|
Deoxyuridine Monophosphate In Active Site Of Ribonuclease 4
Deoxyuridine (dU) is a compound and a nucleoside.It belongs to a class of compounds known as Pyrimidine 2'-deoxyribonucleosides and closely resembles the chemical composition of uridine but without the presence of the 2' hydroxyl group. Idoxuridine and Trifluridine are variants of deoxyuridine used as antiviral drugs. They are similar enough to be incorporated as part of DNA replication, but they possess side groups on the uracil component (an iodine and a CF3 group, respectively), that prevent base pairing. A known use of dU is as a precursor in the synthesis of Edoxudine Edoxudine (or edoxudin) is an antiviral drug. It is an analog of thymidine, a nucleoside Nucleosides are glycosylamines that can be thought of as nucleotides without a phosphate group. A nucleoside consists simply of a nucleobase (also terme .... This compound exists in all living organisms and can become part of DNA in both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells through two mechanisms. The first is the removal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chemical Compound
A chemical compound is a chemical substance composed of many identical molecules (or molecular entities) containing atoms from more than one chemical element held together by chemical bonds. A molecule consisting of atoms of only one element is therefore not a compound. A compound can be transformed into a different substance by a chemical reaction, which may involve interactions with other substances. In this process, bonds between atoms may be broken and/or new bonds formed. There are four major types of compounds, distinguished by how the constituent atoms are bonded together. Molecular compounds are held together by covalent bonds; ionic compounds are held together by ionic bonds; intermetallic compounds are held together by metallic bonds; coordination complexes are held together by coordinate covalent bonds. Non-stoichiometric compounds form a disputed marginal case. A chemical formula specifies the number of atoms of each element in a compound molecule, using the s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nucleoside
Nucleosides are glycosylamines that can be thought of as nucleotides without a phosphate group. A nucleoside consists simply of a nucleobase (also termed a nitrogenous base) and a five-carbon sugar (ribose or 2'-deoxyribose) whereas a nucleotide is composed of a nucleobase, a five-carbon sugar, and one or more phosphate groups. In a nucleoside, the anomeric carbon is linked through a glycosidic bond to the N9 of a purine or the N1 of a pyrimidine. Nucleotides are the molecular building-blocks of DNA and RNA. List of nucleosides and corresponding nucleobases The reason for 2 symbols, shorter and longer, is that the shorter ones are better for contexts where explicit disambiguation is superfluous (because context disambiguates) and the longer ones are for contexts where explicit disambiguation is judged to be needed or wise. For example, when discussing long nucleobase sequences in genomes, the CATG symbol system is much preferable to the Cyt-Ade-Thy-Gua symbol system (see '' N ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Idoxuridine
Idoxuridine is an anti-herpesvirus antiviral drug. It is a nucleoside analogue, a modified form of deoxyuridine, similar enough to be incorporated into viral DNA replication, but the iodine atom added to the uracil component blocks base pairing. It is used only topically due to cardiotoxicity. It was synthesized by William Prusoff in the late 1950s. Initially developed as an anticancer drug, idoxuridine became the first antiviral agent in 1962. Clinical use Idoxuridine is mainly used topically to treat herpes simplex keratitis.Goodman and Gilman's The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. Edited by Gilman AG, Rall TW, Nies AS, Taylor P. McGraw-Hill. 8th ed. 1990. Epithelial lesions, especially initial attacks presenting with a dendritic ulcer, are most responsive to therapy, while infection with stromal involvement are less responsive. Idoxuridine is ineffective against herpes simplex virus type 2 and varicella-zoster. Side effects Common side effects of the eye drops include irr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trifluridine
Trifluridine (also called trifluorothymidine; abbreviation TFT or FTD) is an anti-herpesvirus antiviral drug, used primarily on the eye. It was sold under the trade name Viroptic by Glaxo Wellcome, now merged into GlaxoSmithKline. The brand is now owned by Monarch Pharmaceuticals, which is wholly owned by King Pharmaceuticals. Trifluridine was approved for medical use in 1980. It is also a component of the anti-cancer drug trifluridine/tipiracil, which is taken by mouth. Medical uses Trifluridine eye drops are used for the treatment of keratitis and keratoconjunctivitis caused by the herpes simplex virus types 1 and 2, as well as for prevention and treatment of vaccinia virus infections of the eye. A Cochrane Systematic Review showed that trifluridine and aciclovir were a more effective treatment than idoxuridine or vidarabine, significantly increasing the relative number of successfully healed eyes in one to two weeks. For cancer treatment, the combination trifluridine/ti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antiviral Drug
Antiviral drugs are a class of medication used for treating viral infections. Most antivirals target specific viruses, while a broad-spectrum antiviral is effective against a wide range of viruses. Unlike most antibiotics, antiviral drugs do not destroy their target pathogen; instead they inhibit its development. Antiviral drugs are one class of antimicrobials, a larger group which also includes antibiotic (also termed antibacterial), antifungal and antiparasitic drugs, or antiviral drugs based on monoclonal antibodies. Most antivirals are considered relatively harmless to the host, and therefore can be used to treat infections. They should be distinguished from viricides, which are not medication but deactivate or destroy virus particles, either inside or outside the body. Natural viricides are produced by some plants such as eucalyptus and Australian tea trees. Medical uses Most of the antiviral drugs now available are designed to help deal with HIV, herpes viruses, th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DNA Replication
In molecular biology, DNA replication is the biological process of producing two identical replicas of DNA from one original DNA molecule. DNA replication occurs in all living organisms acting as the most essential part for biological inheritance. This is essential for cell division during growth and repair of damaged tissues, while it also ensures that each of the new cells receives its own copy of the DNA. The cell possesses the distinctive property of division, which makes replication of DNA essential. DNA is made up of a double helix of two complementary strands. The double helix describes the appearance of a double-stranded DNA which is thus composed of two linear strands that run opposite to each other and twist together to form. During replication, these strands are separated. Each strand of the original DNA molecule then serves as a template for the production of its counterpart, a process referred to as semiconservative replication. As a result of semi-conservative rep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uracil
Uracil () (symbol U or Ura) is one of the four nucleobases in the nucleic acid RNA. The others are adenine (A), cytosine (C), and guanine (G). In RNA, uracil binds to adenine via two hydrogen bonds. In DNA, the uracil nucleobase is replaced by thymine (T). Uracil is a demethylated form of thymine. Uracil is a common and naturally occurring pyrimidine derivative. The name "uracil" was coined in 1885 by the German chemist Robert Behrend, who was attempting to synthesize derivatives of uric acid. Originally discovered in 1900 by Alberto Ascoli, it was isolated by hydrolysis of yeast nuclein; it was also found in bovine thymus and spleen, herring sperm, and wheat germ. It is a planar, unsaturated compound that has the ability to absorb light. Based on 12C/13C isotopic ratios of organic compounds found in the Murchison meteorite, it is believed that uracil, xanthine, and related molecules can also be formed extraterrestrially. Data from the Cassini mission, orbiting in the Saturn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iodine
Iodine is a chemical element with the symbol I and atomic number 53. The heaviest of the stable halogens, it exists as a semi-lustrous, non-metallic solid at standard conditions that melts to form a deep violet liquid at , and boils to a violet gas at . The element was discovered by the French chemist Bernard Courtois in 1811 and was named two years later by Joseph Louis Gay-Lussac, after the Ancient Greek 'violet-coloured'. Iodine occurs in many oxidation states, including iodide (I−), iodate (), and the various periodate anions. It is the least abundant of the stable halogens, being the sixty-first most abundant element. As the heaviest essential mineral nutrient, iodine is required for the synthesis of thyroid hormones. Iodine deficiency affects about two billion people and is the leading preventable cause of intellectual disabilities. The dominant producers of iodine today are Chile and Japan. Due to its high atomic number and ease of attachment to organic compound ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Base Pair
A base pair (bp) is a fundamental unit of double-stranded nucleic acids consisting of two nucleobases bound to each other by hydrogen bonds. They form the building blocks of the DNA double helix and contribute to the folded structure of both DNA and RNA. Dictated by specific hydrogen bonding patterns, "Watson–Crick" (or "Watson–Crick–Franklin") base pairs (guanine–cytosine and adenine–thymine) allow the DNA helix to maintain a regular helical structure that is subtly dependent on its nucleotide sequence. The Complementarity (molecular biology), complementary nature of this based-paired structure provides a redundant copy of the genetic information encoded within each strand of DNA. The regular structure and data redundancy provided by the DNA double helix make DNA well suited to the storage of genetic information, while base-pairing between DNA and incoming nucleotides provides the mechanism through which DNA polymerase replicates DNA and RNA polymerase transcribes DNA in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
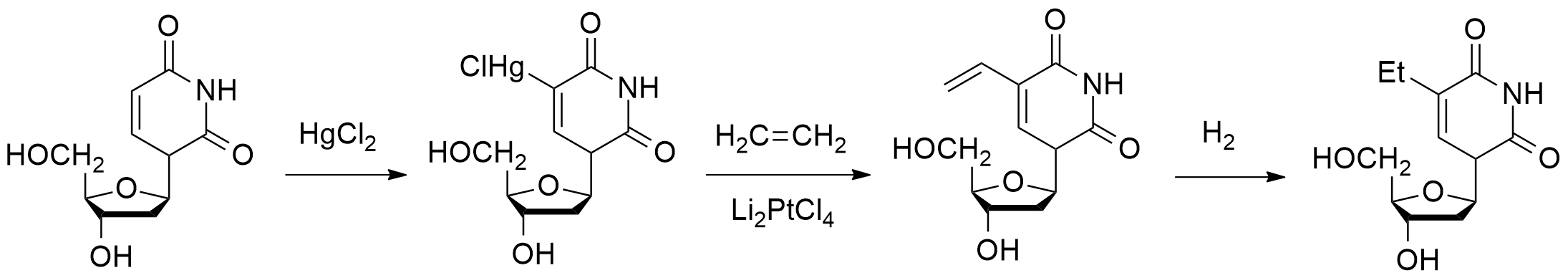
Edoxudine
Edoxudine (or edoxudin) is an antiviral drug. It is an analog of thymidine, a nucleoside Nucleosides are glycosylamines that can be thought of as nucleotides without a phosphate group. A nucleoside consists simply of a nucleobase (also termed a nitrogenous base) and a five-carbon sugar (ribose or 2'-deoxyribose) whereas a nucleoti .... It has shown effectiveness against herpes simplex virus. Synthesis Mercuration of the 2'-deoxyuridine 1 leads to the organometallic derivative 2; reaction of that with ethylene in the presence dilithiopalladium tetrachloride gives the alkylation product 3; this is reduced catalytically in situ. There is thus obtained the antiviral agent edoxudine 4. References Pyrimidinediones {{dermatologic-drug-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nucleosides
Nucleosides are glycosylamines that can be thought of as nucleotides without a phosphate group. A nucleoside consists simply of a nucleobase (also termed a nitrogenous base) and a five-carbon sugar (ribose or 2'-deoxyribose) whereas a nucleotide is composed of a nucleobase, a five-carbon sugar, and one or more phosphate groups. In a nucleoside, the anomeric carbon is linked through a glycosidic bond to the N9 of a purine or the N1 of a pyrimidine. Nucleotides are the molecular building-blocks of DNA and RNA. List of nucleosides and corresponding nucleobases The reason for 2 symbols, shorter and longer, is that the shorter ones are better for contexts where explicit disambiguation is superfluous (because context disambiguates) and the longer ones are for contexts where explicit disambiguation is judged to be needed or wise. For example, when discussing long nucleobase sequences in genomes, the CATG symbol system is much preferable to the Cyt-Ade-Thy-Gua symbol system (see '' N ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)