|
Definition Of Music
A definition of music endeavors to give an accurate and concise explanation of music's basic attributes or essential nature and it involves a process of defining what is meant by the term ''music''. Many authorities have suggested definitions, but defining music turns out to be more difficult than might first be imagined, and there is ongoing debate. A number of explanations start with the notion of music as ''organized sound,'' but they also highlight that this is perhaps too broad a definition and cite examples of organized sound that are not defined as music, such as human speech and sounds found in both natural and industrial environments . The problem of defining music is further complicated by the influence of culture in music cognition. The '' Concise Oxford Dictionary'' defines music as "the art of combining vocal or instrumental sounds (or both) to produce beauty of form, harmony, and expression of emotion". However, some music genres, such as noise music and musiqu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Definition
A definition is a statement of the meaning of a term (a word, phrase, or other set of symbols). Definitions can be classified into two large categories: intensional definitions (which try to give the sense of a term), and extensional definitions (which try to list the objects that a term describes).Lyons, John. "Semantics, vol. I." Cambridge: Cambridge (1977). p.158 and on. Another important category of definitions is the class of ostensive definitions, which convey the meaning of a term by pointing out examples. A term may have many different senses and multiple meanings, and thus require multiple definitions. In mathematics, a definition is used to give a precise meaning to a new term, by describing a condition which unambiguously qualifies what a mathematical term is and is not. Definitions and axioms form the basis on which all of modern mathematics is to be constructed. Basic terminology In modern usage, a definition is something, typically expressed in words, that at ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
North American Indian
The Indigenous peoples of the Americas are the inhabitants of the Americas before the arrival of the European settlers in the 15th century, and the ethnic groups who now identify themselves with those peoples. Many Indigenous peoples of the Americas were traditionally hunter-gatherers and many, especially in the Amazon basin, still are, but many groups practiced aquaculture and agriculture. While some societies depended heavily on agriculture, others practiced a mix of farming, hunting, and gathering. In some regions, the Indigenous peoples created monumental architecture, large-scale organized cities, city-states, chiefdoms, states, kingdoms, republics, confederacies, and empires. Some had varying degrees of knowledge of engineering, architecture, mathematics, astronomy, writing, physics, medicine, planting and irrigation, geology, mining, metallurgy, sculpture, and gold smithing. Many parts of the Americas are still populated by Indigenous peoples; some countries have ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mapuche
The Mapuche ( (Mapuche & Spanish: )) are a group of indigenous inhabitants of south-central Chile and southwestern Argentina, including parts of Patagonia. The collective term refers to a wide-ranging ethnicity composed of various groups who shared a common social, religious, and economic structure, as well as a common linguistic heritage as Mapudungun speakers. Their habitat once extended from Aconcagua Valley to Chiloé Archipelago and later spread eastward to Puelmapu, a land comprising part of the Argentine pampa and Patagonia. Today the collective group makes up over 80% of the indigenous peoples in Chile, and about 9% of the total Chilean population. The Mapuche are particularly concentrated in the Araucanía region. Many have migrated from rural areas to the cities of Santiago and Buenos Aires for economic opportunities. The Mapuche traditional economy is based on agriculture; their traditional social organization consists of extended families, under the direction ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jarawa Language (Nigeria)
Jarawa (also known as Jar, Jara, or in Hausa: ''Jaranci'') is the most populous of the Bantu languages of eastern Nigeria. It is a dialect cluster consisting of many varieties. Dialects Jarawa dialects are: * Zhár (Bankal) * Zugur (Duguri) * Gwak (Gingwak) * Ndaŋshi * Dòòrì * Mbat (Bada) * Mùùn * Kantana * Dàmùl Kantana may be a distinct language. Blench (2019) lists these varieties as dialects of Jar (Jarawa). *Zhar *Ligri *Kantana Kantana Group is a production company established in Bangkok, Thailand in 1951 by Pradit and Somsook Kaljaruek. Kantana took its first step from radio dramas to films, television dramas, variety programs, and eventually moved on to become an int ... *Bobar (?) *Gwak (Gingwak) *Dõõri * Mbat *Mbat-Galamkya References Jarawan languages Languages of Nigeria {{nigeria-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eggon Language
Eggon (also Egon, Ero, or Mo Egon), erroneously referred to as Mada - formerly a Plateau language spoken in central Nigeria. It is one of the major language in Nasarawa State. Classification The exact classification of the Eggon language has been in dispute and it can be said that this issue remains unresolved. Eggon was first classified by Greenberg (1963) as a Plateau language in his group 5, together with Nungu and Yeskwa. In the revision prepared by Carl Hoffman published in Hansford et al. (1976) a Benue group was set up that combined Greenberg's Plateau 5 and 7 with Jukunoid. The new subgrouping classified Eggon together with Nungu, Ake and Jidda-Abu. This concept of a Benue grouping came from the lexicostatistical studies of Shimizu (1975) who argued against the unity of Greenberg's Plateau and proposed the Benue group. However, in 1983, Gerhardt published a convincing rebuttal of Shimizu's arguments. The latest version of classification of Plateau languages in Ger ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Idoma Language
Idoma is the second official language spoken in Benue State in southeast-central Nigeria Nigeria ( ), , ig, Naìjíríyà, yo, Nàìjíríà, pcm, Naijá , ff, Naajeeriya, kcg, Naijeriya officially the Federal Republic of Nigeria, is a country in West Africa. It is situated between the Sahel to the north and the Gulf of G ..., by approximately 600,000 people (1991 estimate). The Idoma language is made up of the dialects of Agatu, Otukpo, Otukpa, Orokam, Akpa Agila, Utonkon, Igede, Etilo, Iyala. The Idoma people are predominantly hunters, farmers and fishermen. They are bordered to the north by Nasarawa, south by cross river, east by Taraba and west by Enugu and Kogi States. Animal names References Idomoid languages {{VoltaNiger-lang-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
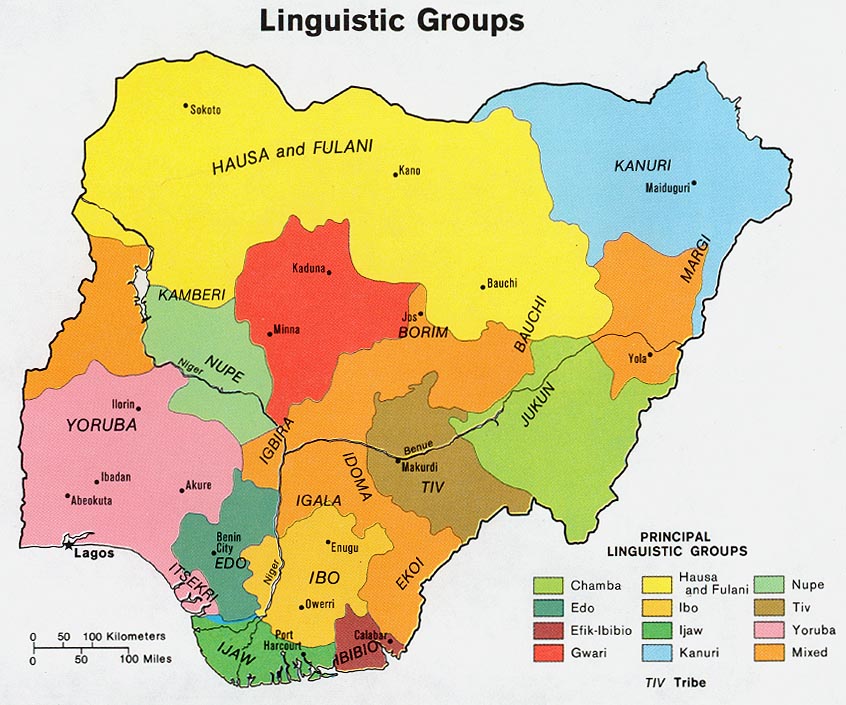
Hausa Language
Hausa (; /; Ajami: ) is a Chadic language spoken by the Hausa people in the northern half of Nigeria, Ghana, Cameroon, Benin and Togo, and the southern half of Niger, Chad and Sudan, with significant minorities in Ivory Coast. Hausa is a member of the Afroasiatic language family and is the most widely spoken language within the Chadic branch of that family. Ethnologue estimated that it was spoken as a first language by some 47 million people and as a second language by another 25 million, bringing the total number of Hausa speakers to an estimated 72 million. In Nigeria, the Hausa-speaking film industry is known as Kannywood. Classification Hausa belongs to the West Chadic languages subgroup of the Chadic languages group, which in turn is part of the Afroasiatic language family. Geographic distribution Native speakers of Hausa, the Hausa people, are mostly found in southern Niger and northern Nigeria. The language is used as a lingua franca by n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Berom Language
Berom or Birom (''Cèn Bèrom'') is the most widely spoken Plateau language in Nigeria. The language is locally numerically important and is consistently spoken by Berom of all ages in rural areas. However, the Berom are shifting to Hausa in cities. The small Cen and Nincut dialects may be separate languages. Approximately 1 million (2010) people speak in this language. Berom is spoken in a large area just to the south of Jos city in Plateau State, Nigeria. History The Berom have a link to the Nok culture, a civilization that existed between 200BC to 1000AD. Generally, the Berom speakers are identified to live in the core Jos Plateau and down the low plains of Kaduna State Kaduna State ( ha, Jihar Kaduna جىِهَر كَدُنا; ff, Leydi Kaduna, script=Latn, ; kcg, Sitet Kaduna) is a state in northern Nigeria. The state capital is its namesake, the city of Kaduna which happened to be the 8th largest city in .... Dialects The Berom dialect clusters are:Blench, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Efik Language
Efik (''Usem Efịk'') is the indigenous language of the Efik people, who are situated in the present-day Cross River state and Akwa Ibom state of Nigeria, as well as in the North-West of Cameroon. The Efik language is mutually intelligible with other lower Cross River languages such as Ibibio, Annang, Oro and Ekid but the degree of intelligibility in the case of Oro and Ekid is unidirectional; in other words, speakers of these languages speak and understand Efik (and Ibibio) but not vice versa. The Efik vocabulary has been enriched and influenced by external contact with the British, Portuguese and other surrounding communities such as Balondo, Oron, Efut, Okoyong, Efiat and Ekoi (Qua). Classification The Efik Language has undergone several linguistic classifications since the 19th century. The first attempt at classifying the Efik Language was by Dr. Baikie in 1854. Baikie, p.420 Dr Baikie had stated, "All the coast dialects from One to Old Kalabar, are, either ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Igbo Language
Igbo ( , ; Igbo: ''Ásụ̀sụ́ Ìgbò'' ) is the principal native language cluster of the Igbo people, a meta-ethnicity from Southeastern Nigeria. The number of Igboid languages depends on how one classifies a language versus a dialect, so there could be around 15 different Igboid languages. The core Igbo cluster or Igbo proper is generally thought to be one language but there is limited mutual intelligibility between the different groupings (north, west, south and east). A standard literary language termed 'Igbo izugbe' (meaning "general igbo") was generically developed and later adopted around 1972, with its core foundation based on the Owerri (Isuama), Anambra (Awka) and Umuahia (Ohuhu) dialects, omitting the nasalization and aspiration of those varieties. However, nobody speaks "general Igbo" natively and it isn't accepted by all Igbo groups. The largest variety of the core Igbo cluster is Ngwa. History The first book to publish Igbo terms was ''History of the M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yoruba Language
Yoruba (, ; Yor. '; Ajami: ) is a language spoken in West Africa, primarily in Southwestern and Central Nigeria. It is spoken by the ethnic Yoruba people. The number of Yoruba speakers is roughly 50 million, plus about 2 million second-language speakers. As a pluricentric language, it is primarily spoken in a dialectal area spanning Nigeria and Benin with smaller migrated communities in Côte d'Ivoire, Sierra Leone and The Gambia. Yoruba vocabulary is also used in the Afro-Brazilian religion known as Candomblé, in the Caribbean religion of Santería in the form of the liturgical Lucumí language and various Afro-American religions of North America. Practitioners of these religions in the Americas no longer speak or understand the Yorùbá language, rather they use remnants of Yorùbá language for singing songs that for them are shrouded in mystery. Usage of a lexicon of Yorùbá words and short phrases during ritual is also common, but they have gone through changes due to th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tiv Language
Tiv is a Tivoid language spoken in some states in North Central Nigeria, with some speakers in Cameroon. It had over 5 million speakers in 2020. The largest population of Tiv speakers are found in Benue state in Nigeria. The language is also widely spoken in the Nigerian states of Plateau, Taraba, Nasarawa and Cross River. It is by far the largest of the Tivoid languages, a group of languages belonging to the Southern Bantoid languages Geographic distribution Tiv is widely spoken in the States of Benue, Nasarawa, Plateau, Taraba, Cross Rivers, Adamawa, Kaduna, and Abuja. Other parts of Nigeria also speak Tiv. Benue state Tarkaa, Makurdi, Gwer East, Gwer west, Ukum, Logo, Konshisha, Gboko, Kwande, Vandeikya, Katsina Ala, Guma, Buruku, and Ushongo Local Government Areas. Nassarawa state Doma, Nasarawa, Lafia, Obi, Keana, and Awe Local Government Areas Plateau state Qua’an Pan and Shendam Local Government Areas Taraba state Bali, Donga, Ibi, Gassol, Takum, Gashaka, Kurmi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

_2007.jpg)