|
Deirochelys
''Deirochelys'' is a genus of freshwater turtle in the family Emydidae, the pond and marsh turtles. It contains one extant species, the chicken turtle (''Deirochelys reticularia''), which is native to the southeastern United States. A second extinct member, ''Deirochelys carri'', is known from a fossil found in Alachua County, Florida. The genus was first described by Louis Agassiz in 1857, and its name is derived from the Ancient Greek words for "neck" (''deirḗ'') and "tortoise" (''khélūs''), referring to the particularly long necks of these turtles. Evolution Like other emydids (members of the family Emydidae), ''Deirochelys'' karyotype consists of 2N=50 chromosomes. A 1996 study of various turtles' mitochondrial DNA supported the partition of Emydidae into two subfamilies, Emydinae and Deirochelyinae, with ''Deirochelys'' placed within the latter. ''Deirochelys'' was reported to be the sister genus to the rest of the subfamily, meaning it shares a common ancestor with the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chicken Turtle
The chicken turtle (''Deirochelys reticularia'') is a turtle native to the southeastern United States. It is the only extant member of the genus ''Deirochelys'' and is a member of the freshwater marsh turtle family Emydidae. The chicken turtle's scientific name refers to its extremely long neck and distinctive net-like pattern on its upper shell. There are three regionally distinct subspecies (eastern, western and Florida), which are thought to have evolved when populations became separated during periods of glaciation. These subspecies can be distinguished by their appearance; the western chicken turtle displays dark markings along the seams of its plastron (lower shell), while the plastron of the Florida subspecies is a bright yellow or orange color. Fossil records show that the chicken turtle has been present in the region for up to five million years. Chicken turtles inhabit shallow, still or slow-moving bodies of water with plenty of vegetation and a muddy substrate. They ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
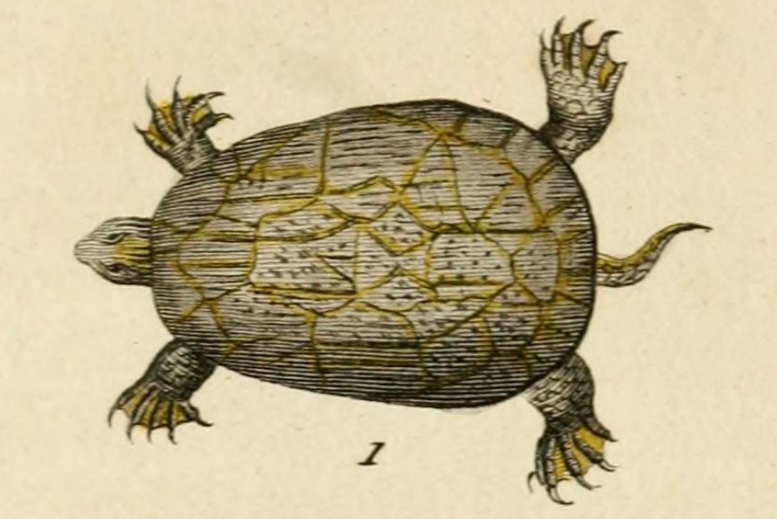
Deirochelys Reticularia
The chicken turtle (''Deirochelys reticularia'') is a turtle native to the southeastern United States. It is the only extant member of the genus ''Deirochelys'' and is a member of the freshwater marsh turtle family Emydidae. The chicken turtle's scientific name refers to its extremely long neck and distinctive net-like pattern on its upper shell. There are three regionally distinct subspecies (eastern, western and Florida), which are thought to have evolved when populations became separated during periods of glaciation. These subspecies can be distinguished by their appearance; the western chicken turtle displays dark markings along the seams of its plastron (lower shell), while the plastron of the Florida subspecies is a bright yellow or orange color. Fossil records show that the chicken turtle has been present in the region for up to five million years. Chicken turtles inhabit shallow, still or slow-moving bodies of water with plenty of vegetation and a muddy substrate. They ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chicken Turtle
The chicken turtle (''Deirochelys reticularia'') is a turtle native to the southeastern United States. It is the only extant member of the genus ''Deirochelys'' and is a member of the freshwater marsh turtle family Emydidae. The chicken turtle's scientific name refers to its extremely long neck and distinctive net-like pattern on its upper shell. There are three regionally distinct subspecies (eastern, western and Florida), which are thought to have evolved when populations became separated during periods of glaciation. These subspecies can be distinguished by their appearance; the western chicken turtle displays dark markings along the seams of its plastron (lower shell), while the plastron of the Florida subspecies is a bright yellow or orange color. Fossil records show that the chicken turtle has been present in the region for up to five million years. Chicken turtles inhabit shallow, still or slow-moving bodies of water with plenty of vegetation and a muddy substrate. They ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deirochelys Carri
''Deirochelys'' is a genus of freshwater turtle in the family Emydidae, the pond and marsh turtles. It contains one extant species, the chicken turtle (''Deirochelys reticularia''), which is native to the southeastern United States. A second extinct member, ''Deirochelys carri'', is known from a fossil found in Alachua County, Florida. The genus was first described by Louis Agassiz in 1857, and its name is derived from the Ancient Greek words for "neck" (''deirḗ'') and "tortoise" (''khélūs''), referring to the particularly long necks of these turtles. Evolution Like other emydids (members of the family Emydidae), ''Deirochelys'' karyotype consists of 2N=50 chromosomes. A 1996 study of various turtles' mitochondrial DNA supported the partition of Emydidae into two subfamilies, Emydinae and Deirochelyinae, with ''Deirochelys'' placed within the latter. ''Deirochelys'' was reported to be the sister genus to the rest of the subfamily, meaning it shares a common ancestor with the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deirochelyinae
The Deirochelyinae are a subfamily of the Emydidae consisting of species native to North and South America, some of which are frequently kept as pets. As a result of pet trade, one species, the red-eared slider The red-eared slider or red-eared terrapin (''Trachemys scripta elegans'') is a subspecies of the pond slider (''Trachemys scripta''), a semiaquatic turtle belonging to the family Emydidae. It is the most popular pet turtle in the United States, ..., can now be found in many parts of the world. Classification Species References External links Family Emydidae on The Reptile Database Emydidae Turtles of North America {{Turtle-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Emydidae
Emydidae (Latin ''emys'' (freshwater tortoise) + Ancient Greek εἶδος (''eîdos'', “appearance, resemblance”)) is a family of testudines (turtles) that includes close to 50 species in 10 genera. Members of this family are commonly called terrapins, pond turtles, or marsh turtles. Several species of Asian box turtles were formerly classified in the family; however, revised taxonomy has separated them to a different family (Geoemydidae). As currently defined, the Emydidae are entirely a Western Hemisphere family, with the exception of two species of pond turtle. Description The upper shell (carapace) of most emydids is the shape of a low arch, although in some species, it is domed. The upper shell may have one or two ridges that run from front to the back of the animal (a projection commonly called a "keel"), or such a feature may be absent. A prominent bridge often connects the top shell to the bottom shell ( plastron). Emydids have large bottom shells, and some memb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Miocene
The Miocene ( ) is the first geological epoch of the Neogene Period and extends from about (Ma). The Miocene was named by Scottish geologist Charles Lyell; the name comes from the Greek words (', "less") and (', "new") and means "less recent" because it has 18% fewer modern marine invertebrates than the Pliocene has. The Miocene is preceded by the Oligocene and is followed by the Pliocene. As Earth went from the Oligocene through the Miocene and into the Pliocene, the climate slowly cooled towards a series of ice ages. The Miocene boundaries are not marked by a single distinct global event but consist rather of regionally defined boundaries between the warmer Oligocene and the cooler Pliocene Epoch. During the Early Miocene, the Arabian Peninsula collided with Eurasia, severing the connection between the Mediterranean and Indian Ocean, and allowing a faunal interchange to occur between Eurasia and Africa, including the dispersal of proboscideans into Eurasia. During the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mitochondrial DNA
Mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA or mDNA) is the DNA located in mitochondria, cellular organelles within eukaryotic cells that convert chemical energy from food into a form that cells can use, such as adenosine triphosphate (ATP). Mitochondrial DNA is only a small portion of the DNA in a eukaryotic cell; most of the DNA can be found in the cell nucleus and, in plants and algae, also in plastids such as chloroplasts. Human mitochondrial DNA was the first significant part of the human genome to be sequenced. This sequencing revealed that the human mtDNA includes 16,569 base pairs and encodes 13 proteins. Since animal mtDNA evolves faster than nuclear genetic markers, it represents a mainstay of phylogenetics and evolutionary biology. It also permits an examination of the relatedness of populations, and so has become important in anthropology and biogeography. Origin Nuclear and mitochondrial DNA are thought to be of separate evolutionary origin, with the mtDNA being derived ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Emydinae
The Emydinae are a subfamily of turtles in the family Emydidae. Classification The genera of the Emydinae remain unresolved, with ''Actinemys'' and ''Emydoidea Blanding's turtle (''Emydoidea blandingii'') is a semi-aquatic turtle of the family Emydidae. This species is native to central and eastern parts of Canada and the United States. It is considered to be an endangered species throughout much of its ...'' being used in some publications. Species References ;Bibliography * * Tetrapod subfamilies {{Turtle-stub de:Neuwelt-Sumpfschildkröten#Systematik ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sister Taxon
In phylogenetics, a sister group or sister taxon, also called an adelphotaxon, comprises the closest relative(s) of another given unit in an evolutionary tree. Definition The expression is most easily illustrated by a cladogram: Taxon A and taxon B are sister groups to each other. Taxa A and B, together with any other extant or extinct descendants of their most recent common ancestor (MRCA), form a monophyletic group, the clade AB. Clade AB and taxon C are also sister groups. Taxa A, B, and C, together with all other descendants of their MRCA form the clade ABC. The whole clade ABC is itself a subtree of a larger tree which offers yet more sister group relationships, both among the leaves and among larger, more deeply rooted clades. The tree structure shown connects through its root to the rest of the universal tree of life. In cladistic standards, taxa A, B, and C may represent specimens, species, genera, or any other taxonomic units. If A and B are at the same taxonomi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maximum Parsimony (phylogenetics)
In phylogenetics, maximum parsimony is an optimality criterion under which the phylogenetic tree that minimizes the total number of character-state changes (or miminizes the cost of differentially weighted character-state changes) is preferred. Under the maximum-parsimony criterion, the optimal tree will minimize the amount of homoplasy (i.e., convergent evolution, parallel evolution, and evolutionary reversals). In other words, under this criterion, the shortest possible tree that explains the data is considered best. Some of the basic ideas behind maximum parsimony were presented by James S. Farris in 1970 and Walter M. Fitch in 1971. Maximum parsimony is an intuitive and simple criterion, and it is popular for this reason. However, although it is easy to ''score'' a phylogenetic tree (by counting the number of character-state changes), there is no algorithm to quickly ''generate'' the most-parsimonious tree. Instead, the most-parsimonious tree must be sought in "tree space" ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Long-branch Attraction
In phylogenetics, long branch attraction (LBA) is a form of systematic error whereby distantly related lineages are incorrectly inferred to be closely related. LBA arises when the amount of molecular or morphological change accumulated within a lineage is sufficient to cause that lineage to appear similar (thus closely related) to another long-branched lineage, solely because they have both undergone a large amount of change, rather than because they are related by descent. Such bias is more common when the overall divergence of some taxa results in long branches within a phylogeny. Long branches are often attracted to the base of a phylogenetic tree, because the lineage included to represent an outgroup is often also long-branched. The frequency of true LBA is unclear and often debated, and some authors view it as untestable and therefore irrelevant to empirical phylogenetic inference. Although often viewed as a failing of parsimony-based methodology, LBA could in principle resul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)




.png)