|
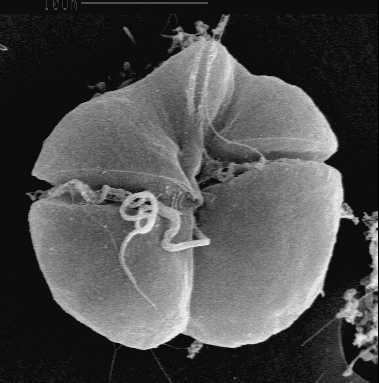
Diarrheal Shellfish Poisoning
Diarrhetic shellfish poisoning (DSP) is one of the four recognized symptom types of shellfish poisoning, the others being paralytic shellfish poisoning, neurotoxic shellfish poisoning and amnesic shellfish poisoning. As the name suggests, this syndrome manifests itself as intense diarrhea and severe abdominal pains. Nausea and vomiting may sometimes occur too. DSP and its symptoms usually set in within about half an hour of ingesting infected shellfish, and last for about one day. A recent case in France, though, with 20 people consuming oysters manifested itself after 36 hours. The causative poison is okadaic acid, which inhibits intestinal cellular de-phosphorylation. This causes the cells to become very permeable to water and causes profuse, intense diarrhea with a high risk of dehydration. As no life-threatening symptoms generally emerge from this, no fatalities from DSP have ever been recorded. See also * Amnesic shellfish poisoning (ASP) * Neurotoxic shellfish poisoning ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shellfish Poisoning
Shellfish poisoning includes four syndromes that share some common features and are primarily associated with bivalve molluscs (such as mussels, clams, oysters and scallops.) As filter feeders, these shellfish may accumulate toxins produced by microscopic algae, such as cyanobacteria, diatoms and dinoflagellates. Syndromes The syndromes are: * Amnesic shellfish poisoning (ASP) * Diarrheal shellfish poisoning (DSP) * Neurotoxic shellfish poisoning (NSP) * Paralytic shellfish poisoning (PSP) See also * Cyanotoxin Cyanotoxins are toxins produced by cyanobacteria (also known as blue-green algae). Cyanobacteria are found almost everywhere, but particularly in lakes and in the ocean where, under high concentration of phosphorus conditions, they reproduce exp ... * Gonyaulax References External links Human Illness Associated with Harmful Algae {{Authority control Seafood Toxic effect of noxious substances eaten as food ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paralytic Shellfish Poisoning
Paralytic shellfish poisoning (PSP) is one of the four recognized syndromes of shellfish poisoning, which share some common features and are primarily associated with bivalve mollusks (such as mussels, clams, oysters and scallops). These shellfish are filter feeders and accumulate neurotoxins, chiefly saxitoxin, produced by microscopic algae, such as dinoflagellates, diatoms, and cyanobacteria. Dinoflagellates of the genus '' Alexandrium'' are the most numerous and widespread saxitoxin producers and are responsible for PSP blooms in subarctic, temperate, and tropical locations. The majority of toxic blooms have been caused by the morphospecies ''Alexandrium catenella, Alexandrium tamarense'', ''Gonyaulax catenella'' and '' Alexandrium fundyense'', which together comprise the ''A. tamarense'' species complex. In Asia, PSP is mostly associated with the occurrence of the species ''Pyrodinium bahamense''. Some pufferfish, including the chamaeleon puffer, also contain saxitoxin, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neurotoxic Shellfish Poisoning
Neurotoxic shellfish poisoning (NSP) is caused by the consumption of brevetoxins, which are marine toxins produced by the dinoflagellate ''Karenia brevis'' (among several others). These toxins can produce a series of gastrointestinal and neurological effects. Outbreaks of NSP commonly take place following harmful algal bloom (HAB) events, commonly referred to as "Florida red tide" (given that blooms are more commonplace along the coasts of Florida and Texas, especially during late summer and early fall). Algal blooms are a naturally-occurring phenomenon, however their frequency has been increasing in recent decades at least in-part due to human activities, climate changes, and the eutrophication (over-abundance of plant nutrients as a result of agricultural runoff, deforestation, river bed erosion, etc.) of marine waters. HABs have been occurring for all of documented history, evidenced by the Native Americans' understanding of the dangers of shellfish consumption during periods of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amnesic Shellfish Poisoning
Amnesic shellfish poisoning (ASP) is an illness caused by consumption of shellfish that contain the marine biotoxin called domoic acid. In mammals, including humans, domoic acid acts as a neurotoxin, causing permanent short-term memory loss, brain damage, and death in severe cases. This toxin is produced naturally by marine diatoms belonging to the genus '' Pseudo-nitzschia'' and the species '' Nitzschia navis-varingica''. When accumulated in high concentrations by shellfish during filter feeding, domoic acid can then be passed on to birds, marine mammals, and humans by consumption of the contaminated shellfish. Although human illness due to domoic acid has only been associated with shellfish, the toxin can bioaccumulate in many marine organisms that consume phytoplankton, such as anchovies and sardines. Intoxication by domoic acid in nonhuman organisms is frequently referred to as domoic acid poisoning. Symptoms and treatment In the brain, domoic acid especially damages ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diarrhea
Diarrhea, also spelled diarrhoea, is the condition of having at least three loose, liquid, or watery bowel movements each day. It often lasts for a few days and can result in dehydration due to fluid loss. Signs of dehydration often begin with loss of the normal stretchiness of the skin and irritable behaviour. This can progress to decreased urination, loss of skin color, a fast heart rate, and a decrease in responsiveness as it becomes more severe. Loose but non-watery stools in babies who are exclusively breastfed, however, are normal. The most common cause is an infection of the intestines due to either a virus, bacterium, or parasite—a condition also known as gastroenteritis. These infections are often acquired from food or water that has been contaminated by feces, or directly from another person who is infected. The three types of diarrhea are: short duration watery diarrhea, short duration bloody diarrhea, and persistent diarrhea (lasting more than two wee ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abdominal Pain
Abdominal pain, also known as a stomach ache, is a symptom associated with both non-serious and serious medical issues. Common causes of pain in the abdomen include gastroenteritis and irritable bowel syndrome. About 15% of people have a more serious underlying condition such as appendicitis, leaking or ruptured abdominal aortic aneurysm, diverticulitis, or ectopic pregnancy. In a third of cases the exact cause is unclear. Given that a variety of diseases can cause some form of abdominal pain, a systematic approach to the examination of a person and the formulation of a differential diagnosis remains important. Differential diagnosis The most frequent reasons for abdominal pain are gastroenteritis (13%), irritable bowel syndrome (8%), urinary tract problems (5%), inflammation of the stomach (5%) and constipation (5%). In about 30% of cases, the cause is not determined. About 10% of cases have a more serious cause including gallbladder ( gallstones or biliary dyskin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nausea
Nausea is a diffuse sensation of unease and discomfort, sometimes perceived as an urge to vomit. While not painful, it can be a debilitating symptom if prolonged and has been described as placing discomfort on the chest, abdomen, or back of the throat. Over 30 definitions of nausea were proposed in a 2011 book on the topic. Nausea is a non-specific symptom, which means that it has many possible causes. Some common causes of nausea are gastroenteritis and other gastrointestinal disorders, food poisoning, motion sickness, dizziness, migraine, fainting, low blood sugar, anxiety, and lack of sleep. Nausea is a side effect of many medications including chemotherapy, or morning sickness in early pregnancy. Nausea may also be caused by disgust and depression. Medications taken to prevent and treat nausea and vomiting are called antiemetics. The most commonly prescribed antiemetics in the US are promethazine, metoclopramide, and the newer ondansetron. The word nausea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vomiting
Vomiting (also known as emesis and throwing up) is the involuntary, forceful expulsion of the contents of one's stomach through the mouth and sometimes the nose. Vomiting can be the result of ailments like food poisoning, gastroenteritis, pregnancy, motion sickness, or hangover; or it can be an after effect of diseases such as brain tumors, elevated intracranial pressure, or overexposure to ionizing radiation. The feeling that one is about to vomit is called nausea; it often precedes, but does not always lead to vomiting. Impairment due to alcohol or anesthesia can cause inhalation of vomit, leading to suffocation. In severe cases, where dehydration develops, intravenous fluid may be required. Antiemetics are sometimes necessary to suppress nausea and vomiting. Self-induced vomiting can be a component of an eating disorder such as bulimia, and is itself now classified as an eating disorder on its own, purging disorder. Complications Aspiration Vomiting is dan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Okadaic Acid
Okadaic acid, C44H68O13, is a toxin produced by several species of dinoflagellates, and is known to accumulate in both marine sponges and shellfish. One of the primary causes of diarrhetic shellfish poisoning, okadaic acid is a potent inhibitor of specific protein phosphatases and is known to have a variety of negative effects on cells. A polyketide, polyether derivative of a C38 fatty acid, okadaic acid and other members of its family have shined light upon many biological processes both with respect to dinoflagellete polyketide synthesis as well as the role of protein phosphatases in cell growth. History As early as 1961, reports of gastrointestinal disorders following the consumption of cooked mussels appeared in both the Netherlands and Los Lagos. Attempts were made to determine the source of the symptoms, however they failed to elucidate the true culprit, instead implicating a species of microplanctonic dinoflagellates. In the summers of the late 1970s, a series of foo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amnesic Shellfish Poisoning
Amnesic shellfish poisoning (ASP) is an illness caused by consumption of shellfish that contain the marine biotoxin called domoic acid. In mammals, including humans, domoic acid acts as a neurotoxin, causing permanent short-term memory loss, brain damage, and death in severe cases. This toxin is produced naturally by marine diatoms belonging to the genus '' Pseudo-nitzschia'' and the species '' Nitzschia navis-varingica''. When accumulated in high concentrations by shellfish during filter feeding, domoic acid can then be passed on to birds, marine mammals, and humans by consumption of the contaminated shellfish. Although human illness due to domoic acid has only been associated with shellfish, the toxin can bioaccumulate in many marine organisms that consume phytoplankton, such as anchovies and sardines. Intoxication by domoic acid in nonhuman organisms is frequently referred to as domoic acid poisoning. Symptoms and treatment In the brain, domoic acid especially damages ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neurotoxic Shellfish Poisoning
Neurotoxic shellfish poisoning (NSP) is caused by the consumption of brevetoxins, which are marine toxins produced by the dinoflagellate ''Karenia brevis'' (among several others). These toxins can produce a series of gastrointestinal and neurological effects. Outbreaks of NSP commonly take place following harmful algal bloom (HAB) events, commonly referred to as "Florida red tide" (given that blooms are more commonplace along the coasts of Florida and Texas, especially during late summer and early fall). Algal blooms are a naturally-occurring phenomenon, however their frequency has been increasing in recent decades at least in-part due to human activities, climate changes, and the eutrophication (over-abundance of plant nutrients as a result of agricultural runoff, deforestation, river bed erosion, etc.) of marine waters. HABs have been occurring for all of documented history, evidenced by the Native Americans' understanding of the dangers of shellfish consumption during periods of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paralytic Shellfish Poisoning
Paralytic shellfish poisoning (PSP) is one of the four recognized syndromes of shellfish poisoning, which share some common features and are primarily associated with bivalve mollusks (such as mussels, clams, oysters and scallops). These shellfish are filter feeders and accumulate neurotoxins, chiefly saxitoxin, produced by microscopic algae, such as dinoflagellates, diatoms, and cyanobacteria. Dinoflagellates of the genus '' Alexandrium'' are the most numerous and widespread saxitoxin producers and are responsible for PSP blooms in subarctic, temperate, and tropical locations. The majority of toxic blooms have been caused by the morphospecies ''Alexandrium catenella, Alexandrium tamarense'', ''Gonyaulax catenella'' and '' Alexandrium fundyense'', which together comprise the ''A. tamarense'' species complex. In Asia, PSP is mostly associated with the occurrence of the species ''Pyrodinium bahamense''. Some pufferfish, including the chamaeleon puffer, also contain saxitoxin, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |