. It was also approved for use in Canada on April 1, 2008. Etravirine is licensed in the United States, Canada, Israel, Russia, Australia and the European Union, and is under regulatory review in Switzerland. Indications and dosage Etravirine, in combination with other anti-retrovirals, is indicated for the treatment of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) infection in antiretrovir ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rilpivirine
Rilpivirine, sold under the brand names Edurant and Rekambys, is a medication, developed by Tibotec, used for the treatment of HIV/AIDS. It is a second-generation non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor (NNRTI) with higher potency (pharmacology), potency, longer biological half-life, half-life and reduced adverse drug reaction, side-effect profile compared with older NNRTIs such as efavirenz. Medical uses In the US, rilpivirine is approved for treatment-naive patients with a viral load of 100,000 copies/mL or less at therapy initiation. It has to be combined with other drugs against HIV.Rilpivirine . Accessed 2021-02-23. In the European Union, rilpivirine is approved in combination with cabotegravir for maintenance treatment of adults who have undetectable HIV levels in the blood (viral load less than 50 copies/ml) with their current antiretroviral treatment, and when the virus has not developed resistance to certain class of anti-HIV medicines called non-nucleoside revers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pyrimidine
Pyrimidine (; ) is an aromatic, heterocyclic, organic compound similar to pyridine (). One of the three diazines (six-membered heterocyclics with two nitrogen atoms in the ring), it has nitrogen atoms at positions 1 and 3 in the ring. The other diazines are pyrazine (nitrogen atoms at the 1 and 4 positions) and pyridazine (nitrogen atoms at the 1 and 2 positions). In nucleic acids, three types of nucleobases are pyrimidine derivatives: cytosine (C), thymine (T), and uracil (U). Occurrence and history The pyrimidine ring system has wide occurrence in nature as substituted and ring fused compounds and derivatives, including the nucleotides cytosine, thymine and uracil, thiamine (vitamin B1) and alloxan. It is also found in many synthetic compounds such as barbiturates and the HIV drug, zidovudine. Although pyrimidine derivatives such as alloxan were known in the early 19th century, a laboratory synthesis of a pyrimidine was not carried out until 1879, when Grimaux reported the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nucleotide
Nucleotides are organic molecules consisting of a nucleoside and a phosphate. They serve as monomeric units of the nucleic acid polymers – deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA), both of which are essential biomolecules within all life-forms on Earth. Nucleotides are obtained in the diet and are also synthesized from common nutrients by the liver. Nucleotides are composed of three subunit molecules: a nucleobase, a five-carbon sugar (ribose or deoxyribose), and a phosphate group consisting of one to three phosphates. The four nucleobases in DNA are guanine, adenine, cytosine and thymine; in RNA, uracil is used in place of thymine. Nucleotides also play a central role in metabolism at a fundamental, cellular level. They provide chemical energy—in the form of the nucleoside triphosphates, adenosine triphosphate (ATP), guanosine triphosphate (GTP), cytidine triphosphate (CTP) and uridine triphosphate (UTP)—throughout the cell for the many cellular func ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reverse Transcriptase
A reverse transcriptase (RT) is an enzyme used to generate complementary DNA (cDNA) from an RNA template, a process termed reverse transcription. Reverse transcriptases are used by viruses such as HIV and hepatitis B to replicate their genomes, by retrotransposon mobile genetic elements to proliferate within the host genome, and by eukaryotic cells to extend the telomeres at the ends of their linear chromosomes. Contrary to a widely held belief, the process does not violate the flows of genetic information as described by the classical central dogma, as transfers of information from RNA to DNA are explicitly held possible. Retroviral RT has three sequential biochemical activities: RNA-dependent DNA polymerase activity, ribonuclease H (RNase H), and DNA-dependent DNA polymerase activity. Collectively, these activities enable the enzyme to convert single-stranded RNA into double-stranded cDNA. In retroviruses and retrotransposons, this cDNA can then integrate into the host genom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Non-nucleoside Reverse Transcriptase Inhibitor
Reverse-transcriptase inhibitors (RTIs) are a class of antiretroviral drugs used to treat HIV infection or AIDS, and in some cases hepatitis B. RTIs inhibit activity of reverse transcriptase, a viral DNA polymerase that is required for replication of HIV and other retroviruses. Mechanism of action When HIV infects a cell, reverse transcriptase copies the viral single stranded RNA genome into a double-stranded viral DNA. The viral DNA is then integrated into the host chromosomal DNA, which then allows host cellular processes, such as transcription and translation, to reproduce the virus. RTIs block reverse transcriptase's enzymatic function and prevent completion of synthesis of the double-stranded viral DNA, thus preventing HIV from multiplying. A similar process occurs with other types of viruses. The hepatitis B virus, for example, carries its genetic material in the form of DNA, and employs an RNA-dependent DNA polymerase to replicate. Some of the same compounds used as RTIs c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antiretroviral Drugs
The management of HIV/AIDS normally includes the use of multiple antiretroviral drugs as a strategy to control HIV infection. There are several classes of antiretroviral agents that act on different stages of the HIV life-cycle. The use of multiple drugs that act on different viral targets is known as highly active antiretroviral therapy (HAART). HAART decreases the patient's total burden of HIV, maintains function of the immune system, and prevents opportunistic infections that often lead to death. HAART also prevents the transmission of HIV between serodiscordant same sex and opposite sex partners so long as the HIV-positive partner maintains an undetectable viral load. Treatment has been so successful that in many parts of the world, HIV has become a chronic condition in which progression to AIDS is increasingly rare. Anthony Fauci, head of the United States National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases, has written, "With collective and resolute action now and a stead ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |