|
Delusion (other)
A delusion is a false fixed belief that is not amenable to change in light of conflicting evidence. As a pathology, it is distinct from a belief based on false or incomplete information, confabulation, dogma, illusion, hallucination, or some other misleading effects of perception, as individuals with those beliefs ''are'' able to change or readjust their beliefs upon reviewing the evidence. However: "The distinction between a delusion and a strongly held idea is sometimes difficult to make and depends in part on the degree of conviction with which the belief is held despite clear or reasonable contradictory evidence regarding its veracity." Delusions have been found to occur in the context of many pathological states (both general physical and mental) and are of particular diagnostic importance in psychotic disorders including schizophrenia, paraphrenia, manic episodes of bipolar disorder, and psychotic depression. Types Delusions are categorized into four differen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Psychiatry
Psychiatry is the medical specialty devoted to the diagnosis, prevention, and treatment of mental disorders. These include various maladaptations related to mood, behaviour, cognition, and perceptions. See glossary of psychiatry. Initial psychiatric assessment of a person typically begins with a case history and mental status examination. Physical examinations and psychological tests may be conducted. On occasion, neuroimaging or other neurophysiological techniques are used. Mental disorders are often diagnosed in accordance with clinical concepts listed in diagnostic manuals such as the ''International Classification of Diseases'' (ICD), edited and used by the World Health Organization (WHO) and the widely used '' Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders'' (DSM), published by the American Psychiatric Association (APA). The fifth edition of the DSM (DSM-5) was published in May 2013 which re-organized the larger categories of various diseases and expanded upon the p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scrupulosity
Scrupulosity is characterized by pathological guilt/anxiety about moral or religious issues. Although it can affect nonreligious people, it is usually related to religious beliefs. It is personally distressing, dysfunctional, and often accompanied by significant impairment in social functioning. It has not been proven to be an actual disorder by medical professionals, though it falls under the anxiety category. It is typically conceptualized as a moral or religious form of obsessive–compulsive disorder (OCD), The term is derived from the Latin ''scrupus'', a sharp stone, implying a stabbing pain on the conscience. Scrupulosity was formerly called ''scruples'' in religious contexts, but the word '' scruple'' now commonly refers to a troubling of the conscience rather than to the disorder. As a personality trait, scrupulosity is a recognized diagnostic criterion for obsessive–compulsive personality disorder. It is sometimes called "scrupulousness", but that word properly appli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diagnostic And Statistical Manual Of Mental Disorders
The ''Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders'' (DSM; latest edition: DSM-5-TR, published in March 2022) is a publication by the American Psychiatric Association (APA) for the classification of mental disorders using a common language and standard criteria and is the main book for the diagnosis and treatment of mental disorders in the United States and is considered one of the "Bibles" of psychiatry along with the ICD, CCMD and the Psychodynamic Diagnostic Manual. It is usedmainly in the United Statesby researchers, psychiatric drug regulation agencies, health insurance companies, pharmaceutical companies, the legal system, and policymakers. Mental health professionals use the manual to determine and help communicate a patient's diagnosis after an evaluation. Hospitals, clinics, and insurance companies in the United States may require a DSM diagnosis for all patients with mental disorders. Health-care researchers use the DSM to categorize patients for research purp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
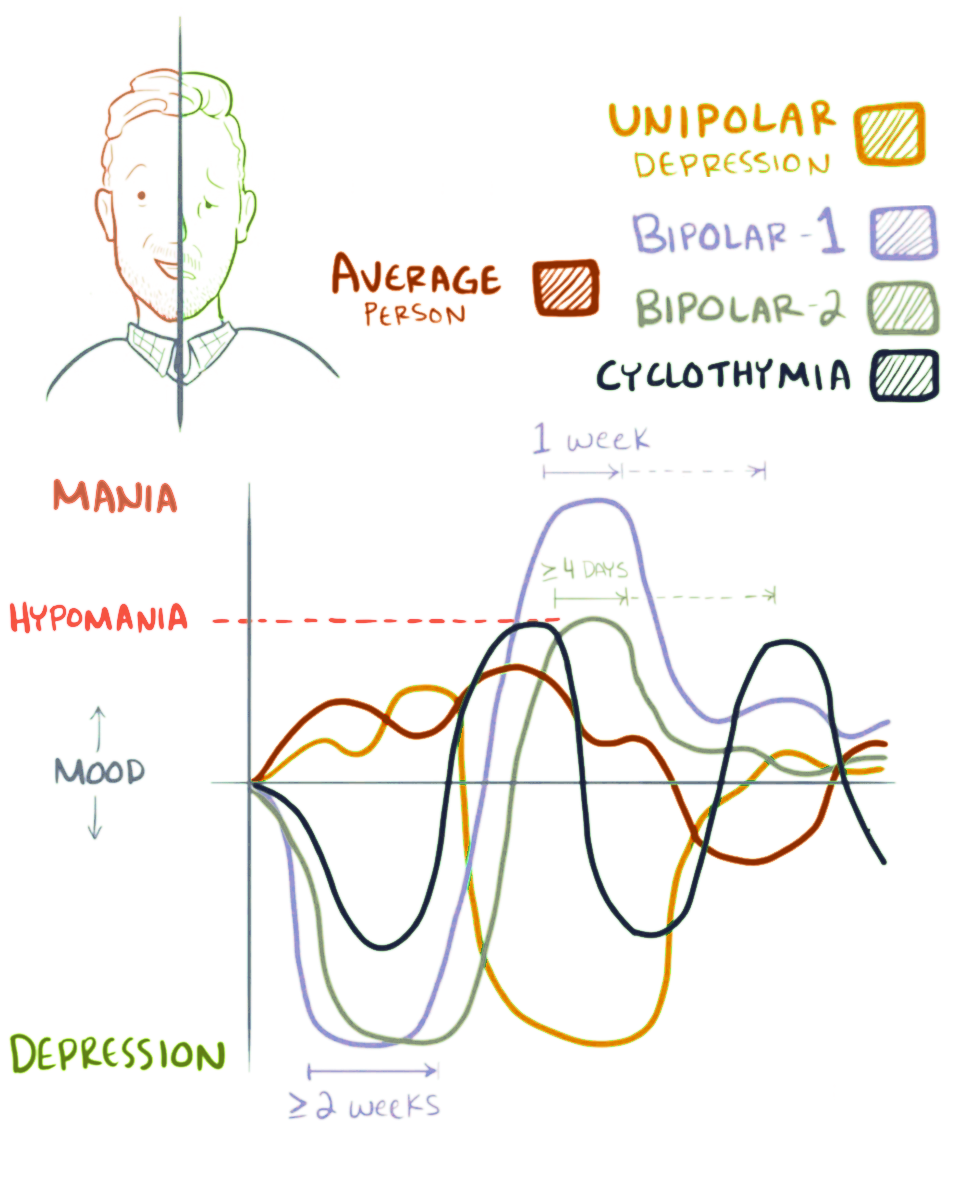
Current Diagnostic Criteria For Bipolar Disorder
Bipolar disorder, previously known as manic depression, is a mental disorder characterized by periods of depression and periods of abnormally elevated mood that last from days to weeks each. If the elevated mood is severe or associated with psychosis, it is called mania; if it is less severe, it is called hypomania. During mania, an individual behaves or feels abnormally energetic, happy or irritable, and they often make impulsive decisions with little regard for the consequences. There is usually also a reduced need for sleep during manic phases. During periods of depression, the individual may experience crying and have a negative outlook on life and poor eye contact with others. The risk of suicide is high; over a period of 20 years, 6% of those with bipolar disorder died by suicide, while 30–40% engaged in self-harm. Other mental health issues, such as anxiety disorders and substance use disorders, are commonly associated with bipolar disorder. While the causes of this ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mania
Mania, also known as manic syndrome, is a mental and behavioral disorder defined as a state of abnormally elevated arousal, affect, and energy level, or "a state of heightened overall activation with enhanced affective expression together with lability of affect." During a manic episode, an individual will experience rapidly changing emotions and moods, highly influenced by surrounding stimuli. Although mania is often conceived as a "mirror image" to depression, the heightened mood can be either euphoric or dysphoric. As the mania intensifies, irritability can be more pronounced and result in anxiety or anger. The symptoms of mania include elevated mood (either euphoric or irritable), flight of ideas and pressure of speech, increased energy, decreased need and desire for sleep, and hyperactivity. They are most plainly evident in fully developed hypomanic states. However, in full-blown mania, they undergo progressively severe exacerbations and become more and more obscured by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Delusional Disorder
Delusional disorder is a mental illness in which a person has delusions, but with no accompanying prominent hallucinations, thought disorder, mood disorder, or significant flattening of affect.American Psychiatric Association. (2013). ''Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders'', (5th ed., text revision). Washington, DC: American Psychiatric Association. Delusions are a specific symptom of psychosis. Delusions can be bizarre or non-bizarre in content; non-bizarre delusions are fixed false beliefs that involve situations that could occur in real life, such as being harmed or poisoned.Hales E and Yudofsky JA, eds, ''The American Psychiatric Press Textbook of Psychiatry'', Washington, DC: American Psychiatric Publishing, Inc., 2003 Apart from their delusion or delusions, people with delusional disorder may continue to socialize and function in a normal manner and their behavior does not necessarily generally seem odd.Winokur, George."Comprehensive Psychiatry-Delusional D ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grandiose Delusions
Grandiose delusions (GD), also known as delusions of grandeur or expansive delusions, are a subtype of delusion that occur in patients with a wide range of psychiatric diseases, including two-thirds of patients in manic state of bipolar disorder, half of those with schizophrenia, patients with the grandiose subtype of delusional disorder, frequently in narcissistic personality disorder, and a substantial portion of those with substance abuse disorders.Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders Fourth edition Text Revision (DSM-IV-TR) American Psychiatric Association (2000) GDs are characterized by fantastical beliefs that one is famous, omnipotent, wealthy, or otherwise very powerful. The delusions are generally fantastic and typically have a religious, science fictional, or supernatural theme. There is a relative lack of research into GD, in contrast to persecutory delusions and auditory hallucinations. Around 10% of healthy people experience grandiose thoughts at so ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Delusional Parasitosis
Delusional parasitosis (DP) is a mental disorder in which individuals have a persistent belief that they are infested with living or nonliving pathogens such as parasites, insects, or bugs, when no such infestation is present. They usually report tactile hallucinations known as formication, a sensation resembling insects crawling on or under the skin. Morgellons is considered to be a subtype of this condition, in which individuals have sores that they believe contain harmful fibers. Delusional parasitosis is classified as a delusional disorder in the '' Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders'' ( DSM5). The cause is unknown, but is thought to be related to excess dopamine in the brain. Delusional parasitosis is diagnosed when the delusion is the only symptom of psychosis and the delusion—that cannot be better explained by another condition—has lasted a month or longer. Few individuals with the condition willingly accept treatment, because they do not recognize ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Somatic Delusion
Somatic may refer to: * Somatic (biology), referring to the cells of the body in contrast to the germ line cells ** Somatic cell, a non-gametic cell in a multicellular organism * Somatic nervous system, the portion of the vertebrate nervous system which regulates voluntary movements of the body * Somatics, a group of alternative medicine approaches, experiential movement disciplines, and dance techniques * Somatic theory, a model of human social behavior Related concepts * Somatic marker hypothesis, an explanation of how emotions affect decision-making * Somatic symptom disorder, aka somatoform disorder, characterized by medically unexplained physical symptoms, and considered to be a mental health issue * Somatotype, the now-discredited idea associating body types with human temperament types * Psychosomatic medicine, an interdisciplinary medical field exploring the relationships among social, psychological, and behavioral factors on bodily processes and quality of life in huma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Religious Delusion
A religious delusion is defined as a delusion, or fixed belief not amenable to change in light of conflicting evidence, involving religious themes or subject matter., cited in: Religious faith, meanwhile, is defined as a belief in God or a religious doctrine in the absence of evidence.Russell, Bertrand"Will Religious Faith Cure Our Troubles?" ''Human Society in Ethics and Politics''. Ch 7. Pt 2. Retrieved 16 August 2009. Psychologists, scientists, and philosophers have debated the distinction between the two, which is subjective and cultural. Definition Individuals experiencing religious delusions are preoccupied with religious subjects that are not within the expected beliefs for an individual's background, including culture, education, and known experiences of religion. These preoccupations are incongruous with the mood of the subject. Falling within the definition also are delusions arising in psychotic depression; however, these must present within a major depressive episode ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Erotomania
Erotomania, also known as de Clérambault's Syndrome, named after French people, French psychiatrist Gaëtan Gatian de Clérambault, is listed in the DSM-5 as a subtype of a delusional disorder. It is a relatively uncommon paranoia, paranoid condition that is characterized by an individual's delusions of another person being infatuation, infatuated with them. This disorder is most often seen (though not exclusively) in female patients who are shy, dependent and sexually inexperienced. The object of the delusion is typically a male who is unattainable due to high social or financial status, marriage or uninterest. The object of obsession may also be imaginary, deceased or someone the patient has never met. Delusions of reference are common, as the erotomanic individual often perceives that they are being sent messages from the secret admirer through innocuous events such as seeing license plates from specific states, but has no proof. Commonly, the onset of erotomania is sudden, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ideas Of Reference
Ideas of reference and delusions of reference describe the phenomenon of an individual experiencing innocuous events or mere coincidences and believing they have strong personal significance. It is "the notion that everything one perceives in the world relates to one's own destiny", usually in a negative and hostile manner. In psychiatry, delusions of reference form part of the diagnostic criteria for psychotic illnesses such as schizophrenia, delusional disorder, bipolar disorder (during the elevated stages of mania), narcissistic personality disorder, and schizotypal personality disorder, and even autism when under periods of intense stress. To a lesser extent, it can be a hallmark of paranoid personality disorder as well as body dysmorphic disorder. Such symptoms can also be caused by intoxication, such as from stimulants like methamphetamine. Psychoanalytic views In Sigmund Freud's view, "Delusions of being watched present this power in a regressive form, thus revealing ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |