|
Deoxy
Deoxygenation is a chemical reaction involving the removal of oxygen atoms from a molecule. The term also refers to the removal of molecular oxygen (O2) from gases and solvents, a step in air-free technique and gas purifiers. As applied to organic compounds, deoxygenation is a component of fuels production as well a type of reaction employed in organic synthesis, e.g. of pharmaceuticals. Deoxygenation of C-O bonds With replacement by H2 The main examples involving the replacement of an oxo group by two hydrogen atoms (A=O → AH2) are hydrogenolysis. Typical examples use metal catalysts and H2 as the reagent. Conditions are typically more forcing than hydrogenation. Stoichiometric reactions that effect deoxygenation include the Wolff–Kishner reduction for aryl ketones. The replacement of a hydroxyl group by hydrogen (A-OH → A-H) is the point of the Barton–McCombie deoxygenation and the Markó–Lam deoxygenation. Biomass valorization Deoxygenation is an important ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Barton–McCombie Deoxygenation
The Barton–McCombie deoxygenation is an organic reaction in which a hydroxy functional group in an organic compound is replaced by a hydrogen to give an alkyl group. It is named after British chemists Sir Derek Harold Richard Barton and Stuart W. McCombie. This deoxygenation reaction is a radical substitution. In the related Barton decarboxylation the reactant is a carboxylic acid. Mechanism The reaction mechanism consists of a catalytic radical initiation step and a propagation step. The alcohol (1) is first converted into a reactive carbonothioyl intermediate such as a thionoester or xanthate 2. Heating of AIBN results in its homolytic cleavage, generating two 2-cyanoprop-2-yl radicals 9 which each abstract a proton from tributylstannane 3 to generate tributylstannyl radicals 4 and inactive 10. The tributyltin radical abstracts the xanthate group from 2 by attack of 4 at the sulfur atom with concurrent homolytic cleavage of the C-S π bond. This leaves a carbon centered ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Markó–Lam Deoxygenation
The Markó–Lam deoxygenation is an organic chemistry reaction where the hydroxy functional group in an organic compound is replaced by a hydrogen atom to give an alkyl group. The Markó-Lam reaction is a variant of the Bouveault–Blanc reduction and an alternative to the classical Barton–McCombie deoxygenation. It is named for the Belgian chemists István Markó and Kevin Lam. The main features of the reaction are: *short reaction time (5 seconds to 5 minutes). *the use of a stable toluate derivative. *the use of SmI2/HMPA system or electrolysis instead of the classical and difficult to remove tributyltin hydride. Mechanism A hydroxyl group is first derivitised into a stable and very often crystalline toluate derivative. The aromatic ester is submitted to a monoelectronical reduction, by the use of SmI2/HMPA Hexamethylphosphoramide, often abbreviated HMPA, is a phosphoramide (an amide of phosphoric acid) with the formula This colorless liquid is a useful reagent in o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phosphine Oxide
Phosphine oxides are phosphorus compounds with the formula OPX3. When X = alkyl or aryl, these are organophosphine oxides. Triphenylphosphine oxide is an example. An inorganic phosphine oxide is phosphoryl chloride (POCl3). Structure and bonding Tertiary phosphine oxides Tertiary phosphine oxides are the most commonly encountered phosphine oxides. With the formula R3PO, they are tetrahedral compounds. They are usually prepared by oxidation of tertiary phosphines. The P-O bond is short and polar. According to molecular orbital theory, the short P–O bond is attributed to the donation of the lone pair electrons from oxygen p-orbitals to the antibonding phosphorus-carbon bonds. The nature of the P–O bond was once hotly debated. Some discussions invoked a role for phosphorus-centered d-orbitals in bonding, but this analysis is not supported by computational analyses. In terms of simple Lewis structure, the bond is more accurately represented as a dative bond, as is currently us ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sulfoxide
In organic chemistry, a sulfoxide, also called a sulphoxide, is an organosulfur compound containing a sulfinyl () functional group attached to two carbon atoms. It is a polar functional group. Sulfoxides are oxidized derivatives of sulfides. Examples of important sulfoxides are alliin, a precursor to the compound that gives freshly crushed garlic its aroma, and dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO), a common solvent. Structure and bonding Sulfoxides feature relatively short S–O distances. In DMSO, the S–O distance is 1.531 Å. The sulfur center is pyramidal; the sum of the angles at sulfur is about 306°.. Sulfoxides are generally represented with the structural formula R−S(=O)−R', where R and R' are organic groups. The bond between the sulfur and oxygen atoms is intermediate of a dative bond and a polarized double bond. The double-bond resonance form implies 10 electrons around sulfur (10-S-3 in N-X-L notation). The double-bond character of the S−O bond may be accoun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Air-free Technique
Air-free techniques refer to a range of manipulations in the chemistry laboratory for the handling of compounds that are air-sensitive. These techniques prevent the compounds from reacting with components of air, usually water and oxygen; less commonly carbon dioxide and nitrogen. A common theme among these techniques is the use of a fine (100–10−3 Torr) or high (10−3–10−6 Torr) vacuum to remove air, and the use of an inert gas: preferably argon, but often nitrogen. The two most common types of air-free technique involve the use of a glovebox and a Schlenk line, although some rigorous applications use a high-vacuum line. In both methods, glassware (often Schlenk tubes) are pre-dried in ovens prior to use. They may be flame-dried to remove adsorbed water. Prior to coming into an inert atmosphere, vessels are further dried by ''purge-and-refill'' — the vessel is subjected to a vacuum to remove gases and water, and then refilled with inert gas. This cycle is usually r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrogen Purifier
A hydrogen purifier is a device to purify hydrogen if hydrogen production is done from hydrocarbon sources, the ultra-high purified hydrogen is needed for applications like PEM fuel cells . Palladium membrane hydrogen purifiers The palladium membrane is typically a metallic tube of a palladium and silver alloy material possessing the unique property of allowing only monatomic hydrogen to pass through its crystal lattice when it is heated above 300°C. Dense thin-metal membrane purifier Dense thin-metal membrane purifiers are compact, relatively inexpensive and simple to use. Pressure swing adsorption Pressure swing adsorption is used for the removal of carbon dioxide (CO2) as the final step in the large-scale commercial synthesis of hydrogen. It can also remove methane, carbon monoxide, nitrogen, moisture and in some cases, argon, from hydrogen. Catalytic recombination or deoxygenation purifier Catalytic recombination or deoxygenation is used to remove oxygen (O2) impurities. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alkene
In organic chemistry, an alkene is a hydrocarbon containing a carbon–carbon double bond. Alkene is often used as synonym of olefin, that is, any hydrocarbon containing one or more double bonds.H. Stephen Stoker (2015): General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry'. 1232 pages. Two general types of monoalkenes are distinguished: terminal and internal. Also called α-olefins, terminal alkenes are more useful. However, the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC) recommends using the name "alkene" only for acyclic hydrocarbons with just one double bond; alkadiene, alkatriene, etc., or polyene for acyclic hydrocarbons with two or more double bonds; cycloalkene, cycloalkadiene, etc. for cyclic ones; and "olefin" for the general class – cyclic or acyclic, with one or more double bonds. Acyclic alkenes, with only one double bond and no other functional groups (also known as mono-enes) form a homologous series of hydrocarbons with the general formula with '' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oxophilic
Oxophilicity is the tendency of certain chemical compounds to form oxides by hydrolysis or abstraction of an oxygen atom from another molecule, often from organic compounds. The term is often used to describe metal centers, commonly the early transition metals such as titanium, niobium, and tungsten. Oxophilicity is often stated to be related to the hardness of the element, within the HSAB theory ( hard and soft (Lewis) acids and bases), but it has been shown that oxophilicity depends more on the electronegativity and effective nuclear charge of the element than on its hardness. This explains why the early transition metals, whose electronegativities and effective nuclear charges are low, are very oxophilic. Many main group compounds are also oxophilic, such as derivatives of aluminium, silicon, and phosphorus(III). The handling of oxophilic compounds often requires air-free techniques. Examples Complexes of oxophilic metals typically are prone to hydrolysis. For example, the high v ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
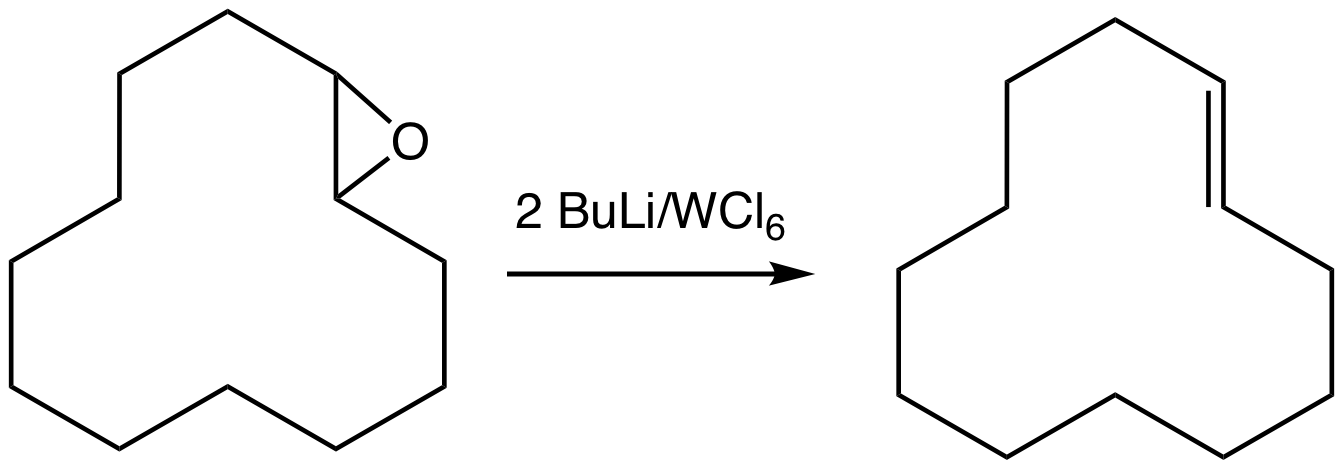
Epoxide
In organic chemistry, an epoxide is a cyclic ether () with a three-atom ring. This ring approximates an equilateral triangle, which makes it strained, and hence highly reactive, more so than other ethers. They are produced on a large scale for many applications. In general, low molecular weight epoxides are colourless and nonpolar, and often volatile. Nomenclature A compound containing the epoxide functional group can be called an epoxy, epoxide, oxirane, and ethoxyline. Simple epoxides are often referred to as oxides. Thus, the epoxide of ethylene (C2H4) is ethylene oxide (C2H4O). Many compounds have trivial names; for instance, ethylene oxide is called "oxirane". Some names emphasize the presence of the epoxide functional group, as in the compound ''1,2-epoxyheptane'', which can also be called ''1,2-heptene oxide''. A polymer formed from epoxide precursors is called an ''epoxy'', but such materials do not contain epoxide groups (or contain only a few residual epoxy grou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wolff–Kishner Reduction
The Wolff–Kishner reduction is a reaction used in organic chemistry to convert carbonyl functionalities into methylene groups. In the context of complex molecule synthesis, it is most frequently employed to remove a carbonyl group after it has served its synthetic purpose of activating an intermediate in a preceding step. As such, there is no obvious retron for this reaction. The reaction was reported by Nikolai Kischner in 1911 and Ludwig Wolff in 1912, In general, the reaction mechanism first involves the ''in situ'' generation of a hydrazone by condensation of hydrazine with the ketone or aldehyde substrate. Sometimes it is however advantageous to use a pre-formed hydrazone as substrate (see modifications). The rate determining step of the reaction is de-protonation of the hydrazone by an alkoxide base to form a diimide anion by a concerted, solvent mediated protonation/de-protonation step. Collapse of this alkyldiimide with loss of N2 leads to formation of an alkylanion whic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alcohol (chemistry)
In chemistry, an alcohol is a type of organic compound that carries at least one hydroxyl () functional group bound to a saturated carbon atom. The term ''alcohol'' originally referred to the primary alcohol ethanol (ethyl alcohol), which is used as a drug and is the main alcohol present in alcoholic drinks. An important class of alcohols, of which methanol and ethanol are the simplest examples, includes all compounds which conform to the general formula . Simple monoalcohols that are the subject of this article include primary (), secondary () and tertiary () alcohols. The suffix ''-ol'' appears in the IUPAC chemical name of all substances where the hydroxyl group is the functional group with the highest priority. When a higher priority group is present in the compound, the prefix ''hydroxy-'' is used in its IUPAC name. The suffix ''-ol'' in non-IUPAC names (such as paracetamol or cholesterol) also typically indicates that the substance is an alcohol. However, some compou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
McMurry Reaction
The McMurry reaction is an organic reaction in which two ketone or aldehyde groups are coupled to form an alkene using a titanium chloride compound such as titanium(III) chloride and a reducing agent. The reaction is named after its co-discoverer, John E. McMurry. The McMurry reaction originally involved the use of a mixture TiCl3 and LiAlH4, which produces the active reagents. Related species have been developed involving the combination of TiCl3 or TiCl4 with various other reducing agents, including potassium, zinc, and magnesium. This reaction is related to the Pinacol coupling reaction which also proceeds by reductive coupling of carbonyl compounds. Reaction mechanism This reductive coupling can be viewed as involving two steps. First is the formation of a pinacolate (1,2-diolate) complex, a step which is equivalent to the pinacol coupling reaction. The second step is the deoxygenation of the pinacolate, which yields the alkene, this second step exploits the oxophilicity of tit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |