|
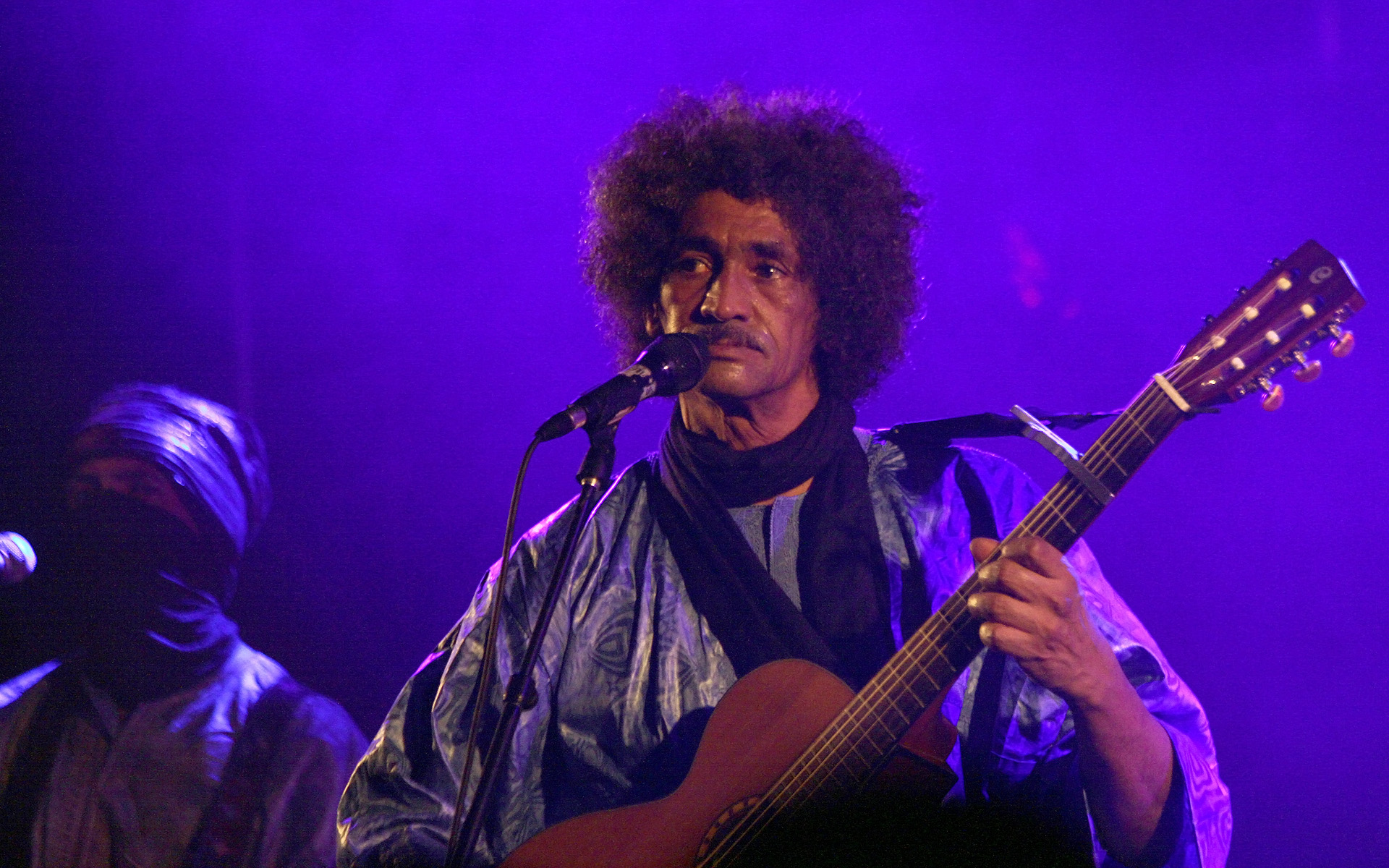
Desert Blues
Tishoumaren (ⵜⵉⵛⵓⵎⴰⵔⴻⵏ in Neo-Tifinagh script) or assouf, internationally known as desert blues, is a style of music from the Sahara region of northern and west Africa. Critics describe the music as a fusion of blues and rock music with Tuareg, Malian or North African music. Various other terms are used to describe it including desert rock, Saharan rock, Takamba, Mali blues, Tuareg rock or simply "guitar music". The style has been pioneered by Tuareg musicians in the Sahara region, particularly in Mali, Niger, Libya, Western Sahara, Algeria, Burkina Faso and others. The musical style took shape as an expression of the culture of the traditionally nomadic Tuareg people, amid their difficult sociopolitical situation, including rebellions, widespread displacement and exile in post-colonial Africa. The word ''Tishoumaren'' is derived from the French word ''chômeur'', meaning "the unemployed". The genre was first pioneered by and popularized outside of Africa b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tinariwen
Tinariwen (Tamasheq: , with vowels , pronounced ''tinariwen'' "deserts", plural of ''ténéré'' "desert") is a collective of Tuareg musicians from the Sahara Desert region of northern Mali. Considered a pioneer of desert blues, the group's guitar-driven style combines traditional Tuareg and African music with Western rock music. They have released eight albums since their formation and have toured internationally. The group was founded by Ibrahim Ag Alhabib, along with Alhassane Ag Touhami and brothers Inteyeden Ag Ablil and Liya Ag Ablil (aka "Diarra"). The as then unnamed musical group was formed in 1979 while exiled in Tamanrasset, Algeria. Tinariwen formed as a musical collective while in military training in Libya, aiming to write songs about issues facing the Tuareg people. They returned to Mali in 1989, with some members joining as fighters in a Tuareg rebellion before dedicating themselves to music full-time in 1991 after a peace accord was reached. Tinariwen first start ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neo-Tifinagh
Tifinagh ( Tuareg Berber language: or , ) is a script used to write the Berber languages. Tifinagh is descended from the ancient Libyco-Berber alphabet. The traditional Tifinagh, sometimes called Tuareg Tifinagh, is still favored by the Tuareg Berbers of the Sahara desert in southern Algeria, northeastern Mali, northern Niger and northern Burkina Faso for use writing the Tuareg Berber language. Neo-Tifinagh () is an alphabet developed by Berber Academy to adopt Tuareg Tifinagh for use with Kabyle; it has been since modified for use across North Africa. Tifinagh is one of three major competing Berber orthographies alongside the Berber Latin alphabet and the Arabic script. Tifinagh is the official script for Tamazight, an official language of Morocco. However, outside of symbolic cultural uses, Latin remains the dominant script for writing Berber languages both in Morocco and throughout North Africa. The ancient Libyco-Berber script (or the Libyc script) was used by the an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ali Farka Touré
Ali Ibrahim "Ali Farka" Touré (31 October 1939 – 6 March 2006) was a Malian singer and multi-instrumentalist, and one of the African continent's most internationally renowned musicians. His music blends traditional Malian music and its derivative, African American blues and is considered a pioneer of African desert blues. Touré was ranked number 76 on ''Rolling Stone''s list of "The 100 Greatest Guitarists of All Time" and number 37 on ''Spin'' magazine's "100 Greatest Guitarists of All Time". Some years after his death, a group of musicians playing in his style performed as the Ali Farka Touré Allstars (2012), and later the Ali Farka Touré Band (formed 2014). Early life Touré was born in 1939 in the village of Kanau, on the banks of the Niger River in Gourma-Rharous Cercle in the northwestern Malian region of Tombouctou. His family belonged to the Arma community and moved to the nearby village of Niafunké when he was still an infant. His father died serving in th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chômeur
The chômeur, in the context of grammar, is an element of a sentence that has been syntactically "demoted" from the nucleus to the periphery of a clause. The term comes from the French word for "unemployed". In a passive sentence, the agent is a chômeur, having been "demoted" from the central or nuclear function of subject. For instance, by changing the sentence ''Dogs attack the postman'' into ''The postman is attacked by dogs'', one transforms "dogs" into a chômeur. The concept was introduced and used extensively in relational grammar. The term was suggested by the linguist Colette Craig. See also * Arc pair grammar In linguistics, arc pair grammar (APG) is a theory of syntax that aims to formalize and expand upon relational grammar. It primarily builds upon the relational grammar concept of an arc, but also makes use of more formally stated ideas from model ... Sources * Perlmutter, David M. (Ed.). (1983). ''Studies in relational grammar 1''. Chicago: Chicago Universit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
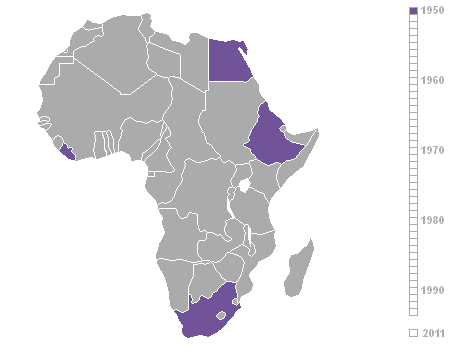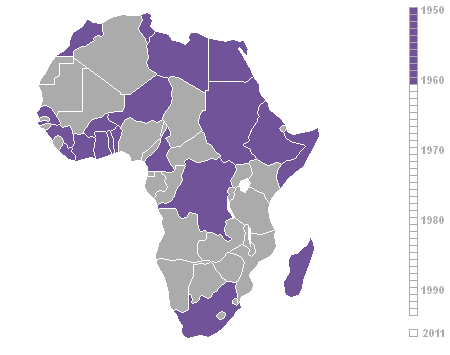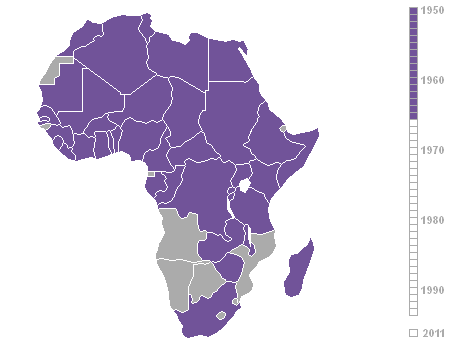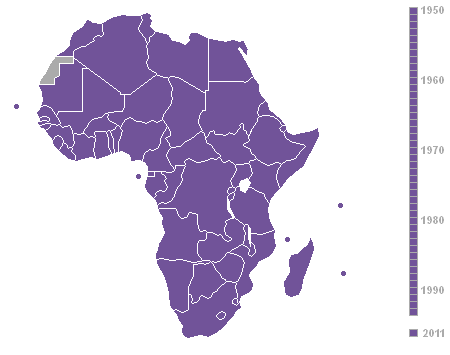
Decolonisation Of Africa
The decolonisation of Africa was a process that took place in the Scramble for Africa, mid-to-late 1950s to 1975 during the Cold War, with radical government changes on the continent as Colonialism, colonial governments made the transition to Sovereign state, independent states. The process was often marred with violence, political turmoil, widespread unrest, and organised revolts in both northern and sub-Saharan countries including the Algerian War in French Algeria, the Angolan War of Independence in Portuguese Angola, the Congo Crisis in the Belgian Congo, the Mau Mau Uprising in Kenya Colony, British Kenya, the Zanzibar Revolution in the Sultanate of Zanzibar, and the Nigerian Civil War in the secessionist state of Biafra. Background The "Scramble for Africa" between 1870 and 1914 was a significant period of European imperialism in Africa that ended with almost all of Africa, and its natural resources, being controlled as colonies by a small number of European states. Racin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tuareg Rebellion (other)
Tuareg rebellion may refer to various armed conflicts involving the Tuareg people of the northern parts of Mali and Niger: * Kaocen revolt (1916–1917) *Tuareg rebellion (1962–1964) *Tuareg rebellion (1990–1995) *Tuareg rebellion (2007–2009) *Tuareg rebellion (2012) *Tuareg involvement in the Northern Mali conflict (2012–) *Tuareg involvement in the Second Libyan Civil War (2014–2020) See also *Ansar Dine *Movement for Oneness and Jihad in West Africa *Tuareg militias of Ghat Tuareg militias of Ghat are ethnic Tuareg tribal militias, operating in South-West Libya desert areas during the Second Libyan Civil War. The militias rose to prominence in the district of Ghat, which has a Tuareg majority. Gradually, the Tuareg ... {{Disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Music Of Burkina Faso
The music of Burkina Faso includes the folk music of 60 different ethnic groups. The Mossi people, centrally located around the capital, Ouagadougou, account for 40% of the population while, to the south, Gurunsi, Gurma, Dagaaba and Lobi populations, speaking Gur languages closely related to the Mossi language, extend into the coastal states. In the north and east the Fulani of the Sahel preponderate, while in the south and west the Mande languages are common; Samo, Bissa, Bobo, Senufo and Marka. Burkinabé traditional music has continued to thrive and musical output remains quite diverse. Popular music is mostly in French: Burkina Faso has yet to produce a major pan-African success. Popular music Burkina Faso's popular music scene has not yet garnered the fame of that of other West African countries, and many popular recordings are imported from Europe, the United States and Democratic Republic of the Congo. In spite of this influx of popular styles, a few early musical ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Music Of Libya
Various kinds of Arab music are popular in Libya such as Andalusi music, locally known as Ma'luf, Chabi and Arab classical music. The Tuareg in the south have their own distinctive folk music. There is little or no pop music industry. Among the Tuareg, women are the musicians. They play a one-stringed violin called an anzad, as well as a variety of drums. Two of the most famous musicians of Libya are Ahmed Fakroun and Mohamed Hassan. Among Libyan Arabs, instruments include the zokra (a bagpipe), flute (made of bamboo), tambourine, oud (a fretless lute) and darbuka, a goblet drum held sideways and played with the fingers. Intricate clapping is also common in Libyan folk music. Traveling Bedouin poet-singers have spread many popular songs across Libya. Among their styles is huda, the camel driver's song, the rhythm of which is said to mimic the feet of a walking camel. During the 2011 revolution, the Berber singer Dania Ben Sassi Dania Ben Sassi, Tamazight: Danya ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tuareg People
The Tuareg people (; also spelled Twareg or Touareg; endonym: ''Imuhaɣ/Imušaɣ/Imašeɣăn/Imajeɣăn'') are a large Berber ethnic group that principally inhabit the Sahara in a vast area stretching from far southwestern Libya to southern Algeria, Niger, Mali, and Burkina Faso. Traditionally nomadic pastoralists, small groups of Tuareg are also found in northern Nigeria. The Tuareg speak languages of the same name (also known as ''Tamasheq''), which belong to the Berber branch of the Afroasiatic family. The Tuaregs have been called the "blue people" for the indigo dye coloured clothes they traditionally wear and which stains their skin. They are a semi-nomadic people who practice Islam, and are descended from the indigenous Berber communities of Northern Africa, which have been described as a mosaic of local Northern African (Taforalt), Middle Eastern, European (Early European Farmers), and Sub-Saharan African-related ancestries, prior to the Arab expansion. Tuareg peopl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Guardian
''The Guardian'' is a British daily newspaper. It was founded in 1821 as ''The Manchester Guardian'', and changed its name in 1959. Along with its sister papers ''The Observer'' and ''The Guardian Weekly'', ''The Guardian'' is part of the Guardian Media Group, owned by the Scott Trust. The trust was created in 1936 to "secure the financial and editorial independence of ''The Guardian'' in perpetuity and to safeguard the journalistic freedom and liberal values of ''The Guardian'' free from commercial or political interference". The trust was converted into a limited company in 2008, with a constitution written so as to maintain for ''The Guardian'' the same protections as were built into the structure of the Scott Trust by its creators. Profits are reinvested in journalism rather than distributed to owners or shareholders. It is considered a newspaper of record in the UK. The editor-in-chief Katharine Viner succeeded Alan Rusbridger in 2015. Since 2018, the paper's main news ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Takamba
Takamba is a music and dance native to the Songhai and Tuareg peoples of Niger and Mali. It is both a musical composition and a dance. The musicians play a traditional instrument known as the Kurbu or Tehardent and a traditional African Calabash. The Takamba dance includes graceful and rhythmic movements performed both seated and standing where the shoulders and arms sway with the flow of the music . Origin Takamba music and dance originated from the Songhai Empire. Before being known as Takamba, it was performed by the nomadic Tuareg griots and blacksmiths to celebrate the end of good harvest, cheer warriors back from the battle and to praise noble families. The griot in a sitting position, would play the ngoni or commonly known by the Tuareg as "tehardent". The word ‘Takamba’ has its etymology from the Songhai language The Songhay, Songhai or Ayneha languages (, or ) are a group of closely related languages/dialects centred on the middle stretches of the Niger River ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Economist
''The Economist'' is a British weekly newspaper printed in demitab format and published digitally. It focuses on current affairs, international business, politics, technology, and culture. Based in London, the newspaper is owned by The Economist Group, with its core editorial offices in the United States, as well as across major cities in continental Europe, Asia, and the Middle East. In 2019, its average global print circulation was over 909,476; this, combined with its digital presence, runs to over 1.6 million. Across its social media platforms, it reaches an audience of 35 million, as of 2016. The newspaper has a prominent focus on data journalism and interpretive analysis over original reporting, to both criticism and acclaim. Founded in 1843, ''The Economist'' was first circulated by Scottish economist James Wilson to muster support for abolishing the British Corn Laws (1815–1846), a system of import tariffs. Over time, the newspaper's coverage expanded further into ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |