|
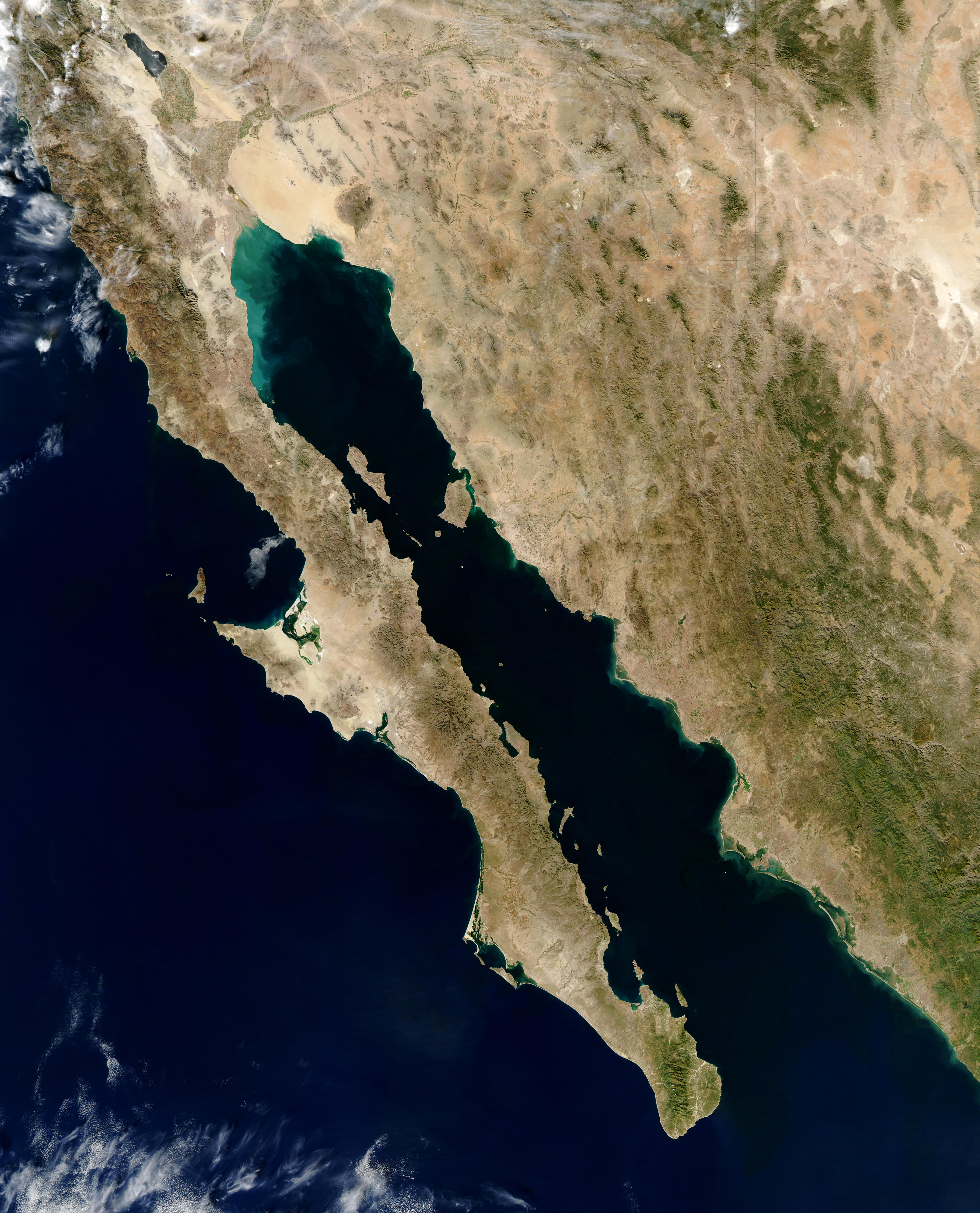
Delfin Basin
The Delfin Basin (''delfín'' is Spanish for "dolphin") is a pair of interconnected submarine depressions located on the seabed of the northern Gulf of California. The northernmost of these is called the Upper Delfin Basin while the southernmost is called the Lower Delfin Basin. Both of these features are areas of subsidence caused by extensional forces imparted by a spreading center associated with the East Pacific Rise. The two basins are linked by a short transform fault which was the apparent source of an earthquake of magnitude 5.5 on November 26, 1997. The Delfin Basin is linked to the Guaymas Basin located about 325 km to the south by a series of four transform faults called the Guaymas Transform Fault System The Guaymas Fault, named for the city of Guaymas, Sonora, Mexico, is a major right lateral-moving transform fault which runs along the seabed of the Gulf of California. It is an integral part of the Gulf of California Rift Zone, the northern extr .... It is a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gulf Of California
The Gulf of California ( es, Golfo de California), also known as the Sea of Cortés (''Mar de Cortés'') or Sea of Cortez, or less commonly as the Vermilion Sea (''Mar Bermejo''), is a marginal sea of the Pacific Ocean that separates the Baja California Peninsula from the Mexican mainland. It is bordered by the states of Baja California, Baja California Sur, Sonora, and Sinaloa with a coastline of approximately . Rivers that flow into the Gulf of California include the Colorado, Fuerte, Mayo, Sinaloa, Sonora, and the Yaqui. The surface of the gulf is about . Maximum depths exceed because of the complex geology, linked to plate tectonics. The gulf is thought to be one of the most diverse seas on Earth and is home to more than 5,000 species of micro-invertebrates. Parts of the Gulf of California are a UNESCO World Heritage Site. Geography History The marine expeditions of Fortún Ximénez, Hernán Cortés, Juan Rodríguez Cabrillo, Francisco de Ulloa, Hernando de Alarc� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
East Pacific Rise
The East Pacific Rise is a mid-ocean rise (termed an oceanic rise and not a mid-ocean ridge due to its higher rate of spreading that results in less elevation increase and more regular terrain), a divergent tectonic plate boundary located along the floor of the Pacific Ocean. It separates the Pacific Plate to the west from (north to south) the North American Plate, the Rivera Plate, the Cocos Plate, the Nazca Plate, and the Antarctic Plate. It runs south from the Gulf of California in the Salton Sea basin in Southern California to a point near 55° S, 130° W, where it joins the Pacific-Antarctic Ridge trending west-southwest towards Antarctica, near New Zealand (though in some uses the PAR is regarded as the southern section of the EPR). Much of the rise lies about 3200 km (2000 mi) off the South American coast and rises about 1,800–2,700 m (6,000–9,000 ft) above the surrounding seafloor. Overview The oceanic crust is moving away ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transform Fault
A transform fault or transform boundary, is a fault along a plate boundary where the motion is predominantly horizontal. It ends abruptly where it connects to another plate boundary, either another transform, a spreading ridge, or a subduction zone. A transform fault is a special case of a ''strike-slip fault'' that also forms a plate boundary. Most such faults are found in oceanic crust, where they accommodate the lateral offset between segments of divergent boundaries, forming a zigzag pattern. This is a result of oblique seafloor spreading where the direction of motion is not perpendicular to the trend of the overall divergent boundary. A smaller number of such faults are found on land, although these are generally better-known, such as the San Andreas Fault and North Anatolian Fault. Nomenclature Transform boundaries are also known as conservative plate boundaries because they involve no addition or loss of lithosphere at the Earth's surface. Background Geophysi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Guaymas Basin
The Guaymas Basin is a marginal rift basin, the largest such basin in the Gulf of California. It consists of two axial troughs (northern and southern). The basin results from the activity of one of the several spreading centers in the Gulf. The basin is linked to the Carmen Fault to the south, and the Guaymas Fault to the north. The Guaymas seafloor has high heat flow, hydrothermal plumes, and hydrocarbon seeps. Features Northern trough Southern trough Biology Especially in the southern trough, the Guaymas Basin supports a unique and vibrant ecosystem. Heterotrophs consume organic matter rained down from the productive surface waters, while chemolithoautotrophs metabolize chemicals in the reduced hydrothermal fluid (often cycling these chemicals with syntrophic partners). Of note are the colonies of ''Riftia'' tubeworms, ''Beggiatoa'' and other microbial mats, and thermophilic A thermophile is an organism—a type of extremophile—that thrives at relatively h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Guaymas Transform Fault System
The Guaymas Fault, named for the city of Guaymas, Sonora, Mexico, is a major right lateral-moving transform fault which runs along the seabed of the Gulf of California. It is an integral part of the Gulf of California Rift Zone, the northern extremity of the East Pacific Rise. The Guaymas Fault runs from the San Pedro Martir Basin located at the southern end of the San Lorenzo Fault (the next transform to the north), and extends southward to the Guaymas Basin, a heavily sedimented rift which includes both continental and oceanic crust and contains numerous hydrothermal vents. The Guaymas Fault is often grouped together with the three transform faults to its north as the Guaymas Transform Fault System. These faults are, from north to south, the Ballenas, Partida, San Lorenzo, and Guaymas. This system of fault extends some 325 km, linking the Delfin Basin The Delfin Basin (''delfín'' is Spanish for "dolphin") is a pair of interconnected submarine depressions located on th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Consag Basin
The Consag Basin is a submarine depression in the far northern part of the Gulf of California associated with the East Pacific Rise. It lies south of the Wagner Basin with which it is closely linked. The depression is a result of subsidence caused by the extensional forces probably imparted by the same spreading center which has produced the Wagner Basin. Both basins are bounded on their eastern side by the Wagner Fault, a primarily normal (vertical motion) fault which dips approximately 60 degrees to the northwest. The western side of the basin is bounded by another normal fault, the Consag Fault which dips in a direction opposite the Wagner Fault. The seabed between these faults is sinking. The Consag Basin is linked to the Delfin Basin located to its south by a poorly understood deformation zone which further research may eventually define as a transform fault. The basin is named for a rocky outcrop in its vicinity, the Roca Consag Roca Consag (Consag Rock) is a granitic (or mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gulf Of California Rift Zone
The Gulf of California Rift Zone (GCRZ) is the northernmost extension of the East Pacific Rise which extends some from the mouth of the Gulf of California to the southern terminus of the San Andreas Fault at the Salton Sink. The GCRZ is an incipient rift zone akin to the Red Sea Rift. In the GCRZ continental crust originally associated with the North American Plate has been pulled apart by tectonic forces and is being replaced by newly formed oceanic crust and seafloor spreading. The rifting has resulted in the transfer of the Baja California Peninsula to the Pacific Plate. List of GCRZ transform faults From north to south: * Imperial Fault Zone * Cerro Prieto Fault * Ballenas Fault * Partida Fault * San Lorenzo Fault * Guaymas Fault * Carmen Fault * Farallon Fault * Atl Fault * Pescadero Fault * Tamayo Fault List of GCRZ rift basins From north to south: * Brawley Seismic Zone * Cerro Prieto * Wagner Basin * Consag Basin * Adair-Tepoca Basin * Tiburon Basin * Delfin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |