|
Devghat Rural Municipality
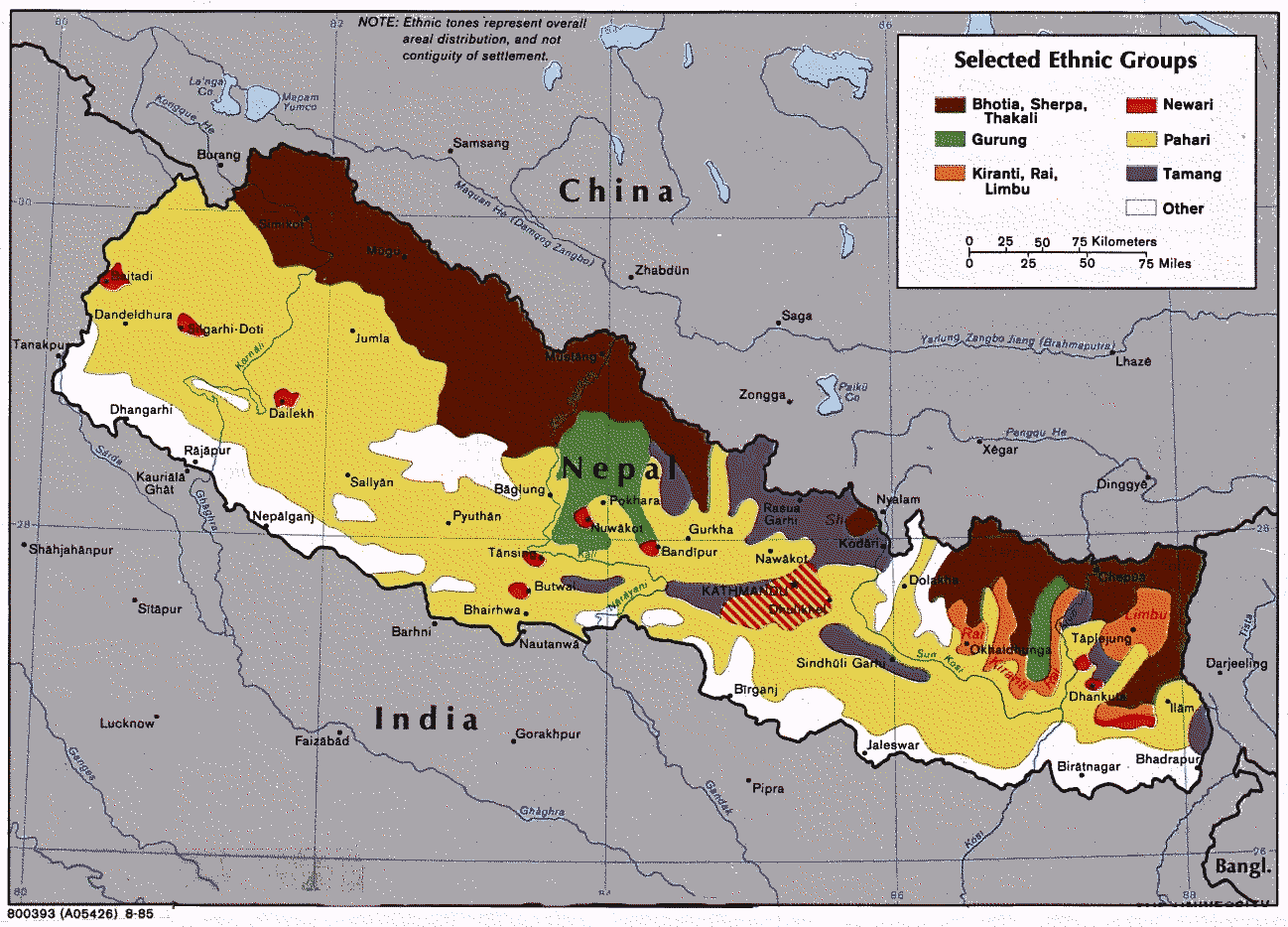
Devghat is a Rural municipality located within the Tanahun District of the Gandaki Province of Nepal. The rural municipality spans of area, with a total population of 16,131 according to a 2011 Nepal census. On March 10, 2017, the Government of Nepal restructured the local level bodies into 753 new local level structures. The previous Devghat, Kota, Chhipchhipe and part of Baidi VDCs were merged to form Devghat Rural Municipality. Devghat is divided into 5 wards, with Devghat VDC declared the administrative center of the rural municipality. Demographics At the time of the 2011 Nepal census, Devghat Rural Municipality had a population of 16,478. Of these, 44.1% spoke Nepali, 27.7% Magar, 22.0% Gurung, 3.6% Bhujel, 1.3% Bote, 0.6% Tamang, 0.4% Newar, 0.1% Chepang, 0.1% Sign language and 0.1% other languages as their first language. In terms of ethnicity/caste, 34.8% were Magar, 31.5% Gurung, 8.8% Hill Brahmin, 6.5% Gharti/ Bhujel, 3.8% Thakuri, 3.5% Chhetri, 2. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gaunpalika
A gaunpalika ( ne, गाउँपालिका, lit=rural municipality, translit=Gāum̐pālikā ) is an administrative division in Nepal. The Ministry of Federal Affairs and Local Development dissolved the existing village development committees and announced the establishment of this new local body. It is a sub-unit of a district. There are currently 460 rural municipalities. History The village development committee was the previous governing body of villages in Nepal. They were replaced on 10 May 2017 by the rural municipalities which were formed by combining different VDCs. The decision was taken by the cabinet of Nepal after modifications in the report proposed by the Local Level Restructuring Commission. Initially 481 rural municipalities were formed but it was later changed to 460 municipalities. According to the Ministry of Federal Affairs and Local Development the new bodies were to be called "rural municipality" and not "village council" which was the literal tran ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Village Development Committee (Nepal)
A village development committee ( ne, गाउँ विकास समिति; ''gāum̐ vikās samiti'') in Nepal was the lower administrative part of its Ministry of Federal Affairs and Local Development. Each district had several VDCs, similar to municipalities but with greater public-government interaction and administration. There were 3,157 village development committees in Nepal. Each village development committee was further divided into several wards ( ne, वडा) depending on the population of the district, the average being nine wards. Purpose The purpose of village development committees is to organise village people structurally at a local level and creating a partnership between the community and the public sector for improved service delivery system. A village development committee has status as an autonomous institution and authority for interacting with the more centralised institutions of governance in Nepal. In doing so, the village development co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bahun
Bahun ( ne, बाहुन) or Khas Brahmin ( ne, खस ब्राह्मण) is a caste ( ''Varna'') among Khas people of Nepal. Their origins are from the Indo-Aryan Khasa tribe of Nepal and South Asia. According to the 2011 Nepal census, Bahun is the second most populous group after Chhetri, another Varna within the hill Hindus in Nepal. According to 1854 ''Muluki Ain'' (Nepalese Legal Code), Bahuns were regarded as caste among sacred thread bearers (Tagadhari) and twice-born Hindus. Origin Traditionally, Bahuns were members of the Khas community together with Chhetris and Hill Dalits. Possibly due to political power of the Khasa Malla kingdom, Khas Bahun and Khas Rajput (Chhetris) had high social status like plain Brahmins and Rajputs in the present-day western Nepal. Bahuns, regarded as upper class Khas group together with Chhetri, were associated mostly with the Gorkha Kingdom. Bahuns were original inhabitants of Karnali region of Nepal. The immigration ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gurung People
Gurung (exonym; ) or Tamu (endonym; Gurung: ) are an ethnic group indigenous to the hills and mountains of Gandaki Province of Nepal. Gurung people predominantly live around the Annapurna region in Manang, Mustang, Dolpo, Kaski, Lamjung, Gorkha, Parbat and Syangja districts of Nepal. They are one of the main Gurkha tribes. They are also scattered across India in Sikkim, Assam, Delhi, West Bengal ( Darjeeling area) and other regions with a predominant Nepali diaspora population. They speak the Sino-Tibetan Gurung language and practice Bon religion alongside Tibetan Buddhism and Hinduism. Gurung caste The Tibetan societies from which the Gurungs came had no caste system and within themselves. Yet for several centuries the Gurungs and other hill peoples have been mixing with the caste cultures of Aryan and they have been influenced by them in various ways. As a result, Gurung caste system has been fragmented into two parts: the four-caste (''Songhi/ Char-jat'') and sixteen-cas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magars
The Magar, also spelled as Mangar, and Mongar, are the third largest ethnolinguistic groups of Nepal, indigenous to Western Nepal and representing 7.1% of Nepal's total population according to the 2011 Nepal census. The original home of the Magar people was to the west of Gandaki river, and roughly speaking, consisted of that portion of Nepal which lies between and around about Gulmi, Arghakhanchi, and Palpa. This part of the country was divided into twelve districts known as "''Bahra Magarat''" (Confederation of Twelve Magar Kingdoms), which included the following regions of that period: Argha, Khanchi, Bhirkot, Dhor, Garhung, Ghiring, Gulmi, Isma, Musikot, Pyung, Rising, Satung, and Pyung. During the medieval period, the whole area from Palpa to Rukum Rolpa was called the "Magarat"'','' a place settled and inhabited by Magars. Another Confederation of Eighteen Magar Kingdoms known as "''Athara Magarat''" also existed, and was originally inhabited by Kham Magars. Origin There ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sign Language
Sign languages (also known as signed languages) are languages that use the visual-manual modality to convey meaning, instead of spoken words. Sign languages are expressed through manual articulation in combination with non-manual markers. Sign languages are full-fledged natural languages with their own grammar and lexicon. Sign languages are not universal and are usually not mutually intelligible, although there are also similarities among different sign languages. Linguists consider both spoken and signed communication to be types of natural language, meaning that both emerged through an abstract, protracted aging process and evolved over time without meticulous planning. Sign language should not be confused with body language, a type of nonverbal communication. Wherever communities of deaf people exist, sign languages have developed as useful means of communication and form the core of local Deaf cultures. Although signing is used primarily by the deaf and hard of hearing, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chepang Language , the language of the Chepang people
{{dab ...
Chepang may refer to: *Chepang people, a group indigenous to the lands of Nepal *Chepang language Chepang may refer to: * Chepang people, a group indigenous to the lands of Nepal * Chepang language, the language of the Chepang people {{dab ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Newar Language
Newar (), or Newari and known officially in Nepal as Nepal Bhasa, is a Sino-Tibetan language spoken by the Newar people, the indigenous inhabitants of Nepal Mandala, which consists of the Kathmandu Valley and surrounding regions in Nepal. "Nepal Bhasa" literally means "Nepalese language", however the language is not the same as Nepali (Devanāgarī: नेपाली), the country's current official language of the central government. The two languages belong to different language families (Sino-Tibetan and Indo-European, respectively), but centuries of contact have resulted in a significant body of shared vocabulary. Newar was Nepal's administrative language from the 14th to the late 18th century. From the early 20th century until democratisation, Newar suffered from official suppression. From 1952 to 1991, the percentage of Newar speakers in the Kathmandu Valley dropped from 75% to 44% and today Newar culture and language are under threat. The language has been listed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tamang Language
Tamang (Devanagari: तामाङ; ''tāmāng'') is a term used to collectively refer to a dialect cluster spoken mainly in Nepal, Sikkim, West Bengal (Darjeeling) and North-Eastern India. It comprises Eastern Tamang, Northwestern Tamang, Southwestern Tamang, Eastern Gorkha Tamang, and Western Tamang. Lexical similarity between Eastern Tamang (which is regarded as the most prominent) and other Tamang languages varies between 81% to 63%. For comparison, lexical similarity between Spanish and Portuguese, is estimated at 89%. Ethnologue report for Spanish Dialects ''Ethnologue'' divides Tamang into the following varieties due to mutual unintelligibility. *Eastern Tamang: 759,000 in Nepal (2000 WCD). Population total all countries: 773,000. Sub-dialects are as follows. **Outer-Eastern Tamang (Sailung Tamang) **Central-Eastern Tamang (Temal Tamang) **Southwestern Tamang (Kath-Bhotiya, Lama Bhote, Murmi, Rongba, Sain, Tamang Gyoi, Tamang Gyot, Tamang Lengmo, Tamang Tam) *Western T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bote-Darai Language
Bote (Bote-Majhi) and Darai are mutually intelligible tribal dialects of Nepal that are close to Danwar Rai but otherwise unclassified. Its speakers are rapidly shifting to Nepali. References Indo-Aryan languages {{IndoAryan-lang-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bhujel Language
Bhujel, also called Bujhyal, is a Chepangic language of Greater Magaric Branch spoken in central Nepal. It is a semi-tonal language, employing a complex array of affixes. It is believed that their original homeland was Nisi-Buji area of Baglung. Bhujel generally refers to the people who used to be Kamara and Bhujel term is given by the government on 2058 BS. Bhujel generally refers to the clan name of Brahmin. In addition, Bhujel term is also the clan name of various ethnic groups including Brahmin, Chhetri & Magar. Bhujel people normally are with Mongoloid features rather than with Caucasoid features. Due to the social structure & social development, This term has been the identity of many other ethnic people too. Geographical distribution Bhujel is spoken in the following villages of Nepal ('' Ethnologue''). *Tanahun District, Gandaki Zone: Kulmun, Arthumpka, Andimul, and Baniyatar *Gorkha District, Gandaki Zone: Beltar *Nawalparasi District, Lumbini Zone: Dhodeni * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gurung Language
Gurung (Devanagari: ), also known as Tamu Kyi (, ; Tibetan: ) or Tamu Bhaasaa (, ), is a language spoken by the Gurung people of Nepal. The total number of all Gurung speakers in Nepal was 227,918 in 1991 and 325,622 in 2011. The official language of Nepal, Nepali, is an Indo-European language, whereas Gurung is a Sino-Tibetan language. Gurung is one of the major languages of Nepal, and is also spoken in India, Bhutan, and by diaspora communities in countries such as Singapore and Hong Kong. Geographical distribution Gurung is spoken in the following districts of Nepal and India (''Ethnologue''): *Gandaki Province: Kaski District, Syangja District, Lamjung District, Tanahu District, Gorkha District, Manang District and Mustang *Dhawalagiri Zone: Parbat district *Sikkim: South Sikkim, West Sikkim, East Sikkim Classification At higher levels, Gurung is a member of the Tibeto-Burman (or Trans-Himalayan) family. Robert Shafer classified Gurung within the Bodic division, sub-gro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)