|
Dhammakaya Movement
The Dhammakaya tradition or Dhammakaya movement (sometimes spelled Thammakaai) is a Thai Buddhist tradition founded by Luang Pu Sodh Candasaro in the early 20th century. It is associated with several temples descended from Wat Paknam Bhasicharoen in Bangkok. The tradition is distinguished from other Thai Buddhist traditions by its teachings on the Buddhist concept of '' Dhammakaya'' and the practice of Dhammakaya meditation (''Vijja Dhammakaya''), a method which scholars have connected to the Yogavacara tradition, which predates the 19th-century reform of Thai Buddhism. The Dhammakaya tradition is known for its teaching that there is a "true self" connected with Nirvana, which was notably criticized in the 1990s as an alleged contradiction of the Buddhist doctrine of ''anattā'' (not-self). The Dhammakaya tradition is seen by its followers as a form of Buddhist revivalism pioneered by Luang Pu Sodh Candasaro. Buddhist Studies scholars have described aspects of its practice ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Wat Phra Dhammakaya
Wat Phra Dhammakaya (, , ) is a Buddhist temple (''wat'') in Khlong Luang district, in the Pathum Thani province north of Bangkok, Thailand. It was founded in 1970 by the ''maechi'' (nun) Chandra Khonnokyoong and Luang Por Dhammajayo. It is the best-known and the fastest growing temple of the Dhammakaya tradition. This tradition, teaching Dhammakaya meditation (''Vijja Dhammakaya''), was started by the meditation master Luang Pu Sodh Candasaro in the early 20th century. Wat Phra Dhammakaya is one of the temples that emerged from this tradition and is part of the Maha Nikaya, Mahā Nikāya fraternity. The temple is legally represented by the Dhammakaya Foundation. It aims to adapt traditional Buddhist values in modern society, doing so through modern technology and marketing methods. The temple has faced controversy and a government crackdown. Wat Phra Dhammakaya plays a leading role in Thai Buddhism, with theologian Edward Irons describing it as "the face of modern Thai Buddhism". ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
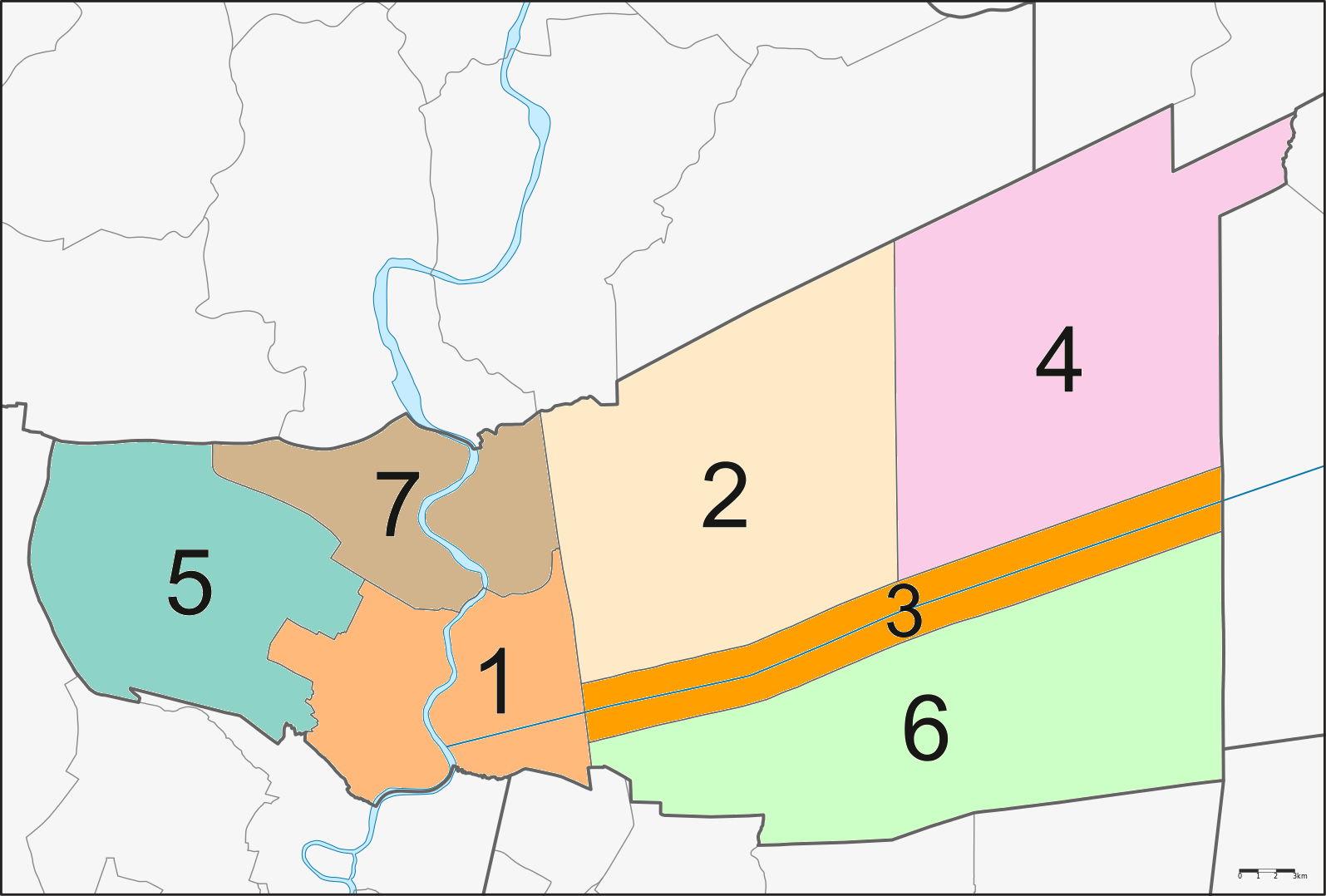
Pathum Thani Province
Pathum Thani (, ) is one of the central provinces (''changwat'') of Thailand. Neighboring provinces are (from north clockwise): Phra Nakhon Si Ayutthaya, Saraburi, Nakhon Nayok, Chachoengsao, Bangkok, and Nonthaburi. The province is north of Bangkok and is part of the Bangkok metropolitan area. In many places, the boundary between the two provinces is not noticeable as both sides of the boundary are equally urbanized. Pathum Thani town is the administrative seat, but Ban Rangsit, seat of Thanyaburi district, is the largest populated place in the province. Pathum Thani is an old province, heavily populated by the Mon people, dotted with 186 temples and parks. The Dream World amusement park is here. Geography The province lies on the low alluvial flats of the Chao Phraya River that flows through the capital. Many canals (''khlongs'') cross the province and feed the rice paddies. There is no forest area in the province. History The city dates back to a settlement founded by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Anattā
In Buddhism, the term ''anattā'' () or ''anātman'' () is the doctrine of "no-self" – that no unchanging, permanent self or essence can be found in any phenomenon. While often interpreted as a doctrine denying the existence of a self, ''anatman'' is more accurately described as a strategy to attain non-attachment by recognizing everything as impermanent, while staying silent on the ultimate existence of an unchanging essence. In contrast, dominant schools of Hinduism assert the existence of Ātman as pure awareness or witness-consciousness, "reify ngconsciousness as an eternal self". Etymology and nomenclature ''Anattā'' is a composite Pali word consisting of ''an'' (not) and ''attā'' (self-existent essence). The term refers to the central Buddhist concept that there is no phenomenon that has a permanent, unchanging "self" or essence. It is one of the three characteristics of all existence, together with '' dukkha'' (suffering, dissatisfaction) and '' anicca'' (imperm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Buddha-nature
In Buddhist philosophy and soteriology, Buddha-nature ( Chinese: , Japanese: , , Sanskrit: ) is the innate potential for all sentient beings to become a Buddha or the fact that all sentient beings already have a pure Buddha-essence within themselves.Heng-Ching ShihThe Significance Of 'Tathagatagarbha' – A Positive Expression Of 'Sunyata'/ref> "Buddha-nature" is the common English translation for several related Mahāyāna Buddhism, Buddhist terms, most notably ''tathāgatagarbha'' and ''buddhadhātu'', but also ''sugatagarbha,'' and ''buddhagarbha''. ''Tathāgatagarbha'' can mean "the womb" or "embryo" (''garbha'') of the "thus-gone one" (''Tathagata, tathāgata''), and can also mean "containing a ''tathāgata''"''. Buddhadhātu'' can mean "buddha-element", "buddha-realm", or "buddha-substrate". Buddha-nature has a wide range of (sometimes conflicting) meanings in Indian Buddhism and later in East Asian Buddhism, East Asian and Tibetan Buddhism, Tibetan Buddhist literatur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |