|
Delta Gruis
The Bayer designation δ Gruis (Delta Gruis) is shared by two stars in the constellation A constellation is an area on the celestial sphere in which a group of visible stars forms Asterism (astronomy), a perceived pattern or outline, typically representing an animal, mythological subject, or inanimate object. The origins of the e ... Grus: * δ1 Gruis * δ2 Gruis {{Set index article , astronomical objects Grus (constellation) Gruis, Delta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bayer Designation
A Bayer designation is a stellar designation in which a specific star is identified by a Greek or Latin letter followed by the genitive form of its parent constellation's Latin name. The original list of Bayer designations contained 1,564 stars. The brighter stars were assigned their first systematic names by the German astronomer Johann Bayer in 1603, in his star atlas ''Uranometria''. Bayer catalogued only a few stars too far south to be seen from Germany, but later astronomers (including Nicolas-Louis de Lacaille and Benjamin Apthorp Gould) supplemented Bayer's catalog with entries for southern constellations. Scheme Bayer assigned a lowercase Greek letter (alpha (α), beta (β), gamma (γ), etc.) or a Latin letter (A, b, c, etc.) to each star he catalogued, combined with the Latin name of the star's parent constellation in genitive (possessive) form. The constellation name is frequently abbreviated to a standard three-letter form. For example, Aldebaran in the constellation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Constellation
A constellation is an area on the celestial sphere in which a group of visible stars forms Asterism (astronomy), a perceived pattern or outline, typically representing an animal, mythological subject, or inanimate object. The origins of the earliest constellations likely go back to prehistory. People used them to relate stories of their beliefs, experiences, creation myth, creation, or mythology. Different cultures and countries adopted their own constellations, some of which lasted into the early 20th century before today's constellations were internationally recognized. The recognition of constellations has changed significantly over time. Many changed in size or shape. Some became popular, only to drop into obscurity. Some were limited to a single culture or nation. The 48 traditional Western constellations are Greek. They are given in Aratus' work ''Phenomena'' and Ptolemy's ''Almagest'', though their origin probably predates these works by several centuries. Constellation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
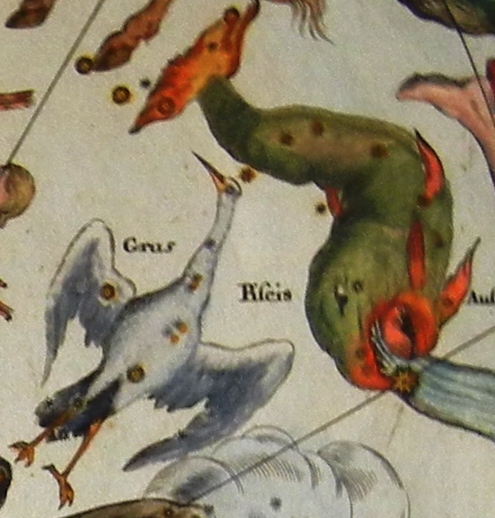
Grus (constellation)
Grus (, or colloquially ) is a constellation in the southern sky. Its name is Latin for the crane, a type of bird. It is one of twelve constellations conceived by Petrus Plancius from the observations of Pieter Dirkszoon Keyser and Frederick de Houtman. Grus first appeared on a celestial globe published in 1598 in Amsterdam by Plancius and Jodocus Hondius and was depicted in Johann Bayer's star atlas ''Uranometria'' of 1603. French explorer and astronomer Nicolas-Louis de Lacaille gave Bayer designations to its stars in 1756, some of which had been previously considered part of the neighbouring constellation Piscis Austrinus. The constellations Grus, Pavo, Phoenix and Tucana are collectively known as the "Southern Birds". The constellation's brightest star, Alpha Gruis, is also known as Alnair and appears as a 1.7-magnitude blue-white star. Beta Gruis is a red giant variable star with a minimum magnitude of 2.3 and a maximum magnitude of 2.0. Six star systems have been foun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Delta1 Gruis
Delta1 Gruis, Latinized from δ1 Gruis, is a candidate binary star system in the constellation Grus. With a peak apparent visual magnitude of 4.0 it is bright enough to be seen with the naked eye at night. The distance to this system, as determined using an annual parallax shift of 10.54 mas as seen from the Earth, is around 309 light years. It is gradually moving away from the Sun with a radial velocity of +4.9 km/s. The brighter component of this system is an evolved, yellow-hued, G-type giant star with a stellar classification of G6/8 III. It is a semiregular variable that ranges between apparent magnitudes 3.99 and 4.2, located 325 light-years from Earth. Delta1 Gruis has around 3 times the mass and 24 times the diameter of the Sun. The fainter companion is a magnitude 12.8 star at an angular separation of 5.6 arc seconds, as of 2008. See also *List of stars in Grus This is the list of notable stars in the constellation Grus, s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Delta2 Gruis
Delta2 Gruis, Latinized from δ2 Gruis, is a solitary, red-hued star in the southern constellation of Grus. It is visible to the naked eye with an apparent visual magnitude of about 4. Based upon an annual parallax shift of 9.88 mas as seen from the Earth, the star is located around 330 light years from the Sun. It is moving further away from the Sun with a radial velocity of +3 km/s. This is an evolved red giant star with a stellar classification of M4.5 IIIa. It is a pulsating variable with multiple periods, including 20.6, 24.1, 24.5, and 32.3 days. The strongest period is 33.3 days with an amplitude of 0.043 magnitude. It has a magnitude 9.71 visual companion at an angular separation of 60.4 arc seconds along a position angle In astronomy, position angle (usually abbreviated PA) is the convention for measuring angles on the sky. The International Astronomical Union defines it as the angle measured relative to the north celestial ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |