|
Diamond Knife
A diamond knife is a very sharp knife in which the edge is made from diamond, invented by Humberto Fernández-Morán in 1955. Diamond knives are used for medical and scientific applications where an extremely sharp and long-lasting edge is essential. The knives are very expensive to purchase, depending on the quality and size of the knife; in addition the knives must be professionally sharpened as the edge dulls. Eye surgery Diamond knives are used in eye surgery, specifically in refractive surgery. In particular they are the main tool, together with the microscope, for the radial keratotomy invented by Svyatoslav Fyodorov to correct myopia and for the Mini Asymmetric Radial Keratotomy (M.A.R.K.), invented by Marco Abbondanza to correct astigmatism and cure the first and second stages of keratoconus. Ultramicrotomy Metal microtome knives or razor blades are too soft and dull to cut ultrathin sections. In 1950, Latta and Hartmann discovered that the edge of broken glass could be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diamond Knife Blade Edge
Diamond is a solid form of the element carbon with its atoms arranged in a crystal structure called diamond cubic. Another solid form of carbon known as graphite is the chemically stable form of carbon at room temperature and pressure, but diamond is metastable and converts to it at a negligible rate under those conditions. Diamond has the highest hardness and thermal conductivity of any natural material, properties that are used in major industrial applications such as cutting and polishing tools. They are also the reason that diamond anvil cells can subject materials to pressures found deep in the Earth. Because the arrangement of atoms in diamond is extremely rigid, few types of impurity can contaminate it (two exceptions are boron and nitrogen). Small numbers of defects or impurities (about one per million of lattice atoms) color diamond blue (boron), yellow (nitrogen), brown (defects), green (radiation exposure), purple, pink, orange, or red. Diamond also has a ver ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diamond
Diamond is a solid form of the element carbon with its atoms arranged in a crystal structure called diamond cubic. Another solid form of carbon known as graphite is the chemically stable form of carbon at room temperature and pressure, but diamond is metastable and converts to it at a negligible rate under those conditions. Diamond has the highest hardness and thermal conductivity of any natural material, properties that are used in major industrial applications such as cutting and polishing tools. They are also the reason that diamond anvil cells can subject materials to pressures found deep in the Earth. Because the arrangement of atoms in diamond is extremely rigid, few types of impurity can contaminate it (two exceptions are boron and nitrogen). Small numbers of defects or impurities (about one per million of lattice atoms) color diamond blue (boron), yellow (nitrogen), brown (defects), green (radiation exposure), purple, pink, orange, or red. Diamond also has a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Humberto Fernández-Morán
Humberto Fernández-Morán Villalobos (February 18, 1924 March 17, 1999) was a Venezuelan research scientist born in Maracaibo, Venezuela, known for inventing the diamond knife or scalpel, significantly advancing the development of electromagnetic lenses for electron microscopy based on superconducting technology, and many other scientific contributions. Career Fernández-Morán founded the Venezuelan Institute for Neurological and Brain Studies, the predecessor of the current Venezuelan Institute of Scientific Research (IVIC). He studied medicine at the University of Munich, where he graduated summa cum laude in 1944. He contributed to the development of the electron microscope and was the first person to use the concept of cryo-ultramicrotomy. After flying over Angel Falls in his home country of Venezuela he was inspired by the concept of the smoothly reoccurring flow system inherent in a waterfall to take his diamond knife invention and combine it with an ultramicrotome to dra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
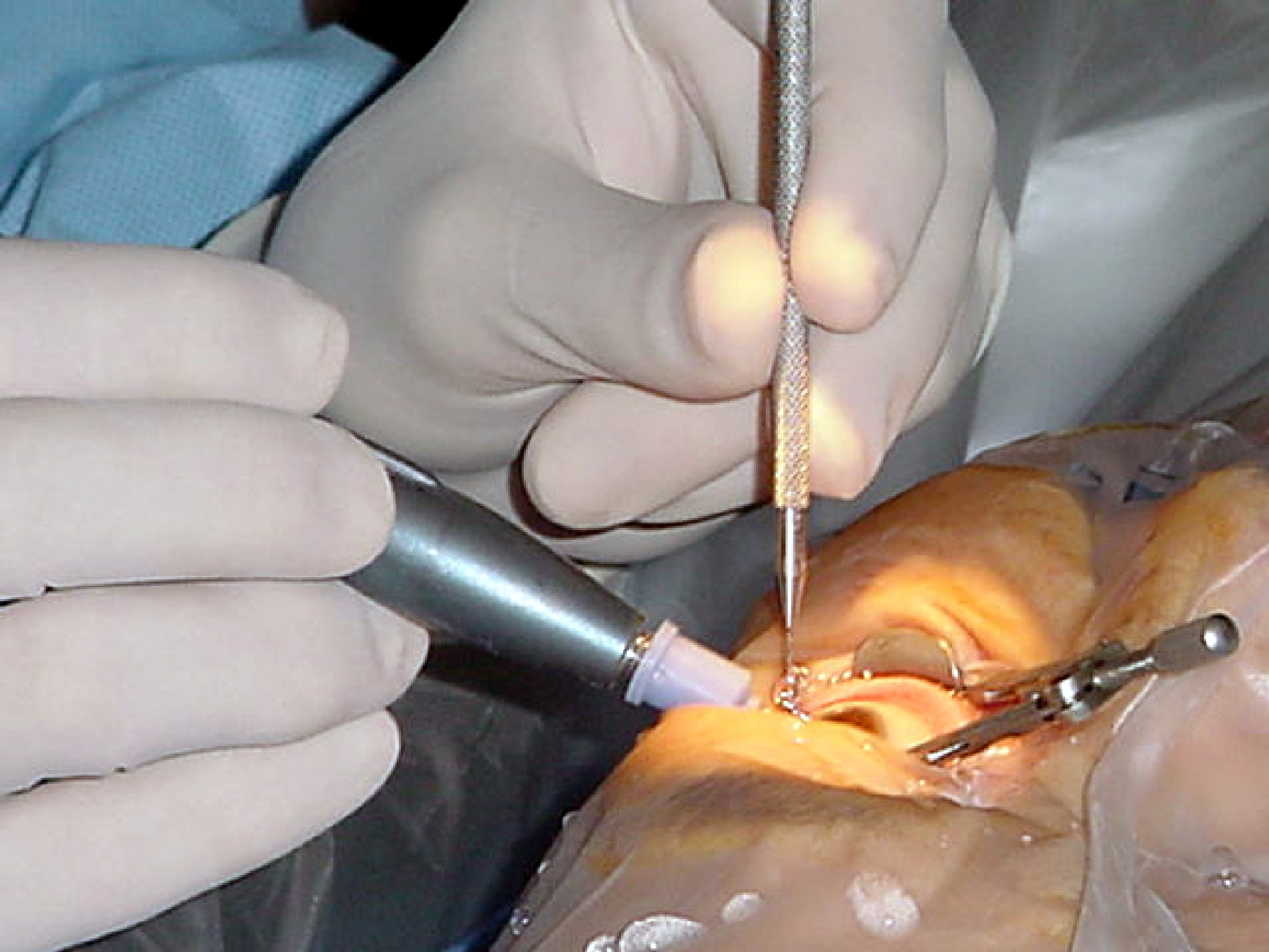
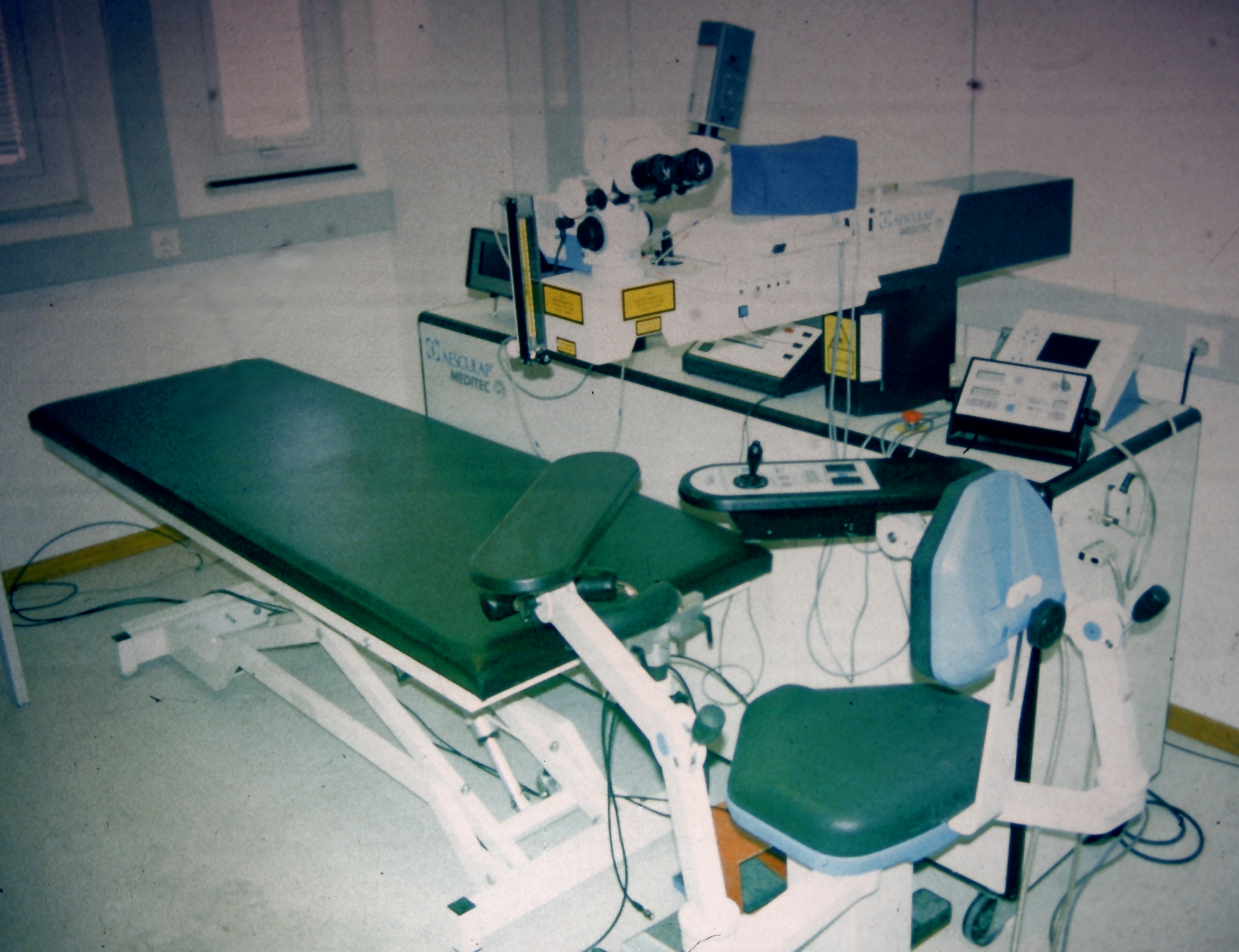
Eye Surgery
Eye surgery, also known as ophthalmic or ocular surgery, is surgery performed on the eye or its adnexa, by an ophthalmologist or sometimes, an optometrist. Eye surgery is synonymous with ophthalmology. The eye is a very fragile organ, and requires extreme care before, during, and after a surgical procedure to minimize or prevent further damage. An expert eye surgeon is responsible for selecting the appropriate surgical procedure for the patient, and for taking the necessary safety precautions. Mentions of eye surgery can be found in several ancient texts dating back as early as 1800 BC, with cataract treatment starting in the fifth century BC. Today it continues to be a widely practiced type of surgery, with various techniques having been developed for treating eye problems. Preparation and precautions Since the eye is heavily supplied by nerves, anesthesia is essential. Local anesthesia is most commonly used. Topical anesthesia using lidocaine topical gel is often used f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Refractive Surgery
Refractive eye surgery is optional eye surgery used to improve the refractive state of the eye and decrease or eliminate dependency on glasses or contact lenses. This can include various methods of surgical remodeling of the cornea ( keratomileusis), lens implantation or lens replacement. The most common methods today use excimer lasers to reshape the curvature of the cornea. Refractive eye surgeries are used to treat common vision disorders such as myopia, hyperopia, presbyopia and astigmatism. History The first theoretical work on the potential of refractive surgery was published in 1885 by Hjalmar August Schiøtz, an ophthalmologist from Norway. In 1930, the Japanese ophthalmologist Tsutomu Sato made the first attempts at performing this kind of surgery, hoping to correct the vision of military pilots. His approach was to make radial cuts in the cornea, correcting effects by up to 6 diopters. The procedure unfortunately produced a high rate of corneal degeneration ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Svyatoslav Fyodorov
Svyatoslav Nikolayevich Fyodorov (; August 8, 1927 – June 2, 2000) was a Russian ophthalmologist, politician, professor, full member of the Russian Academy of Sciences and Russian Academy of Medical Sciences. He is considered to be a pioneer of refractive surgery. He was also one of the candidates in the 1996 Russian presidential election, running as a member of the Party of Workers' Self-Government. Life and career Fyodorov was born in ''Proskurov'', Ukrainian SSR (now Khmelnytskyi, Ukraine), to ethnic Russian parents. Fyodorov graduated from Rostov Medical Institute in Rostov on Don, then worked as a practicing ophthalmologist in a small town in Rostov Oblast. Cataract surgery In the 1960s he studied the pioneering work of the English ophthalmic surgeon Sir Harold Ridley, the inventor of the intraocular lens (IOL). Fyodorov began to use Ridley's intraocular lenses in his treatment of cataract. At first he used lenses manufactured by the Rayner company in England bu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
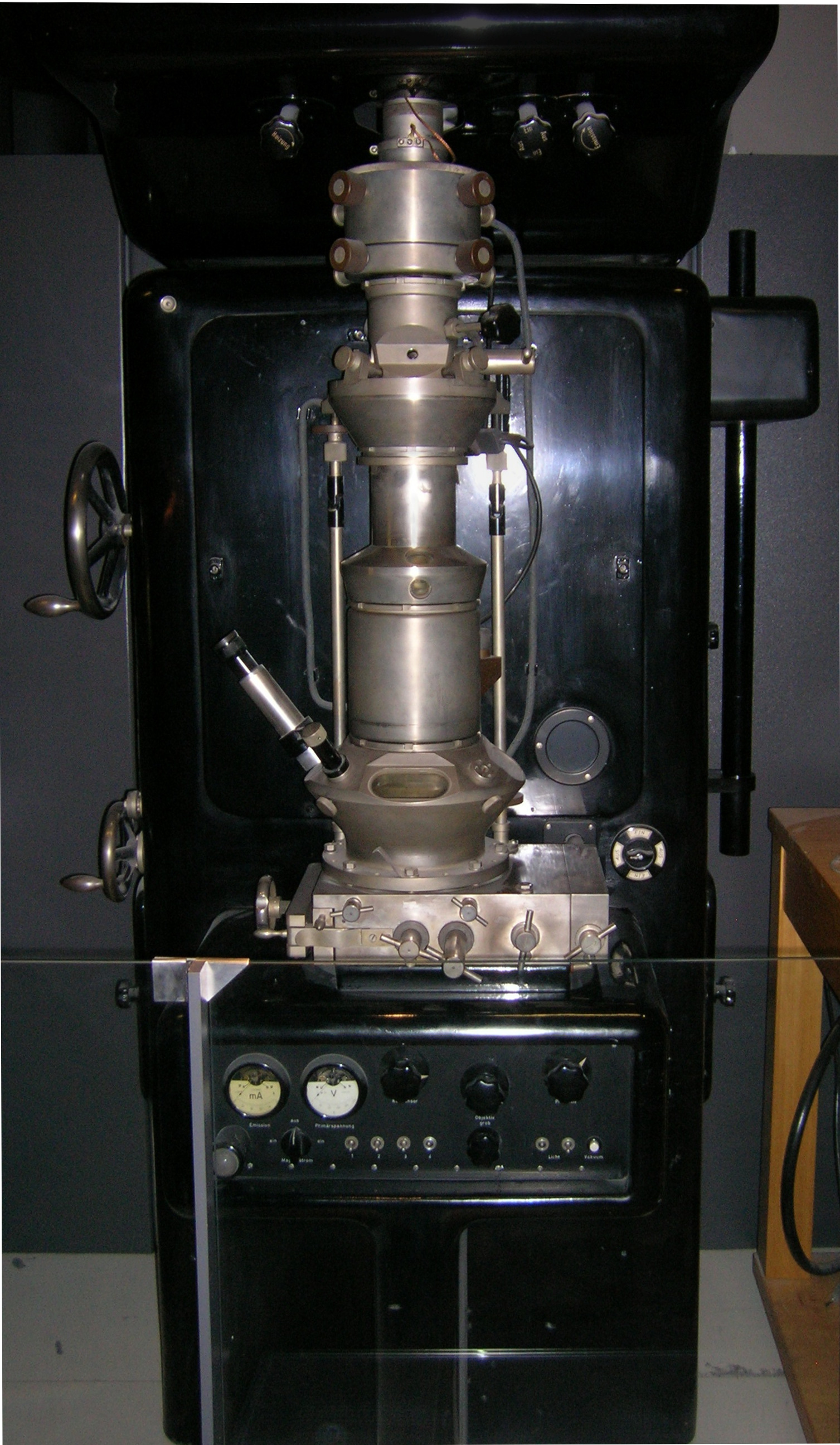
Transmission Electron Microscopy
Transmission electron microscopy (TEM) is a microscopy technique in which a beam of electrons is transmitted through a specimen to form an image. The specimen is most often an ultrathin section less than 100 nm thick or a suspension on a grid. An image is formed from the interaction of the electrons with the sample as the beam is transmitted through the specimen. The image is then magnified and focused onto an imaging device, such as a fluorescent screen, a layer of photographic film, or a sensor such as a scintillator attached to a charge-coupled device. Transmission electron microscopes are capable of imaging at a significantly higher resolution than light microscopes, owing to the smaller de Broglie wavelength of electrons. This enables the instrument to capture fine detail—even as small as a single column of atoms, which is thousands of times smaller than a resolvable object seen in a light microscope. Transmission electron microscopy is a major analytical method ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glass Knife
A glass knife is a knife with a blade made of glass, with a fracture line forming an extremely sharp cutting edge. Glass knives were used in antiquity due to their natural sharpness and the ease with which they could be manufactured. In modern electron microscopy glass knives are used to make the ultrathin sections needed for imaging. History In the Stone Age, bladed tools were made by chipping suitable stones which broke with a conchoidal fracture, a process known as knapping or lithic reduction. The same technique was used to make tools, including knives, out of obsidian, natural volcanic glass. From the 1920s until the 1940s, Dur-X glass fruit and cake knives were sold for use in kitchens under a 1938 US Patent. Before the wide availability of inexpensive stainless steel cutlery, they were used for cutting citrus fruit, tomatoes and other acidic foods, the flavor of which would be tainted by steel knives and which would stain ordinary steel knives. They were molded in temp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ultramicrotomy
Ultramicrotomy is a method for cutting specimens into extremely thin slices, called ultra-thin sections, that can be studied and documented at different magnifications in a transmission electron microscope (TEM). It is used mostly for biological specimens, but sections of plastics and soft metals can also be prepared. Sections must be very thin because the 50 to 125 kV electrons of the standard electron microscope cannot pass through biological material much thicker than 150 nm. For best resolutions, sections should be from 30 to 60 nm. This is roughly the equivalent to splitting a 0.1 mm-thick human hair into 2,000 slices along its diameter, or cutting a single red blood cell into 100 slices. Ultramicrotomy process Ultra-thin sections of specimens are cut using a specialized instrument called an "ultramicrotome". The ultramicrotome is fitted with either a diamond knife, for most biological ultra-thin sectioning, or a glass knife, often used for initial cuts. There ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wood's Metal
Wood's metal, also known as Lipowitz's alloy or by the commercial names Cerrobend, Bendalloy, Pewtalloy and MCP 158, is a metal alloy that is useful for soldering and making custom metal parts, but which is toxic to touch or breathe vapors from. The alloy is named for Barnabas Wood, who first created and patented the alloy in 1860. It is a eutectic, fusible alloy of 50% bismuth, 26.7% lead, 13.3% tin, and 10% cadmium by mass. It has a melting point of approximately . Applications Wood's metal is useful as a low-melting solder, low-temperature casting metal, high-temperature coupling fluid in heat baths, and as a fire-melted valve element in fire sprinkler systems in buildings. Medical gas cylinders in the United Kingdom have a Wood's metal seal, which melts in fire, allowing the gas to escape and reducing the risk of gas explosion. Wood's metal is commonly used as a filler when bending thin-walled metal tubes. For this use the tubing is filled with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transmission Electron Microscope
Transmission electron microscopy (TEM) is a microscopy technique in which a beam of electrons is transmitted through a specimen to form an image. The specimen is most often an ultrathin section less than 100 nm thick or a suspension on a grid. An image is formed from the interaction of the electrons with the sample as the beam is transmitted through the specimen. The image is then magnified and focused onto an imaging device, such as a fluorescent screen, a layer of photographic film, or a sensor such as a scintillator attached to a charge-coupled device. Transmission electron microscopes are capable of imaging at a significantly higher resolution than light microscopes, owing to the smaller de Broglie wavelength of electrons. This enables the instrument to capture fine detail—even as small as a single column of atoms, which is thousands of times smaller than a resolvable object seen in a light microscope. Transmission electron microscopy is a major analytical method i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.jpg)
