|
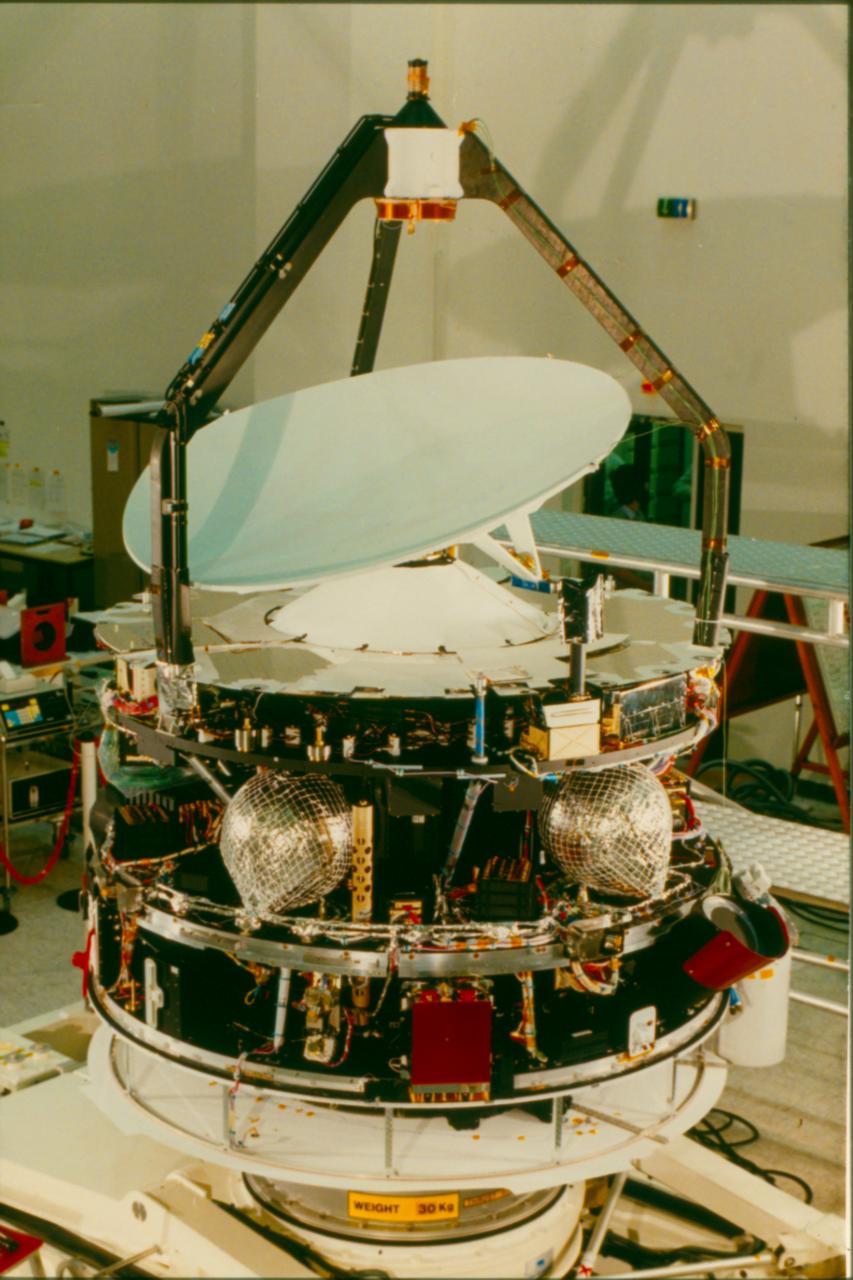
Deep Impact (space Mission)
''Deep Impact'' was a NASA space probe launched from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station on January 12, 2005. It was designed to study the interior composition of the comet Tempel 1 (9P/Tempel), by releasing an impactor into the comet. At 05:52 UTC on July 4, 2005, the Impactor successfully collided with the comet's nucleus. The impact excavated debris from the interior of the nucleus, forming an impact crater. Photographs taken by the spacecraft showed the comet to be more dusty and less icy than had been expected. The impact generated an unexpectedly large and bright dust cloud, obscuring the view of the impact crater. Previous space missions to comets, such as ''Giotto'', ''Deep Space 1'', and '' Stardust'', were fly-by missions. These missions were able to photograph and examine only the surfaces of cometary nuclei, and even then from considerable distances. The ''Deep Impact'' mission was the first to eject material from a comet's surface, and the mission garnered considerabl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
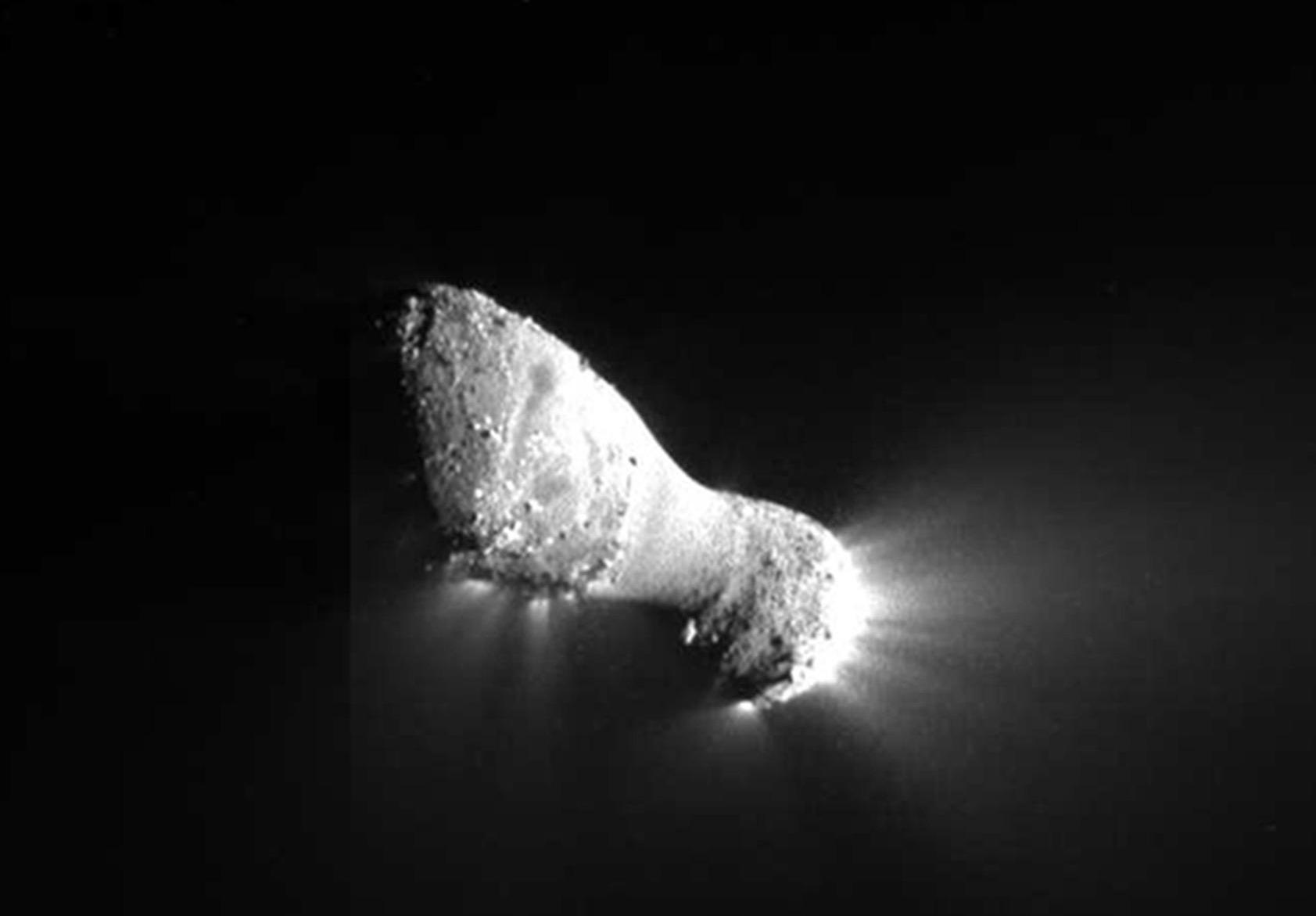
Tempel 1
Tempel 1 (official designation: 9P/Tempel) is a periodic Jupiter-family comet discovered by Wilhelm Tempel in 1867. It completes an orbit of the Sun every 5.5 years. Tempel 1 was the target of the ''Deep Impact'' space mission, which photographed a deliberate high-speed impact upon the comet in 2005. It was re-visited by the ''Stardust'' spacecraft on February 14, 2011 and came back to perihelion in August 2016. Discovery and orbital history Tempel 1 was discovered on April 3, 1867, by Wilhelm Tempel, who was working at Marseille. At the time of discovery, it approached perihelion once every 5.68 years (designations 9P/1867 G1 and 1867 II). It was subsequently observed in 1873 (9P/1873 G1, 1873 I, 1873a) and in 1879 (1879 III, 1879b). Photographic attempts during 1898 and 1905 failed to recover the comet, and astronomers surmised that it had disintegrated, when in reality, its orbit had changed. Tempel 1's orbit occasionally brings it sufficiently close to Jupiter to be alte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Space Probe
A space probe is an artificial satellite that travels through space to collect scientific data. A space probe may orbit Earth; approach the Moon; travel through interplanetary space; flyby, orbit, or land or fly on other planetary bodies; or enter interstellar space. Many countries and private companies have launched probes to planets, asteroids, moons around the Solar System, including the Soviet Union, the United States, India, and many more. History On 4 October 1957, the first artificial satellite to orbit Earth was Sputnik 1, launched by the USSR. Four months later, on 1 February 1958, Explorer 1 was launched by the United States, being the first space probe. Explorer 1, collecting data on temperature, cosmic rays, and micrometeorite impacts. The first attempted lunar probe was the Luna E-1 No.1, launched on 23 September 1958. The goal of a lunar probe repeatedly failed until 4 January 1959 when Luna 1 orbited around the moon and then the sun. The success of these ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cornell University
Cornell University is a private statutory land-grant research university based in Ithaca, New York. It is a member of the Ivy League. Founded in 1865 by Ezra Cornell and Andrew Dickson White, Cornell was founded with the intention to teach and make contributions in all fields of knowledge—from the classics to the sciences, and from the theoretical to the applied. These ideals, unconventional for the time, are captured in Cornell's founding principle, a popular 1868 quotation from founder Ezra Cornell: "I would found an institution where any person can find instruction in any study." Cornell is ranked among the top global universities. The university is organized into seven undergraduate colleges and seven graduate divisions at its main Ithaca campus, with each college and division defining its specific admission standards and academic programs in near autonomy. The university also administers three satellite campuses, two in New York City and one in Education City, Qatar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Michael A'Hearn
Michael Francis A'Hearn (November 17, 1940 – May 29, 2017) was an American astronomer and astronomy professor at the University of Maryland College of Computer, Mathematical, and Natural Sciences. He was also the principal investigator for NASA's EPOXI mission. Career He received his B.A. in science at Boston College and his Ph.D. in Astronomy at the University of Wisconsin–Madison. He was the principal investigator for the NASA '' Deep Impact'' mission. He aided in the development of systems for surveying abundances in comets as well as techniques for determining the sizes of cometary nuclei which uses optical and infrared measurements. His studies focused on comets as well as asteroids and he also supervises numerous graduate students. He was an elected fellow of the AAAS. He authored over 100 papers published in journals and was also an avid sailor who had a commercial coast guard license. In June 1986, the main-belt asteroid 3192 A'Hearn, discovered by American astr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
103P/Hartley
Comet Hartley 2, designated as 103P/Hartley by the Minor Planet Center, is a small periodic comet with an orbital period of 6.46 years. It was discovered by Malcolm Hartley in 1986 at the Schmidt Telescope Unit, Siding Spring Observatory, Australia. Its diameter is estimated to be . Hartley 2 was the target of a flyby of the Deep Impact spacecraft, as part of the EPOXI mission, on 4 November 2010, which was able to approach within of Hartley 2 as part of its extended mission. Hartley 2 is the smallest comet which has been visited. It is the fifth comet visited by spacecraft, and the second comet visited by the Deep Impact spacecraft, which first visited comet Tempel 1 on 4 July 2005. Discovery and orbit Comet Hartley 2 is a small Jupiter-family comet having an orbital period of 6.46 years. It was discovered by Malcolm Hartley in 1986 at the Schmidt Telescope Unit, Siding Spring Observatory, Australia. It has the perihelion near the Earth's orbit at 1.05 AU from the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Extrasolar Planet
An exoplanet or extrasolar planet is a planet outside the Solar System. The first possible evidence of an exoplanet was noted in 1917 but was not recognized as such. The first confirmation of detection occurred in 1992. A different planet, initially detected in 1988, was confirmed in 2003. There are many methods of detecting exoplanets. Transit (astronomy), Transit photometry and Doppler spectroscopy have found the most, but these methods suffer from a clear observational bias favoring the detection of planets near the star; thus, 85% of the exoplanets detected are inside the tidal locking zone. In several cases, List of multiplanetary systems, multiple planets have been observed around a star. About 1 in 5 Solar analog, Sun-like starsFor the purpose of this 1 in 5 statistic, "Sun-like" means G-type star. Data for Sun-like stars was not available so this statistic is an extrapolation from data about K-type star, K-type stars. have an "Earth-sized"For the purpose of this 1 in 5 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
EPOXI
''EPOXI'' was a compilation of NASA Discovery program missions led by the University of Maryland and principal investigator Michael A'Hearn, with co-operation from the Jet Propulsion Laboratory and Ball Aerospace. ''EPOXI'' uses the '' Deep Impact'' spacecraft in a campaign consisting of two missions: the ''Deep Impact Extended Investigation'' (DIXI) and ''Extrasolar Planet Observation and Characterization'' (EPOCh). ''DIXI'' aimed to send the ''Deep Impact'' spacecraft on a flyby of another comet, after its primary mission was completed in July 2005, while ''EPOCh'' saw the spacecraft's photographic instruments as a space observatory, studying extrasolar planets. ''DIXI'' successfully sent the ''Deep Impact'' spacecraft on a flyby of comet Hartley 2 on November 4, 2010, revealing a "hyperactive, small and feisty" comet, after three gravity assists from Earth in December 2007, December 2008 and June 2010. The ''DIXI'' mission was not without problems, however; the spacecraft ha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flyby (spaceflight)
A flyby () is a spaceflight operation in which a spacecraft passes in proximity to another body, usually a target of its space exploration mission and/or a source of a gravity assist to impel it towards another target. Spacecraft which are specifically designed for this purpose are known as flyby spacecraft, although the term has also been used in regard to asteroid flybys of Earth for example. Important parameters are the time and distance of closest approach. Spacecraft flyby Flyby maneuvers can be conducted with a planet, a natural satellite or a non-planetary object such as a small Solar System body. Planetary flybys have occurred with Mars or Earth for example: *List of Earth flybys * Mars flyby An example of a comet flyby is when International Cometary Explorer (formerly ISEE-3) passed about from the nucleus of Comet Giacobini-Zinner in September 1985. Another application of the flyby is of Earth's Moon, usually called a lunar flyby. The Apollo 13 spacecraft had an exp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stardust (spacecraft)
''Stardust'' was a 385-kilogram robotic space probe launched by NASA on 7 February 1999. Its primary mission was to collect dust samples from the coma of comet Wild 2, as well as samples of cosmic dust, and return them to Earth for analysis. It was the first sample return mission of its kind. En route to comet Wild 2, it also flew by and studied the asteroid 5535 Annefrank. The primary mission was successfully completed on 15 January 2006 when the sample return capsule returned to Earth. A mission extension, codenamed ''NExT'', culminated in February 2011 with ''Stardust'' intercepting comet Tempel 1, a small Solar System body previously visited by '' Deep Impact'' in 2005. ''Stardust'' ceased operations in March 2011. On 14 August 2014, scientists announced the identification of possible interstellar dust particles from the ''Stardust'' capsule returned to Earth in 2006. Mission background History Beginning in the 1980s, scientists began seeking a dedicated mis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deep Space 1
''Deep Space 1'' (DS1) was a NASA technology demonstration spacecraft which flew by an asteroid and a comet. It was part of the New Millennium Program, dedicated to testing advanced technologies. Launched on 24 October 1998, the ''Deep Space 1'' spacecraft carried out a flyby of asteroid 9969 Braille, which was its primary science target. The mission was extended twice to include an encounter with comet 19P/Borrelly and further engineering testing. Problems during its initial stages and with its star tracker led to repeated changes in mission configuration. While the flyby of the asteroid was only a partial success, the encounter with the comet retrieved valuable information. The Deep Space series was continued by the ''Deep Space 2'' probes, which were launched in January 1999 piggybacked on the Mars Polar Lander and were intended to strike the surface of Mars (though contact was lost and the mission failed). ''Deep Space 1'' was the first NASA spacecraft to use ion thruster, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Giotto Mission
''Giotto'' was a European robotic spacecraft mission from the European Space Agency. The spacecraft flew by and studied Halley's Comet and in doing so became the first spacecraft to make close up observations of a comet. On 13 March 1986, the spacecraft succeeded in approaching Halley's nucleus at a distance of 596 kilometers. It was named after the Early Italian Renaissance painter Giotto di Bondone. He had observed Halley's Comet in 1301 and was inspired to depict it as the star of Bethlehem in his painting ''Adoration of the Magi'' in the Scrovegni Chapel. Mission Originally a United States partner probe was planned that would accompany ''Giotto'', but this fell through due to budget cuts at NASA. There were plans to have observation equipment on board a Space Shuttle in low-Earth orbit around the time of ''Giotto''s fly-by, but they in turn fell through with the ''Challenger'' disaster. The plan then became a cooperative armada of five space probes including ''Giotto'', ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Impact Crater
An impact crater is a circular depression in the surface of a solid astronomical object formed by the hypervelocity impact of a smaller object. In contrast to volcanic craters, which result from explosion or internal collapse, impact craters typically have raised rims and floors that are lower in elevation than the surrounding terrain. Lunar impact craters range from microscopic craters on lunar rocks returned by the Apollo Program and small, simple, bowl-shaped depressions in the lunar regolith to large, complex, multi-ringed impact basins. Meteor Crater is a well-known example of a small impact crater on Earth. Impact craters are the dominant geographic features on many solid Solar System objects including the Moon, Mercury, Callisto, Ganymede and most small moons and asteroids. On other planets and moons that experience more active surface geological processes, such as Earth, Venus, Europa, Io and Titan, visible impact craters are less common because they become eroded ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |





.png)