|
Deinodus
''Deinodus'' is a form genus that includes two species: the form found in the Onondaga Formation of western New York, ''Deinodus bennetti'', and the form found in the Columbus and Limestone of central Ohio, ''Deinodus ohioensis''. Both species are limited to the Eifelian age of the middle Devonian Period, which occurred 398-391 million years ago (Martin, 2002). Denison (1978) postulates that the genus could be an arthrodire or ptyctodont, but places it in his "incertae sedis" section. Individual specimens tend to resemble the ptyctodonts from the same units and ptyctodonts from Australia, so ''Deinodus'' is most likely a ptyctodont. Specimens interpreted as lateral spines may show that ''Deinodus'' was a basal ptyctodont, not far removed from the petalichthids (Martin, 2002). ''Deinodus bennetti'' was first described in 1919 (Hussakof and Bryant). Specimens of ''Deinodus'' exhibit a variety of shapes, though most possess the characteristic large tubercles reported by Hussakof ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ptyctodont
The ptyctodontids ("folded-teeth") are placoderms of the order Ptyctodontida, containing the family Ptyctodontidae. With their big heads, big eyes, reduced armor and long bodies, the ptyctodontids bore a superficial resemblance to modern day chimaeras (Holocephali). Their armor was reduced to a pattern of small plates around the head and neck. Like the extinct and related acanthothoracids, and the living and unrelated holocephalians, most of the ptyctodontids are thought to have lived near the sea bottom and preyed on shellfish. On account of their radically reduced armor, some paleontologists have suggested that the Ptyctodontida were not actually placoderms, but actual holocephalians, some primitive group of elasmobranch fish, or even were the ancestors of the holocephalians, including the chimaeras. Thorough anatomical examinations of whole fossil specimens reveal that the profound similarities between these two groups are actually very superficial. The major differences ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Australia
Australia, officially the Commonwealth of Australia, is a Sovereign state, sovereign country comprising the mainland of the Australia (continent), Australian continent, the island of Tasmania, and numerous List of islands of Australia, smaller islands. With an area of , Australia is the largest country by area in Oceania and the world's List of countries and dependencies by area, sixth-largest country. Australia is the oldest, flattest, and driest inhabited continent, with the least fertile soils. It is a Megadiverse countries, megadiverse country, and its size gives it a wide variety of landscapes and climates, with Deserts of Australia, deserts in the centre, tropical Forests of Australia, rainforests in the north-east, and List of mountains in Australia, mountain ranges in the south-east. The ancestors of Aboriginal Australians began arriving from south east Asia approximately Early human migrations#Nearby Oceania, 65,000 years ago, during the Last Glacial Period, last i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paleontology In New York (state)
Paleontology in New York refers to paleontological research occurring within or conducted by people from the U.S. state of New York. New York has a very rich fossil record, especially from the Devonian. However, a gap in this record spans most of the Mesozoic and early Cenozoic. Much of New York was covered in seawater during the early part of the Paleozoic era. This sea came to be inhabited by invertebrates like brachiopods, conodonts, eurypterids, jellyfish, and trilobites. Local marine vertebrates included arthrodires, chimaeroids, lobe-finned fishes, and lungfish. By the Devonian the state was home to some of the oldest known forests. The Carboniferous and Permian are missing from the local rock record. Little is known about Mesozoic New York, but during the early part of the era, carnivorous dinosaurs left behind footprints which later fossilized. The early to mid Cenozoic is also mostly absent from the local rock record. However, evidence indicates that during the Ice Age t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Devonian Placoderms
The Devonian ( ) is a geologic period and system of the Paleozoic era, spanning 60.3 million years from the end of the Silurian, million years ago (Mya), to the beginning of the Carboniferous, Mya. It is named after Devon, England, where rocks from this period were first studied. The first significant adaptive radiation of life on dry land occurred during the Devonian. Free-sporing vascular plants began to spread across dry land, forming extensive forests which covered the continents. By the middle of the Devonian, several groups of plants had evolved leaves and true roots, and by the end of the period the first seed-bearing plants appeared. The arthropod groups of myriapods, arachnids and hexapods also became well-established early in this period, after starting their expansion to land at least from the Ordovician period. Fish reached substantial diversity during this time, leading the Devonian to often be dubbed the Age of Fishes. The placoderms began dominating ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
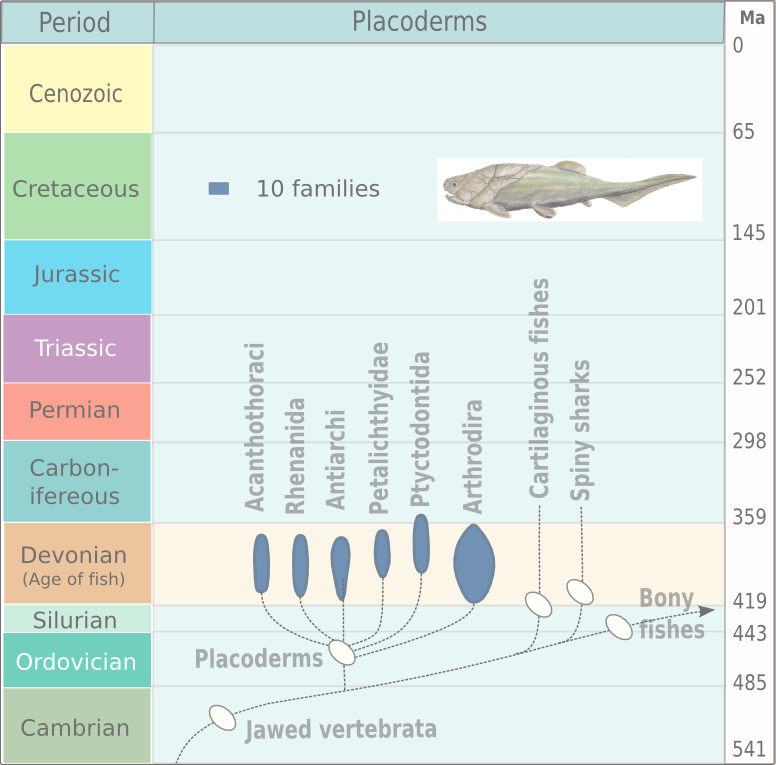
Placoderms Of North America
Placodermi (from Greek πλάξ 'plate' and δέρμα 'skin', literally 'plate-skinned') is a class of armoured prehistoric fish, known from fossils, which lived from the Silurian to the end of the Devonian period. Their head and thorax were covered by articulated armoured plates and the rest of the body was scaled or naked, depending on the species. Placoderms were among the first jawed fish; their jaws likely evolved from the first of their gill arches. Placoderms are thought to be paraphyletic, consisting of several distinct outgroups or sister taxa to all living jawed vertebrates, which originated among their ranks. In contrast, one 2016 analysis concluded that placodermi are likely monophyletic, though these analyses have been further dismissed with more transitional taxa between placoderms and modern gnathosthomes, solidifying their paraphyletic status. Placoderms were also the first fish to develop pelvic fins, the precursor to hindlimbs in tetrapods, as well as true t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Placodermi Enigmatic Taxa
Placodermi (from Greek πλάξ 'plate' and δέρμα 'skin', literally 'plate-skinned') is a class of armoured prehistoric fish, known from fossils, which lived from the Silurian to the end of the Devonian period. Their head and thorax were covered by articulated armoured plates and the rest of the body was scaled or naked, depending on the species. Placoderms were among the first jawed fish; their jaws likely evolved from the first of their gill arches. Placoderms are thought to be paraphyletic, consisting of several distinct outgroups or sister taxa to all living jawed vertebrates, which originated among their ranks. In contrast, one 2016 analysis concluded that placodermi are likely monophyletic, though these analyses have been further dismissed with more transitional taxa between placoderms and modern gnathosthomes, solidifying their paraphyletic status. Placoderms were also the first fish to develop pelvic fins, the precursor to hindlimbs in tetrapods, as well as true t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Durophagy
Durophagy is the eating behavior of animals that consume hard-shelled or exoskeleton bearing organisms, such as corals, shelled mollusks, or crabs. It is mostly used to describe fish, but is also used when describing reptiles, including fossil turtles, placodonts and invertebrates, as well as "bone-crushing" mammalian carnivores such as hyenas. Durophagy requires special adaptions, such as blunt, strong teeth and a heavy jaw. Bite force is necessary to overcome the physical constraints of consuming more durable prey and gain a competitive advantage over other organisms by gaining access to more diverse or exclusive food resources earlier in life. Those with greater bite forces require less time to consume certain prey items as a greater bite force can increase the net rate of energy intake when foraging and enhance fitness in durophagous species. In the order Carnivora there are two dietary categories of durophagy; bonecrackers and bamboo eaters. Bonecrackers are exemplified by hy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ontogeny
Ontogeny (also ontogenesis) is the origination and development of an organism (both physical and psychological, e.g., moral development), usually from the time of fertilization of the egg to adult. The term can also be used to refer to the study of the entirety of an organism's lifespan. Ontogeny is the developmental history of an organism within its own lifetime, as distinct from phylogeny, which refers to the evolutionary history of a species. Another way to think of ontogeny is that it is the process of an organism going through all of the developmental stages over its lifetime. The developmental history includes all the developmental events that occur during the existence of an organism, beginning with the changes in the egg at the time of fertilization and events from the time of birth or hatching and afterward (i.e., growth, remolding of body shape, development of secondary sexual characteristics, etc.). While developmental (i.e., ontogenetic) processes can influence sub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Petalichthyida
Petalichthyida is an extinct order of small, flattened placoderm fish. They are typified by their splayed pectoral fins, exaggerated lateral spines, flattened bodies, and numerous tubercles that decorated all of the plates and scales of their armor. They reached a peak in diversity during the Early Devonian and were found throughout the world, particularly in Europe (especially in Germany), North America, Asia, South America, and Australia. The petalichthids '' Lunaspis'' and '' Wijdeaspis'' are among the best known. The earliest and most primitive known petalichthyid is '' Diandongpetalichthys'', which is from earliest Devonian-aged strata of Yunnan. The presence of ''Diandongpetalichthys'', along with other primitive petalichthyids including '' Neopetalichthys'' and '' Quasipetalichthys'', and more advanced petalichthyids, suggest that the order may have arisen in China, possibly during the late Silurian. Because they had compressed body forms, it is speculated they wer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eifelian
The Eifelian is the first of two faunal stages in the Middle Devonian Epoch. It lasted from 393.3 ± 1.2 million years ago to 387.7 ± 0.8 million years ago. It was preceded by the Emsian Stage and followed by the Givetian Stage. North American subdivisions of the Eifelian Stage include Southwood, and part of Cazenovia (or Cazenovian). Name and definition The Eifelian is named after the Eifel Mountains of Western Germany, which exposed the GSSP section at the Wetteldorf Richtschnitt outcrop. The base of the Eifelian is defined by the start of the '' Polygnathus partitus'' conodont zone. This layer lies within the Upper Heisdorf Formation, below the base of the Lauch Formation. Extinctions The end of the Eifelian was marked by a biological crisis known as the Kačák Event, a two-part interval of extinction which led to ecological turnover among ammonoids, conodonts, and other free-swimming animals. In deep marine waters, the event is indicated by anoxic black shales. Ther ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Animal
Animals are multicellular, eukaryotic organisms in the Kingdom (biology), biological kingdom Animalia. With few exceptions, animals Heterotroph, consume organic material, Cellular respiration#Aerobic respiration, breathe oxygen, are Motility, able to move, can Sexual reproduction, reproduce sexually, and go through an ontogenetic stage in which their body consists of a hollow sphere of Cell (biology), cells, the blastula, during Embryogenesis, embryonic development. Over 1.5 million Extant taxon, living animal species have been Species description, described—of which around 1 million are Insecta, insects—but it has been estimated there are over 7 million animal species in total. Animals range in length from to . They have Ecology, complex interactions with each other and their environments, forming intricate food webs. The scientific study of animals is known as zoology. Most living animal species are in Bilateria, a clade whose members have a Symmetry in biology#Bilate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |