|
Deng Yi
Deng Yi (birth and death year unknown) was a government official and administrator who lived in the late Eastern Han dynasty of China. Deng Yi served under the warlord Liu Biao in Jing Province (covering present-day Hubei and Hunan). After the death of Liu Biao and his son Liu Cong's surrender to Cao Cao, Deng served as an official () under Cao Cao. Life The 漢晉春秋 records that in 196, Deng advised Liu Biao not to form an alliance with Yuan Shao. Liu did not heed this advice and dismissed Deng from office. In 208, Liu Biao died and his son Liu Cong surrendered to the rival warlord Cao Cao. Cao Cao appointed Deng as an official. See also * Lists of people of the Three Kingdoms References * 漢晉春秋 * Chen, Shou (3rd century). ''Records of the Three Kingdoms'' (''Sanguozhi''). * Fan, Ye (5th century). ''Book of the Later Han The ''Book of the Later Han'', also known as the ''History of the Later Han'' and by its Chinese name ''Hou Hanshu'' (), is one of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Emperor Xian Of Han
Emperor Xian of Han (2 April 181 – 21 April 234), personal name Liu Xie (劉協), courtesy name Bohe, was the 14th and last emperor of the Eastern Han dynasty in China. He reigned from 28 September 189 until 11 December 220. Liu Xie was a son of Liu Hong (Emperor Ling) and was a younger half-brother of his predecessor, Liu Bian (Emperor Shao). In 189, at the age of eight, he became emperor after the warlord Dong Zhuo, who had seized control of the Han central government, deposed Emperor Shao and replaced him with Liu Xie. The newly enthroned Liu Xie, historically known as Emperor Xian, was in fact a puppet ruler under Dong Zhuo's control. In 190, when a coalition of regional warlords launched a punitive campaign against Dong Zhuo in the name of freeing Emperor Xian, Dong Zhuo ordered the destruction of the imperial capital, Luoyang, and forcefully relocated the imperial capital along with its residents to Chang'an. After Dong Zhuo's assassination in 192, Emperor Xian fell u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lists Of People Of The Three Kingdoms
The following are lists of people significant to the Three Kingdoms period (220–280) of Chinese history. Their names in Mandarin pinyin are sorted in alphabetical order. Fictional characters in the 14th-century historical novel ''Romance of the Three Kingdoms'' and those found in other cultural references to the Three Kingdoms are listed separately in List of fictional people of the Three Kingdoms. Notes The states of Cao Wei, Shu Han, and Eastern Wu were officially established in 220, 221, and 229 respectively. Therefore, certain people in the list who died before these years have their respective lords' names, in place of either of the three states, listed in the allegiance column. Take Guan Yu for example — he died before Liu Bei established Shu Han in 221, so his allegiance is listed as "Liu Bei" instead of "Shu Han". See also * List of fictional people of the Three Kingdoms The following is a list of fictional people significant to the Three Kingdoms period (220� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
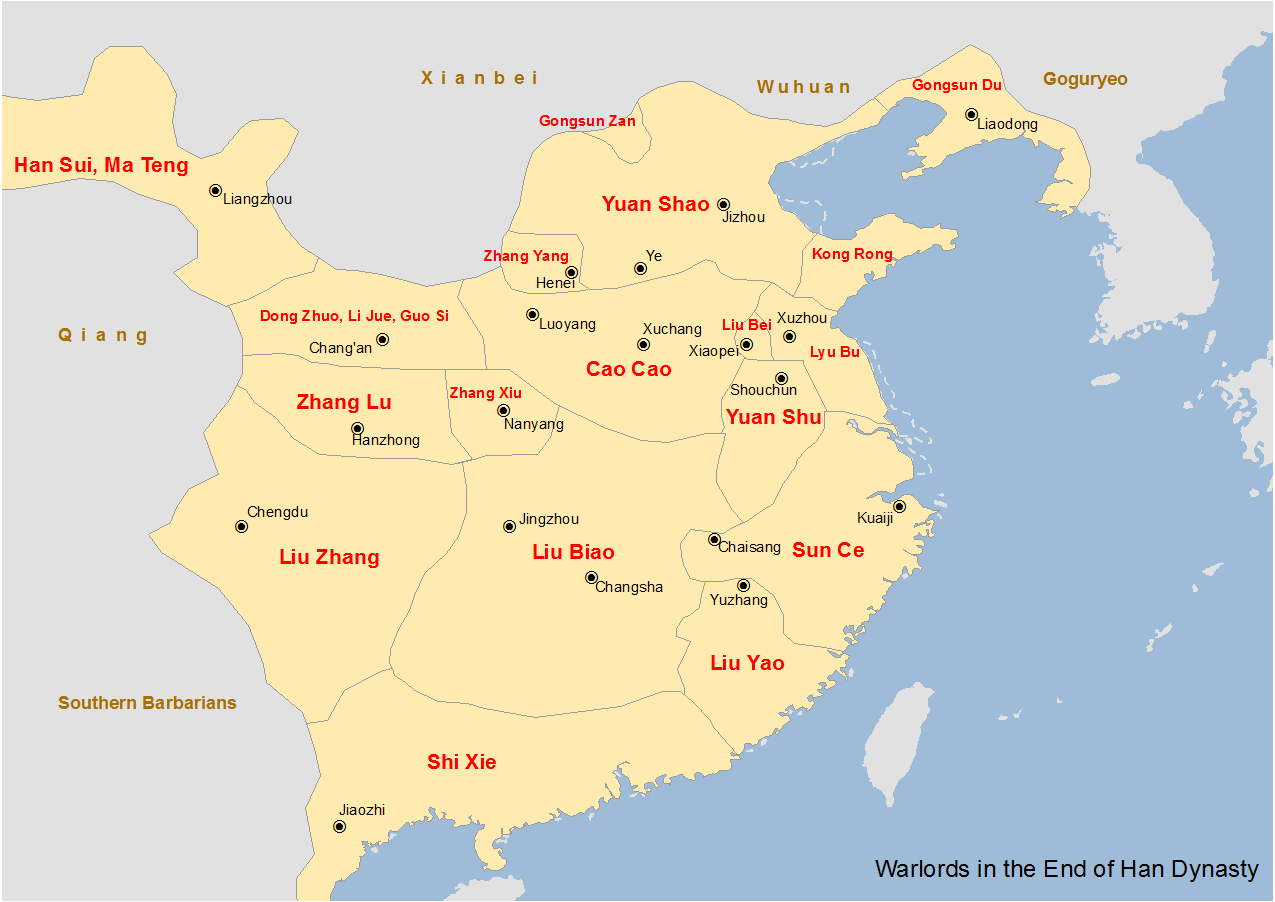
Liu Biao And Associates
/ ( or ) is an East Asian surname. pinyin: in Mandarin Chinese, in Cantonese. It is the family name of the Han dynasty emperors. The character originally meant 'kill', but is now used only as a surname. It is listed 252nd in the classic text Hundred Family Surnames. Today, it is the 4th most common surname in Mainland China as well as one of the most common surnames in the world. Distribution In 2019 劉 was the fourth most common surname in Mainland China. Additionally, it was the most common surname in Jiangxi province. In 2013 it was found to be the 5th most common surname, shared by 67,700,000 people or 5.1% of the population, with the province with the most people being Shandong.中国四百大姓, 袁义达, 邱家儒, Beijing Book Co. Inc., 1 January 2013 Origin One source is that they descend from the Qí (祁) clan of Emperor Yao. For example the founding emperor of the Han dynasty (one of China's golden ages), Liu Bang (Emperor Gaozu of Han) was a descendant of E ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Romance Of The Three Kingdoms
''Romance of the Three Kingdoms'' () is a 14th-century historical novel attributed to Luo Guanzhong. It is set in the turbulent years towards the end of the Han dynasty and the Three Kingdoms period in Chinese history, starting in 184 AD and ending with the reunification of the land in 280 by Western Jin. The novel is based primarily on the ''Records of the Three Kingdoms'' (), written by Chen Shou. The story – part historical and part fictional – romanticises and dramatises the lives of feudal lords and their retainers, who tried to replace the dwindling Han dynasty or restore it. While the novel follows hundreds of characters, the focus is mainly on the three power blocs that emerged from the remnants of the Han dynasty, and would eventually form the three states of Cao Wei, Shu Han, and Eastern Wu. The novel deals with the plots, personal and military battles, intrigues, and struggles of these states to achieve dominance for almost 100 years. ''Romance of the Three Kin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Luo Guanzhong
Luo Ben (c. 1330–1400, or c.1280–1360), better known by his courtesy name Guanzhong (Mandarin pronunciation: ), was a Chinese writer who lived during the Ming dynasty. He was also known by his pseudonym Huhai Sanren (). Luo was attributed with writing ''Romance of the Three Kingdoms'', one of the Four Great Classical Novels of Chinese literature. Identity The location and date of Luo's birth are controversial. One possibility was that he was from Taiyuan, and lived in the late Yuan dynasty and early Ming dynasty by the record of his contemporary, the playwright Jia Zhongming (賈仲明), who said that he had met him in 1364. Another possibility was that he was born in Dongping County, Dongyuan, the province of Shandong, in about 1280 – 1360. Literary historians suggest other possibilities for his home, also including Hangzhou and Jiangnan. According to Meng Fanren (孟繁仁), Luo can be identified in the pedigree of the Luo family, and Taiyuan is most likely his ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Book Of The Later Han
The ''Book of the Later Han'', also known as the ''History of the Later Han'' and by its Chinese name ''Hou Hanshu'' (), is one of the Twenty-Four Histories and covers the history of the Han dynasty from 6 to 189 CE, a period known as the Later or Eastern Han. The book was compiled by Fan Ye and others in the 5th century during the Liu Song dynasty, using a number of earlier histories and documents as sources. Background In 23 CE, Han dynasty official Wang Mang was overthrown by a peasants' revolt known as the Red Eyebrows. His fall separates the Early (or Western) Han Dynasty from the Later (or Eastern) Han Dynasty. As an orthodox history, the book is unusual in being completed over two hundred years after the fall of the dynasty. Fan Ye's primary source was the ''Dongguan Han Ji'' (東觀漢記; "Han Records of the Eastern Lodge"), which was written during the Han dynasty itself. Contents References Citations Sources ; General * Chavannes, Édouard (1906).T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fan Ye (historian)
Fan Ye (398 – 23 January 446), courtesy name Weizong (蔚宗), was a Chinese historian and politician of the Liu Song dynasty during the Southern and Northern dynasties period. He was the compiler of the historical text ''Book of the Later Han''. The fourthThe age order of Fan Ye and his brothers was listed in Fan Tai's biography in ''Book of Song'' (volume 60) son of Fan Tai (范泰), Fan Ye was born in present-day Shaoxing, Zhejiang, but his ancestral home was in Nanyang, Henan. He was a noted atheist who heavily criticised Buddhism, Yin and Yang, and the concept of the Mandate of Heaven. To this end, he cited Zhang Heng's scientific studies as evidence. Fan has a biography in the ''Book of Song'' (volume 69). References Sources * Tan, Jiajian"Hou Hanshu" ("Book of Later Han") ''Encyclopedia of China The ''Encyclopedia of China'' () is the first large-entry modern encyclopedia in the Chinese language. The compilation began in 1978. Published by the Encyclopedia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Records Of The Three Kingdoms
The ''Records or History of the Three Kingdoms'', also known by its Chinese name as the Sanguo Zhi, is a Chinese historical text which covers the history of the late Eastern Han dynasty (c. 184–220 AD) and the Three Kingdoms period (220–280 AD). It is widely regarded as the official and authoritative source historical text for that period. Written by Chen Shou in the third century, the work synthesizes the histories of the rival states of Cao Wei, Shu Han and Eastern Wu in the Three Kingdoms period into a single compiled text. The ''Records of the Three Kingdoms'' is the main source of influence for the 14th century historical novel ''Romance of the Three Kingdoms,'' considered one of the great four novels of Chinese classical literature. Major chunks of the records have been translated into English, but the tome has yet to be fully translated. Origin and structure The ''Records of the Grand Historian'', ''Book of Han'' and '' Book of the Later Han'', and the ''Record ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chen Shou
Chen Shou (; 233–297), courtesy name Chengzuo (), was a Chinese historian, politician, and writer who lived during the Three Kingdoms period and Jin dynasty of China. Chen Shou is most known for his most celebrated work, the ''Records of the Three Kingdoms'' (''Sanguozhi''), which records the history of the late Eastern Han dynasty and the Three Kingdoms period. Chen Shou wrote the Sanguozhi primarily in the form of biographies of notable persons of those eras. Today, Chen's ''Records of the Three Kingdoms'' is part of the ''Twenty-Four Histories'' canon of ancient Chinese history. Historical sources on Chen Shou's life There are two biographies of Chen Shou. The first one is in the ''Chronicles of Huayang'', which was written by Chang Qu in the fourth century during the Eastern Jin dynasty. The second one is in the ''Book of Jin'', which was written by Fang Xuanling and others in the seventh century during the Tang dynasty. Life He started his career as an official in th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yuan Shao
Yuan Shao (, ; died 28 June 202), courtesy name Benchu (), was a Chinese military general, politician, and warlord who lived in the late Eastern Han dynasty. He occupied the northern territories of China during the civil wars that occurred towards the end of the Han dynasty. He was also an elder half-brother of Yuan Shu, a warlord who controlled the Huai River region, though the two were not on good terms with each other. One of the most powerful warlords of his time, Yuan Shao spearheaded a coalition of warlords against Dong Zhuo, who held Emperor Xian hostage in the imperial capital, Luoyang, but failed due to internal disunity. In 200, he launched a campaign against his rival Cao Cao but was defeated at the Battle of Guandu. He died of illness two years later in Ye. His eventual failure despite his illustrious family background and geographical advantages was commonly blamed on his indecisiveness and inability to heed the advice of his advisors. Family background Yua ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deng (Chinese Surname)
Deng is an East Asian surname of Chinese origin which has many variant spellings and transliterations. It is a transcription of wikt:邓, 邓 (simplified Chinese character) or wikt:鄧, 鄧 (Traditional Chinese character, traditional). In 2019 Deng was 21st most common surname in Mainland China. Variant spellings It is transliterated as ''Dèng'' in pinyin and Teng, or Then, in Wade-Giles. In Cantonese, it is ''Dahng'' in Yale romanization of Cantonese, Yale and ''Dang6'' in Jyutping. In Southern Min, Minnan or Taiwanese Minnan, Taiwanese, it is ''Tēng'' in Pe̍h-ōe-jī. The surname originating from the same Chinese character or more specifically, Han character in Vietnamese language, Vietnamese is ''Đặng'' and it is one of the top ten surnames in Vietnam. The name is transliterated as ''Deung'' in Korean language, Korean but is very rare in Korea. Deng is one of the surnames of the Nanyang, Henan, Nanyang, Henan Chinese clan#Tang hao, ancestral hall (). In addition to spell ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cao Cao
Cao Cao () (; 155 – 15 March 220), courtesy name Mengde (), was a Chinese statesman, warlord and poet. He was the penultimate Grand chancellor (China), grand chancellor of the Eastern Han dynasty, and he amassed immense power in the End of the Han dynasty, dynasty's final years. As one of the central figures of the Three Kingdoms period, Cao Cao laid the foundations for what became the state of Cao Wei, and he was posthumously honoured as "Emperor Wu of Wei", despite the fact that he never officially proclaimed himself Emperor of China or Son of Heaven. Cao Cao remains a controversial historical figure—he is often portrayed as a cruel and merciless tyrant in literature, but he has also been praised as a brilliant ruler, military genius, and great poet possessing unrivalled charisma, who treated his subordinates like family. During the fall of the Eastern Han dynasty, Cao Cao was able to secure most of northern China—which was at the time the most populated and developed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)
.jpg)
