|
Derivational Morphology
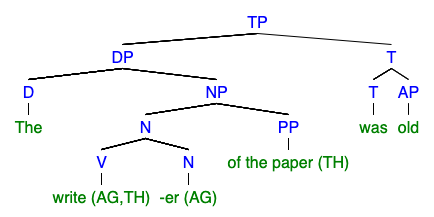
Morphological derivation, in linguistics, is the process of forming a new word from an existing word, often by adding a prefix or suffix, such as For example, ''unhappy'' and ''happiness'' derive from the root word ''happy.'' It is differentiated from inflection, which is the modification of a word to form different grammatical categories without changing its core meaning: ''determines'', ''determining'', and ''determined'' are from the root ''determine''. Derivational patterns Derivational morphology often involves the addition of a derivational suffix or other affix. Such an affix usually applies to words of one lexical category (part of speech) and changes them into words of another such category. For example, one effect of the English derivational suffix ''-ly'' is to change an adjective into an adverb (''slow'' → ''slowly''). Here are examples of English derivational patterns and their suffixes: * adjective-to-noun: ''-ness'' (''slow'' → ''slowness'') * adjective- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Linguistics
Linguistics is the scientific study of human language. It is called a scientific study because it entails a comprehensive, systematic, objective, and precise analysis of all aspects of language, particularly its nature and structure. Linguistics is concerned with both the cognitive and social aspects of language. It is considered a scientific field as well as an academic discipline; it has been classified as a social science, natural science, cognitive science,Thagard, PaulCognitive Science, The Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy (Fall 2008 Edition), Edward N. Zalta (ed.). or part of the humanities. Traditional areas of linguistic analysis correspond to phenomena found in human linguistic systems, such as syntax (rules governing the structure of sentences); semantics (meaning); morphology (structure of words); phonetics (speech sounds and equivalent gestures in sign languages); phonology (the abstract sound system of a particular language); and pragmatics (how soc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Labial Consonant
Labial consonants are consonants in which one or both lips are the active articulator. The two common labial articulations are bilabials, articulated using both lips, and labiodentals, articulated with the lower lip against the upper teeth, both of which are present in English. A third labial articulation is dentolabials, articulated with the upper lip against the lower teeth (the reverse of labiodental), normally only found in pathological speech. Generally precluded are linguolabials, in which the tip of the tongue contacts the posterior side of the upper lip, making them coronals, though sometimes, they behave as labial consonants. The most common distribution between bilabials and labiodentals is the English one, in which the nasal and the stops, , , and , are bilabial and the fricatives, , and , are labiodental. The voiceless bilabial fricative, voiced bilabial fricative, and the bilabial approximant do not exist as the primary realizations of any sounds in Engl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Agglutination
In linguistics, agglutination is a morphological process in which words are formed by stringing together morphemes, each of which corresponds to a single syntactic feature. Languages that use agglutination widely are called agglutinative languages. Turkish is an example of an agglutinative language. The Turkish word ("from your houses") consists of the morphemes ''ev-ler-iniz-den,'' literally translated morpheme-by-morpheme as ''house-plural-your(plural)-from''. Agglutinative languages are often contrasted with isolating languages, in which words are monomorphemic, and fusional languages, in which words can be complex, but morphemes may correspond to multiple features. Examples of agglutinative languages Although agglutination is characteristic of certain language families, this does not mean that when several languages in a certain geographic area are all agglutinative they are necessarily related phylogenetically. In the past, this assumption led linguists to propose t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Productivity (linguistics)
In linguistics, productivity is the degree to which speakers of a language use a particular grammatical process, especially in word formation. It compares grammatical processes that are in frequent use to less frequently used ones that tend towards lexicalization. Generally the test of productivity concerns identifying which grammatical forms would be used in the coining of new words: these will tend to only be converted to other forms using productive processes. Examples in English In standard English, the formation of preterite and past participle forms of verbs by means of ablaut (as Germanic strong verbs, for example, ''sing''–''sang''–''sung'') is no longer considered productive. Newly coined verbs in English overwhelmingly use the 'weak' (regular) ending ''-ed'' for the past tense and past participle (for example, '' spammed'', '' e-mailed''). Similarly, the only clearly productive plural ending is ''-(e)s''; it is found on the vast majority of English count noun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Word Form
In linguistics, morphology () is the study of words, how they are formed, and their relationship to other words in the same language. It analyzes the structure of words and parts of words such as stems, root words, prefixes, and suffixes. Morphology also looks at parts of speech, intonation and stress, and the ways context can change a word's pronunciation and meaning. Morphology differs from morphological typology, which is the classification of languages based on their use of words, and lexicology, which is the study of words and how they make up a language's vocabulary. While words, along with clitics, are generally accepted as being the smallest units of syntax, in most languages, if not all, many words can be related to other words by rules that collectively describe the grammar for that language. For example, English speakers recognize that the words ''dog'' and ''dogs'' are closely related, differentiated only by the plurality morpheme "-s", only found bound to n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Compound (linguistics)
In linguistics, a compound is a lexeme (less precisely, a word or sign) that consists of more than one stem. Compounding, composition or nominal composition is the process of word formation that creates compound lexemes. Compounding occurs when two or more words or signs are joined to make a longer word or sign. A compound that uses a space rather than a hyphen or concatenation is called an open compound or a spaced compound; the alternative is a closed compound. The meaning of the compound may be similar to or different from the meaning of its components in isolation. The component stems of a compound may be of the same part of speech—as in the case of the English word ''footpath'', composed of the two nouns ''foot'' and ''path''—or they may belong to different parts of speech, as in the case of the English word ''blackbird'', composed of the adjective ''black'' and the noun ''bird''. With very few exceptions, English compound words are stressed on their first compo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bound Morpheme
In linguistics, a bound morpheme is a morpheme A morpheme is the smallest meaningful constituent of a linguistic expression. The field of linguistic study dedicated to morphemes is called morphology. In English, morphemes are often but not necessarily words. Morphemes that stand alone ar ... (the elementary unit of morphosyntax) that can appear only as part of a larger expression; a free morpheme (or unbound morpheme) is one that can stand alone. A bound morpheme is a type of bound form, and a free morpheme is a type of free form. Occurrence in isolation A form is a free form if it can occur in isolation as a complete utterance, e.g. ''Johnny is running'', or ''Johnny'', or ''running'' (this can occur as the answer to a question such as ''What is he doing?''). A form that cannot occur in isolation is a bound form, e.g. ''-y'', ''is'', and ''-ing'' (in ''Johnny is running''). Non-occurrence in isolation is given as the primary criterion for boundness in most linguistics text ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Word Formation
In linguistics, word formation is an ambiguous term that can refer to either: * the processes through which words can change (i.e. morphology), or * the creation of new lexemes in a particular language Morphological A common method of word formation is the attachment of inflectional or derivational affixes. Derivation Examples include: * the words ''governor'', ''government'', ''governable'', ''misgovern'', ''ex-governor'', and ''ungovernable'' are all derived from the base word ''(to) govern'' Inflection Inflection is modifying a word for the purpose of fitting it into the grammatical structure of a sentence. For example: * ''manages'' and ''managed'' are inflected from the base word ''(to) manage'' * ''worked'' is inflected from the verb ''(to) work'' * ''talks'', ''talked'', and ''talking'' are inflected from the base ''(to) talk'' Nonmorphological Abbreviation Examples includes: * ''etc.'' from et caetera Acronyms & Initialisms An acronym is a word formed from th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Morphemes
A morpheme is the smallest meaningful constituent of a linguistic expression. The field of linguistic study dedicated to morphemes is called morphology. In English, morphemes are often but not necessarily words. Morphemes that stand alone are considered roots (such as the morpheme ''cat''); other morphemes, called affixes, are found only in combination with other morphemes. For example, the ''-s'' in ''cats'' indicates the concept of plurality but is always bound to another concept to indicate a specific kind of plurality. This distinction is not universal and does not apply to, for example, Latin, in which many roots cannot stand alone. For instance, the Latin root ''reg-'' (‘king’) must always be suffixed with a case marker: ''rex'' (''reg-s''), ''reg-is'', ''reg-i'', etc. For a language like Latin, a root can be defined as the main lexical morpheme of a word. These sample English words have the following morphological analyses: * "Unbreakable" is composed of three mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nominalization
In linguistics, nominalization or nominalisation is the use of a word that is not a noun (e.g., a verb, an adjective or an adverb) as a noun, or as the head of a noun phrase. This change in functional category can occur through morphological transformation, but it does not always. Nominalization can refer, for instance, to the process of producing a noun from another part of speech by adding a derivational affix (e.g., the noun ''legalization'' from the verb ''legalize''), but it can also refer to the complex noun that is formed as a result. Nominalization is also known as "nouning". Some languages simply allow verbs to be used as nouns without inflectional difference (conversion or zero derivation), while others require some form of morphological transformation. English has cases of both. Nominalization is a natural part of language, but some instances are more noticeable than others. Writing advice sometimes focuses on avoiding overuse of nominalization. In various langu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
English Verb
Verbs constitute one of the main parts of speech (word classes) in the English language. Like other types of words in the language, English verbs are not heavily inflected. Most combinations of tense, aspect, mood and voice are expressed periphrastically, using constructions with auxiliary verbs. Generally, the only inflected forms of an English verb are a third person singular present tense form ending in ''-s'', a past tense (also called preterite), a past participle (which may be the same as the past tense), and a form ending in '' -ing'' that serves as a present participle and gerund. Most verbs inflect in a simple regular fashion, although there are about 200 irregular verbs; the irregularity in nearly all cases concerns the past tense and past participle forms. The copula verb ''be'' has a larger number of different inflected forms, and is highly irregular. For details of the uses of particular verb tenses and other forms, see the article Uses of English verb form ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Part Of Speech
In grammar, a part of speech or part-of-speech ( abbreviated as POS or PoS, also known as word class or grammatical category) is a category of words (or, more generally, of lexical items) that have similar grammatical properties. Words that are assigned to the same part of speech generally display similar syntactic behavior (they play similar roles within the grammatical structure of sentences), sometimes similar morphological behavior in that they undergo inflection for similar properties and even similar semantic behavior. Commonly listed English parts of speech are noun, verb, adjective, adverb, pronoun, preposition, conjunction, interjection, numeral, article, and determiner. Other terms than ''part of speech''—particularly in modern linguistic classifications, which often make more precise distinctions than the traditional scheme does—include word class, lexical class, and lexical category. Some authors restrict the term ''lexical category'' to refer only to a par ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |