|
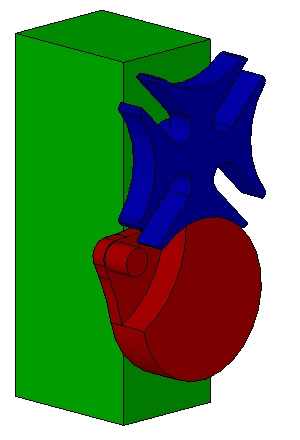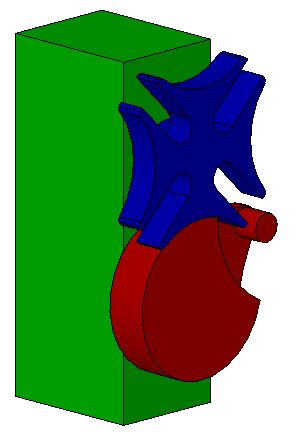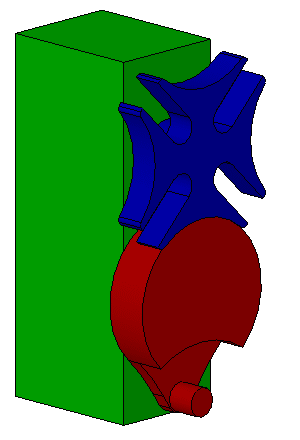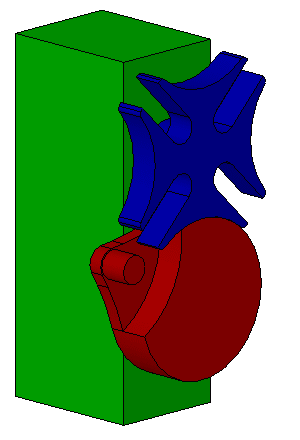
Desmodromic Valve
:''In general mechanical terms, the word ''desmodromic'' is used to refer to mechanisms that have different controls for their actuation in different directions.'' A desmodromic valve is a reciprocating engine poppet valve that is positively closed by a cam and leverage system, rather than by a more conventional spring. The valves in a typical four-stroke engine allow the air/fuel mixture into the cylinder at the beginning of the cycle and exhaust spent gases at the end of the cycle. In a conventional four-stroke engine, valves are opened by a cam and closed by return spring. An engine using desmodromic valves has two cams and two actuators, each for positive opening and closing without a return spring. Etymology The word comes from the Greek words ''desmos'' (, translated as "bond" or "knot") and ''dromos'' (, "track" or "way"). This denotes the major characteristic of the valves being continuously "bound" to the camshaft. Idea The common valve spring system is satisfactory f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ducati
Ducati Motor Holding S.p.A. () is the motorcycle-manufacturing division of Italian company Ducati, headquartered in Bologna, Italy. The company is directly owned by Italian automotive manufacturer Lamborghini, whose German parent company is Audi, itself owned by the Volkswagen Group. History In 1926 Antonio Cavalieri Ducati and his three sons, Adriano, Marcello, and Bruno, founded ''Società Scientifica Radiobrevetti Ducati'' (SSR Ducati) in Bologna to produce vacuum tubes, condensers and other radio components. In 1935 they had become successful enough to enable construction of a new factory in the Borgo Panigale area of the city. Production was maintained during World War II, despite the Ducati factory being a repeated target of Allied bombing. It was finally destroyed by around 40 Consolidated B-24 Liberators on 12 October 1944 as part of the United States Army Air Forces's Operation Pancake, which involved some 700 aircraft flying from airfields in the Province of Foggi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kinetic Energy
In physics, the kinetic energy of an object is the energy that it possesses due to its motion. It is defined as the work needed to accelerate a body of a given mass from rest to its stated velocity. Having gained this energy during its acceleration, the body maintains this kinetic energy unless its speed changes. The same amount of work is done by the body when decelerating from its current speed to a state of rest. Formally, a kinetic energy is any term in a system's Lagrangian which includes a derivative with respect to time. In classical mechanics, the kinetic energy of a non-rotating object of mass ''m'' traveling at a speed ''v'' is \fracmv^2. In relativistic mechanics, this is a good approximation only when ''v'' is much less than the speed of light. The standard unit of kinetic energy is the joule, while the English unit of kinetic energy is the foot-pound. History and etymology The adjective ''kinetic'' has its roots in the Greek word κίνησι� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Galling
Galling is a form of wear caused by adhesion between sliding surfaces. When a material galls, some of it is pulled with the contacting surface, especially if there is a large amount of force compressing the surfaces together. Galling is caused by a combination of friction and adhesion between the surfaces, followed by slipping and tearing of crystal structure beneath the surface. This will generally leave some material stuck or even friction welded to the adjacent surface, whereas the galled material may appear gouged with balled-up or torn lumps of material stuck to its surface. Galling is most commonly found in metal surfaces that are in sliding contact with each other. It is especially common where there is inadequate lubrication between the surfaces. However, certain metals will generally be more prone to galling, due to the atomic structure of their crystals. For example, aluminium is a metal that will gall very easily, whereas annealed (softened) steel is slightly mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hertzian Contact Stress
{{disambiguation ...
Hertzian may refer to: * Hertzian antenna * Hertzian cone, the cone produced when an object passes through a solid, such as a bullet through glass * Hertzian contact stress, localized stresses that develop as two curved surfaces come in contact and deform slightly under imposed loads * Hertzian dipole, defined as a finite oscillating current over an infinitesimal length at a specified position * Hertzian wave, the original name of radio waves * Hertzian wave telegraphy Wireless telegraphy or radiotelegraphy is transmission of text messages by radio waves, analogous to electrical telegraphy using cables. Before about 1910, the term ''wireless telegraphy'' was also used for other experimental technologies for tr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mirror Image
A mirror image (in a plane mirror) is a reflected duplication of an object that appears almost identical, but is reversed in the direction perpendicular to the mirror surface. As an optical effect it results from reflection off from substances such as a mirror or water. It is also a concept in geometry and can be used as a conceptualization process for 3-D structures. In geometry and geometrical optics In two dimensions In geometry, the mirror image of an object or two-dimensional figure is the virtual image formed by reflection in a plane mirror; it is of the same size as the original object, yet different, unless the object or figure has reflection symmetry (also known as a P-symmetry). Two-dimensional mirror images can be seen in the reflections of mirrors or other reflecting surfaces, or on a printed surface seen inside-out. If we first look at an object that is effectively two-dimensional (such as the writing on a card) and then turn the card to face a mirror, the o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jerk (physics)
In physics, jerk or jolt is the rate at which an object's acceleration changes with respect to time. It is a vector quantity (having both magnitude and direction). Jerk is most commonly denoted by the symbol and expressed in m/s3 (SI units) or standard gravities per second (''g''0/s). Expressions As a vector, jerk can be expressed as the first time derivative of acceleration, second time derivative of velocity, and third time derivative of position: \mathbf j(t) = \frac = \frac = \frac where * is acceleration * is velocity * is position * is time Third-order differential equations of the form J\left(\overset, \ddot, \dot, x\right) = 0 are sometimes called ''jerk equations''. When converted to an equivalent system of three ordinary first-order non-linear differential equations, jerk equations are the minimal setting for solutions showing chaotic behaviour. This condition generates mathematical interest in ''jerk systems''. Systems involving fourth-order derivatives or hi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rocker Arm
In the context of an internal combustion engine, a rocker arm is a valvetrain component that typically transfers the motion of a pushrod to the corresponding intake/exhaust valve. Rocker arms in automobiles are typically made from stamped steel, or aluminum in higher-revving applications. Some rocker arms (called ''roller rockers'') include a bearing at the contact point, to reduce wear and friction at the contact point. Overview In the typical use-case of an overhead valve (pushrod) engine, the camshaft at the bottom of the engine pushes the pushrod upwards. The top of the pushrod presses upwards on one side of the rocker arm (located at the top of the engine), which causes the rocker arm to rotate. This rotation causes the other end of the rocker arm to press downwards on the top of the valve, which opens the valve by moving it downwards. A ''roller rocker'' is a rocker arm that uses needle bearings (or a single bearing ball in older engines) at the contact point between th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pushrod
A valvetrain or valve train is a mechanical system that controls the operation of the intake and exhaust valves in an internal combustion engine. The intake valves control the flow of air/fuel mixture (or air alone for direct-injected engines) into the combustion chamber, while the exhaust valves control the flow of spent exhaust gasses out of the combustion chamber once combustion is completed. Layout The valvetrain layout is largely dependent on the location of the camshaft. The common valvetrain configurations for piston engines - in order from oldest to newest - are: * Flathead engine: The camshaft and the valves are located in the engine block below the combustion chamber. * Overhead valve engine: The camshaft remains in the block, however the valves are located in the cylinder head above the combustion chamber. * Overhead camshaft engine: The valves and camshaft(s) are in the cylinder head above the combustion chamber. Components The valvetrain consists of all the c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Poppet Valve
A poppet valve (also called mushroom valve) is a valve typically used to control the timing and quantity of gas or vapor flow into an engine. It consists of a hole or open-ended chamber, usually round or oval in cross-section, and a plug, usually a disk shape on the end of a shaft known as a valve stem. The working end of this plug, the valve face, is typically ground at a 45° bevel to seal against a corresponding valve seat ground into the rim of the chamber being sealed. The shaft travels through a valve guide to maintain its alignment. A pressure differential on either side of the valve can assist or impair its performance. In exhaust applications higher pressure against the valve helps to seal it, and in intake applications lower pressure helps open it. The poppet valve was invented in 1833 by American E.A.G. Young of the Newcastle and Frenchtown Railroad. Young had patented his idea, but the Patent Office fire of 1836 destroyed all records of it. Etymology The word po ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Overhead Camshaft
An overhead camshaft (OHC) engine is a piston engine where the camshaft is located in the cylinder head above the combustion chamber. This contrasts with earlier overhead valve engines (OHV), where the camshaft is located below the combustion chamber in the engine block. ''Single overhead camshaft'' (SOHC) engines have one camshaft per bank of cylinders. ''Dual overhead camshaft'' (DOHC, also known as "twin-cam".) engines have two camshafts per bank. The first production car to use a DOHC engine was built in 1910. Use of DOHC engines slowly increased from the 1940s, leading to many automobiles by the early 2000s using DOHC engines. Design In an OHC engine, the camshaft is located at the top of the engine, above the combustion chamber. This contrasts the earlier overhead valve engine (OHV) and flathead engine configurations, where the camshaft is located down in the engine block. The valves in both OHC and OHV engines are located above the combustion chamber; however an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tappet
A tappet is most commonly a component in an internal combustion engine which converts the rotating motion of the camshaft into linear motion of the valves, either directly or indirectly. An earlier use of the term was for part of the valve gear in beam engines beginning in 1715. The term is also used for components in pneumatic cylinders and weaving loom. __TOC__ Beam engines The first recorded use of the term tappet is as part of the valve gear in the 1715 Newcomen engine, an early form of steam engine. Early versions of the Newcomen engines from 1712 had manually operated valves, but by 1715 this repetitive task had been automated through the use of tappets. The beam of the engine had a vertical 'plug rod' hung from it, alongside the cylinder. Adjustable blocks or 'tappets' were attached to this rod and as the beam moved up and down, the tappets pressed against long levers or 'horns' attached to the engine's valves, working the cycle of steam and injection water valves ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |