|
Design Flaws
A product defect is any characteristic of a Product (business), product which hinders its usability for the purpose for which it was Product design, designed and Manufacturing, manufactured. Product defects arise most prominently in legal contexts regarding product safety, where the term is applied to "anything that renders the product not reasonably safe".Patricia A. Robinson, ''Writing and Designing Manuals and Warnings'' (2009), p. 234. The field of law that addresses injuries caused by defective products is called ''product liability''. A wide range of circumstances can render a product defective. The product may have a design defect or design flaw, resulting from the product having been poorly designed or Product testing, tested, so that the design itself yields a product that can not perform its desired function. Even if the design is correct, the product may have a manufacturing defect if it was incorrectly manufactured, for example if the wrong materials are used. A product ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Product (business)
In marketing, a product is an object, or system, or service made available for consumer use as of the consumer demand; it is anything that can be offered to a market to satisfy the desire or need of a customer. In retailing, products are often referred to as '' merchandise'', and in manufacturing, products are bought as raw materials and then sold as finished goods. A service is also regarded as a type of product. In project management, products are the formal definition of the project deliverables that make up or contribute to delivering the objectives of the project. A related concept is that of a sub-product, a secondary but useful result of a production process. Dangerous products, particularly physical ones, that cause injuries to consumers or bystanders may be subject to product liability. Product classification A product can be classified as tangible or intangible. A tangible product is an actual physical object that can be perceived by touch such as a building, ve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brand
A brand is a name, term, design, symbol or any other feature that distinguishes one seller's good or service from those of other sellers. Brands are used in business, marketing, and advertising for recognition and, importantly, to create and store value as brand equity for the object identified, to the benefit of the brand's customers, its owners and shareholders. Brand names are sometimes distinguished from Generic brand, generic or store brands. The practice of branding - in the original literal sense of marking by burning - is thought to have begun with the ancient Egyptians, who are known to have engaged in livestock branding as early as 2,700 BCE. Branding was used to differentiate one person's cattle from another's by means of a distinctive symbol burned into the animal's skin with a hot branding iron. If a person stole any of the cattle, anyone else who saw the symbol could deduce the actual owner. The term has been extended to mean a strategic personality for a produ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quality Management
Quality management ensures that an organization, product or service consistently functions well. It has four main components: quality planning, quality assurance, quality control and quality improvement. Quality management is focused not only on product and service quality, but also on the means to achieve it. Quality management, therefore, uses quality assurance and control of processes as well as products to achieve more consistent quality. Quality control is also part of quality management. What a customer wants and is willing to pay for it, determines quality. It is a written or unwritten commitment to a known or unknown consumer in the market. Quality can be defined as how well the product performs its intended function. Evolution Quality management is a recent phenomenon but important for an organization. Civilizations that supported the arts and crafts allowed clients to choose goods meeting higher quality standards than normal goods. In societies where arts and crafts ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Product Recall
A product recall is a request from a manufacturer to return a product after the discovery of safety issues or product defects that might endanger the consumer or put the maker/seller at risk of legal action. The recall is an effort to limit ruination of the corporate image and limit liability for corporate negligence, which can cause significant legal costs. It can be difficult, if not impossible, to determine how costly can be releasing to the consumer a product that could endanger someone's life and the economic loss resulting from unwanted publicity. Recalls are costly. Costs include having to handle the recalled product, replacing it and possibly being held financially responsible for the consequences of the recalled product. A country's consumer protection laws will have specific requirements in regard to product recalls. Such regulations may include how much of the cost the maker will have to bear, situations in which a recall is compulsory (usually because the risk is b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sarvepalli Radhakrishnan
Sarvepalli Radhakrishnan (; 5 September 1888 – 17 April 1975), natively Radhakrishnayya, was an Indian philosopher and statesman. He served as the 2nd President of India from 1962 to 1967. He also 1st Vice President of India from 1952 to 1962. He was the 2nd Ambassador of India to the Soviet Union from 1949 to 1952. He was also the 4th Vice-Chancellor of Banaras Hindu University from 1939 to 1948 and the 2nd Vice-Chancellor of Andhra University from 1931 to 1936. One of the most distinguished twentieth-century scholars of comparative religion and philosophy, Radhakrishnan held the King George V Chair of Mental and Moral Science at the University of Calcutta from 1921 to 1932 and Spalding Chair of Eastern Religion and Ethics at University of Oxford from 1936 to 1952. Radhakrishnan's philosophy was grounded in Advaita Vedanta, reinterpreting this tradition for a contemporary understanding. He defended Hinduism against what he called "uninformed Western criticism", c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Information Asymmetry
In contract theory and economics, information asymmetry deals with the study of decisions in transactions where one party has more or better information than the other. Information asymmetry creates an imbalance of power in transactions, which can sometimes cause the transactions to be inefficient, causing market failure in the worst case. Examples of this problem are adverse selection, moral hazard, and monopolies of knowledge. A common way to visualise information asymmetry is with a scale with one side being the seller and the other the buyer. When the seller has more or better information the transaction will more likely occur in the seller's favour ("the balance of power has shifted to the seller"). An example of this could be when a used car is sold, the seller is likely to have a much better understanding of the car's condition and hence its market value than the buyer, who can only estimate the market value based on the information provided by the seller and their own a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Supply Chain
In commerce, a supply chain is a network of facilities that procure raw materials, transform them into intermediate goods and then final products to customers through a distribution system. It refers to the network of organizations, people, activities, information, and resources involved in delivering a product or service to a consumer. Supply chain activities involve the transformation of natural resources, raw materials, and components into a finished product and delivering the same to the end customer. In sophisticated supply chain systems, used products may re-enter the supply chain at any point where residual value is recyclable. Supply chains link value chains. Suppliers in a supply chain are often ranked by "tier", with first-tier suppliers supplying directly to the client, second-tier suppliers supplying to the first tier, and so on. Overview A typical supply chain begins with the ecological, biological, and political regulation of natural resources, followed by the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
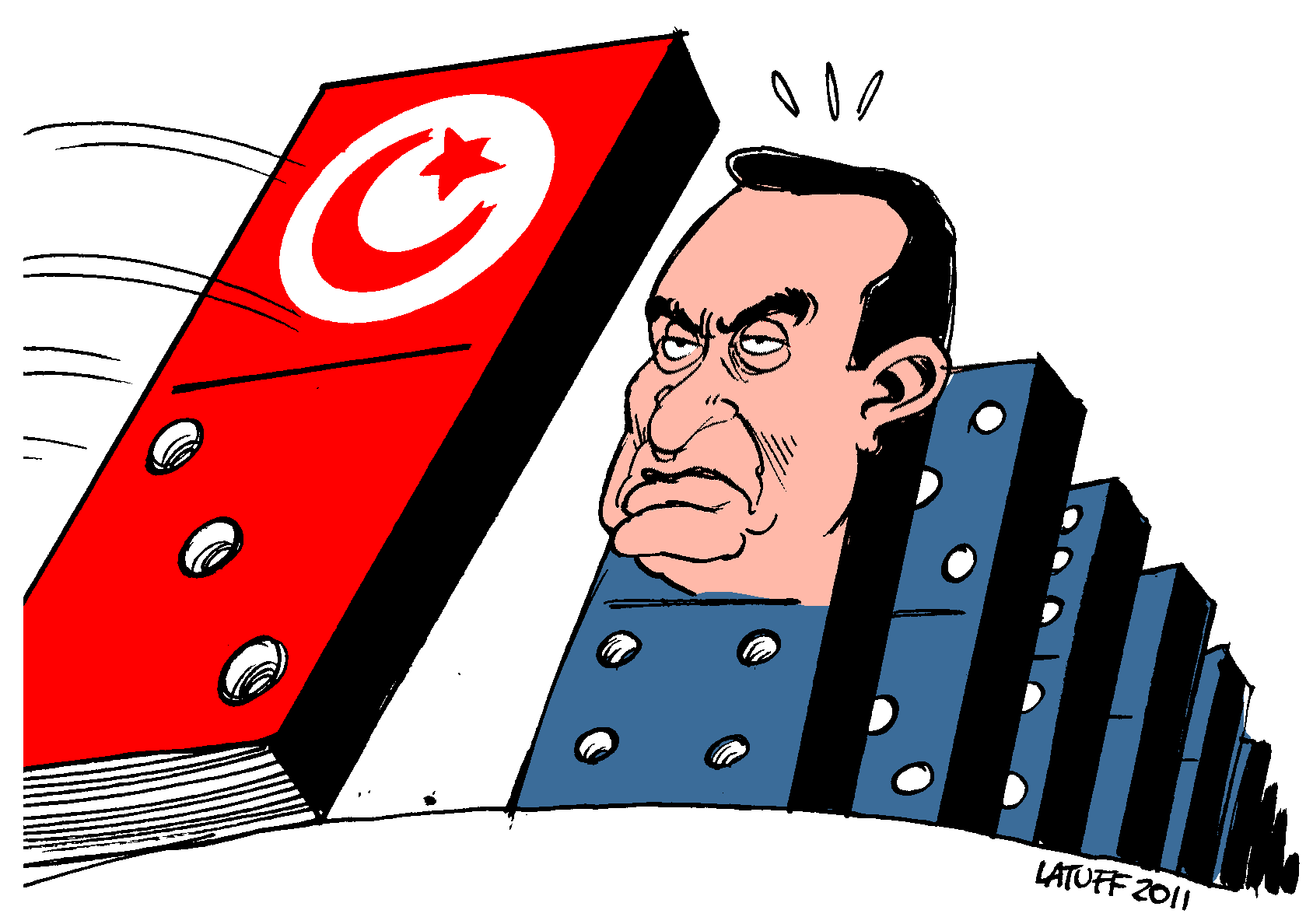
Domino Theory
The domino theory is a geopolitical theory which posits that increases or decreases in democracy in one country tend to spread to neighboring countries in a domino effect. It was prominent in the United States from the 1950s to the 1980s in the context of the Cold War, suggesting that if one country in a region came under the influence of communism, then the surrounding countries would follow. It was used by successive United States administrations during the Cold War to justify the need for American intervention around the world. Former U.S. President Dwight D. Eisenhower described the theory during a news conference on 7 April 1954, when referring to communism in Indochina as follows: Moreover, Eisenhower’s deep belief in the domino theory in Asia heightened the "perceived costs for the United States of pursuing multilateralism" because of multifaceted events including the " 1949 victory of the Chinese Communist Party, the June 1950 North Korean invasion, the 1954 Quemoy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mattel
Mattel, Inc. ( ) is an American multinational toy manufacturing and entertainment company founded in January 1945 and headquartered in El Segundo, California. The company has presence in 35 countries and territories and sells products in more than 150 countries. The company operates through three business segments: North America, International, and American Girl. It is the world's second largest toy maker in terms of revenue, after The Lego Group. Two of its historic and most valuable brands, Barbie and Hot Wheels, were respectively named the top global toy property and the top-selling global toy of the year for 2020 and 2021 by The NPD Group, a global information research company. The name of the company is a portmanteau of the names of two of the company's founders; the surname of Harold Matson and the first name of Elliot Handler. History Origins and early years Harold "Matt" Matson, Ruth Handler, and Elliot Handler founded Mattel as Mattel Creations in January 1945 in a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rework (electronics)
Rework (or re-work) is the term for the refinishing operation or repair of an electronic printed circuit board (PCB) assembly, usually involving desoldering and re-soldering of surface-mounted electronic components (SMD). Mass processing techniques are not applicable to single device repair or replacement, and specialized manual techniques by expert personnel using appropriate equipment are required to replace defective components; area array packages such as ball grid array (BGA) devices particularly require expertise and appropriate tools. A hot air gun or hot air station is used to heat devices and melt solder, and specialised tools are used to pick up and position often tiny components. A rework station is a place to do this work—the tools and supplies for this work, typically on a workbench. Other kinds of rework require other tools. Reasons for rework Rework is practiced in many kinds of manufacturing when defective products are found. For electronics, defects may in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Label
A label (as distinct from signage) is a piece of paper, plastic film, cloth, metal, or other material affixed to a container or product, on which is written or printed information or symbols about the product or item. Information printed directly on a container or article can also be considered labelling. Labels have many uses, including promotion and providing information on a product's origin, the manufacturer (e.g., brand name), use, safety, shelf-life and disposal, some or all of which may be governed by legislation such as that for food in the UK or United States. Methods of production and attachment to packaging are many and various and may also be subject to internationally recognised standards. In many countries, hazardous products such as poisons or flammable liquids must have a warning label. Uses Labels may be used for any combination of identification, information, warning, instructions for use, environmental advice or advertising. They may be stickers, perma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)

.jpg)