|
Dhenki
Dhenki, Dhiki or Dhinki () is an old style rice mill or husk lever found in Nepal, Bangladesh and Indian states of Assam, West Bengal and Odisha. It is usually made of hard wood. It has a fulcrum supporting a weight. Due to the force of the weight upon the rice in the pods, the rice and the golden brown husks separate. Dhenki used to be operated by women to produce rice from paddy and grind rice to powder. Construction ''Dhenki'' is traditionally made of wood and some iron. Carpenters build most parts of it where a blacksmith would attach an iron ring to the tip of the lever. Uses The Assamese farming society uses it to retrieve rice from raw paddy grain, to make dry rice flakes, rice powder later to process it to make various delicious dry food items called '' pithas''. ''Dhenki'' is still in use some part of rural Odisha. Dhenki is also used in parts of rural Bengal. In popular culture In the Satyajit Ray's Bengali movie Ashani Sanket, the actresses were seen operating ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rice Mill
A rice mill is a food-processing facility where paddy is processed to rice to be sold in the market. The entire product is procured from paddy fields, milled and processed hygienically in modern machinery and dust-free environment and cleaned through sorting machines. Paddy procurement Paddy is collected from the fields to be processed. The paddy is again rechecked before the process begins. The procured paddy is checked bag by bag by a team and stored iPaddy Milling Plants Manufacturing process To start with the production process, paddy is cleaned by a paddy pre-cleaning machine and the cleaned paddy is stored in raw paddy storage bins. The stored paddy is moved to food-grade stainless steel soaking tanks. Water is drained from the tank and the wet paddy is ready for boiling. Boiling is done by a steam boiler. The boiled paddy is then moved to the paddy dryer through a belt conveyor. Dryer The boiled wet paddy is dried in a food-grade stainless steel paddy drier usi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Assamese Language
Assamese (), also Asamiya ( ), is an Indo-Aryan language spoken mainly in the north-east Indian state of Assam, where it is an official language, and it serves as a '' lingua franca'' of the wider region. The easternmost Indo-Iranian language, it has over 23 million speakers. Nefamese, an Assamese-based pidgin, is used in Arunachal Pradesh, and Nagamese, an Assamese-based Creole language, is widely used in Nagaland. The Kamtapuri language of Rangpur division of Bangladesh and the Cooch Behar and Jalpaiguri districts of India are linguistically closer to Assamese, though the speakers identify with the Bengali culture and the literary language. In the past, it was the court language of the Ahom kingdom from the 17th century. Along with other Eastern Indo-Aryan languages, Assamese evolved at least before the 7th century CE from the middle Indo-Aryan Magadhi Prakrit. Its sister languages include Angika, Bengali, Bishnupriya Manipuri, Chakma, Chittagonian, Hajong ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
History Of Agriculture In India
History (derived ) is the systematic study and the documentation of the human activity. The time period of event before the invention of writing systems is considered prehistory. "History" is an umbrella term comprising past events as well as the memory, discovery, collection, organization, presentation, and interpretation of these events. Historians seek knowledge of the past using historical sources such as written documents, oral accounts, art and material artifacts, and ecological markers. History is not complete and still has debatable mysteries. History is also an academic discipline which uses narrative to describe, examine, question, and analyze past events, and investigate their patterns of cause and effect. Historians often debate which narrative best explains an event, as well as the significance of different causes and effects. Historians also debate the nature of history as an end in itself, as well as its usefulness to give perspective on the problems of the p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rice Production In India
Rice production in India is an important part of the national economy. India is the world's second-largest producer of rice, and the largest exporter of rice in the world. Production increased from 53.6 million tons in FY 1980 to 120 million tons in FY2020-21. Rice is one of the chief grains of India. Moreover, this country has the largest area under rice cultivation. As it is one of the principal food crops. It is, in fact, the dominant crop of the country. India is one of the leading producers of this crop. Rice is the basic food crop and being a tropical plant, it flourishes comfortably in a hot and humid climate. Rice is mainly grown in rain-fed areas that receive heavy annual rainfall. That is why it is fundamentally a kharif crop in India. It demands a temperature of around 25 degrees Celsius and above, and rainfall of more than 100 cm. Rice is also grown through irrigation in those areas that receive comparatively less rainfall. Rice is the staple food of easter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Agricultural Machinery
Agricultural machinery relates to the mechanical structures and devices used in farming or other agriculture. There are many types of such equipment, from hand tools and power tools to tractors and the countless kinds of farm implements that they tow or operate. Diverse arrays of equipment are used in both organic and nonorganic farming. Especially since the advent of mechanised agriculture, agricultural machinery is an indispensable part of how the world is fed. History The Industrial Revolution With the coming of the Industrial Revolution and the development of more complicated machines, farming methods took a great leap forward. Instead of harvesting grain by hand with a sharp blade, wheeled machines cut a continuous swath. Instead of threshing the grain by beating it with sticks, threshing machines separated the seeds from the heads and stalks. The first tractors appeared in the late 19th century. Steam power Power for agricultural machinery was originally supplie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fakir Mohan Senapati
Fakir Mohan Senapati (Odia: ଫକୀର ମୋହନ ସେନାପତି; 13 January 1843 – 14 June 1918), often referred to as Utkala Byasa Kabi (''Odisha's Vyasa''), was an Indian writer, poet, philosopher and social reformer. He played a leading role in establishing the distinct identity of Odia, a language mainly spoken in the Indian state of Odisha. Senapati is regarded as the father of Odia nationalism and modern Odia literature. Early life and background Born to Lakhmana Charana Senapati and Tulasi Devi Senapati in a middle class Khandayat family. When he was one and half year old his father died. After fourteen months his mother also died. Since childhood he was taken care of by his grand mother. Senapati's uncle was jealous of young Fakir Mohan and did not allow his education. His weak health also contributed to him being a late learner. He paid towards his educational expenses by working as a child labourer. Senapati dedicated his life to the progress of Odia la ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Odia Language
Odia (, ISO: , ; formerly rendered Oriya ) is an Indo-Aryan language spoken in the Indian state of Odisha. It is the official language in Odisha (formerly rendered Orissa), where native speakers make up 82% of the population, and it is also spoken in parts of West Bengal, Jharkhand, Andhra Pradesh and Chhattisgarh. Odia is one of the many official languages of India; it is the official language of Odisha and the second official language of Jharkhand. The language is also spoken by a sizeable population of 700,000 people in Chhattisgarh. Odia is the sixth Indian language to be designated a classical language, on the basis of having a long literary history and not having borrowed extensively from other languages. The earliest known inscription in Odia dates back to the 10th century CE. History Odia is an Eastern Indo-Aryan language belonging to the Indo-Aryan language family. It descends from Odra Prakrit, which evolved from Magadhi Prakrit, which was spoken in east Ind ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ashani Sanket
''Distant Thunder'' ( bn, অশনি সংকেত; translit. Ashani Sanket) is a 1973 Bengali film by the Indian director Satyajit Ray, based on the novel by the same name by Bibhutibhushan Bandopadhyay. Unlike most of Ray's earlier films, ''Distant Thunder'' was filmed in colour. It stars Soumitra Chatterjee, who headlined numerous Ray films, and the Bangladeshi actress Bobita in her only prominent international role. Today the film features in ''The New York Times Guide to the Best 1,000 Movies Ever Made''.The Best 1,000 Movies Ever Made by the film critics of ''The New York Times'', '''', 2002. It marked the debut of the th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pitha
Pithas are a variety of food similar to pancakes, dumplings or fritters, originating from the Indian subcontinent, common in Bangladesh and India. Pitha can be sweet or savoury, and usually made from a dough or batter, which is then steamed, fried or griddled. Very few varieties are oven-baked or boiled, and most are unleavened and cooked on a stovetop (or equivalent). Some versions may have a filling, garnish, or sauce. Few may be set or shaped after cooking. They are typically eaten as a snack with chai, or as treats during special occasions (similar to mithai). Pitha is especially popular in Bangladesh and the eastern Indian states of Bihar, Uttar Pradesh (eastern parts), West Bengal, Odisha, Jharkhand, the South Indian state of Kerala, and the Northeast Indian states, especially Assam. Pithas are typically made of rice flour, although there are some types of pitha made of wheat flour. Less common types of pitha are made of palm or ''ol'' (a local root vegetable). Prep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Husk
Husk (or hull) in botany is the outer shell or coating of a seed. In the United States, the term husk often refers to the leafy outer covering of an ear of maize (corn) as it grows on the plant. Literally, a husk or hull includes the protective outer covering of a seed, fruit, or vegetable. It can also refer to the exuvia of insects or other small animals left behind after moulting. In cooking, hull can also refer to other waste parts of fruits and vegetables, notably the cap or sepal of a strawberry. The husk of a legume and some similar fruits is called a pod. Husking and dehulling Husking of corn is the process of removing its outer layers, leaving only the cob or seed rack of the corn. Dehulling is the process of removing the hulls (or chaff) from beans and other seeds. This is sometimes done using a machine known as a huller. To prepare the seeds to have oils extracted from them, they are cleaned to remove any foreign objects. Next, the seeds have their hulls, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
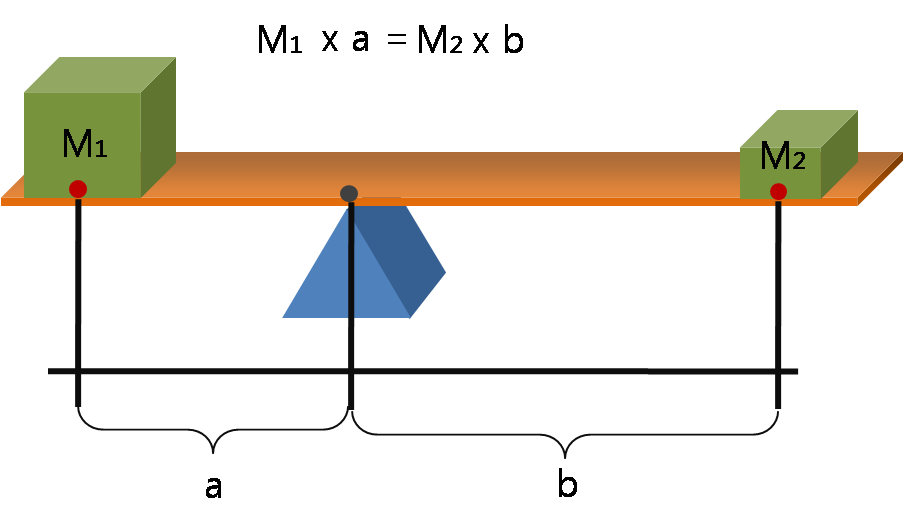
Fulcrum (mechanics)
A lever is a simple machine consisting of a beam or rigid rod pivoted at a fixed hinge, or ''fulcrum''. A lever is a rigid body capable of rotating on a point on itself. On the basis of the locations of fulcrum, load and effort, the lever is divided into three types. Also, leverage is mechanical advantage gained in a system. It is one of the six simple machines identified by Renaissance scientists. A lever amplifies an input force to provide a greater output force, which is said to provide leverage. The ratio of the output force to the input force is the mechanical advantage of the lever. As such, the lever is a mechanical advantage device, trading off force against movement. Etymology The word "lever" entered English around 1300 from Old French, in which the word was ''levier''. This sprang from the stem of the verb ''lever'', meaning "to raise". The verb, in turn, goes back to the Latin ''levare'', itself from the adjective ''levis'', meaning "light" (as in "not heavy"). ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)