|
Deborah Lincoln
According to the Book of Judges, Deborah ( he, דְּבוֹרָה, ''Dəḇōrā'', "bee") was a prophetess of the God of the Israelites, the fourth Judge of pre-monarchic Israel and the only female judge mentioned in the Bible. Many scholars contend that the phrase, "a woman of Lappidot", as translated from biblical Hebrew in Judges 4:4 denotes her marital status as the wife of Lappidot.Van Wijk-Bos, Johanna WH. ''The End of the Beginning: Joshua and Judges''. Wm. B. Eerdmans Publishing, 2019. Alternatively, "lappid" translates as "torch" or "lightning", therefore the phrase, "woman of Lappidot" could be referencing Deborah as a "fiery woman." Deborah told Barak, an Israelite general from Kedesh in Naphtali, that God commanded him to lead an attack against the forces of Jabin king of Canaan and his military commander Sisera (Judges 4:6–7); the entire narrative is recounted in chapter 4. Judges chapter 5 gives the same story in poetic form. This passage, often called ''The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Promptuarii Iconum Insigniorum
''Promptuarium Iconum Insigniorum'' (full title: ''Prima pars Promptuarii iconum insigniorum à seculo hominum, subiectis eorum vitis, per compendium ex probatissimis autoribus desumptis''; ) is an iconography book by Guillaume Rouillé. Its title means ‘wikt:promptuary, Promptuary (Handbook) of the Images of the Renowned [People]’. History It was published in Lyon, France, in 1553. The work includes portraits designed as medals, and brief biographies of many notable figures. Although Julian Sharman, author of ''The Library of Mary Queen of Scots'', judges the work to be "not one of much numismatic interest", he notes that, "This work has been pronounced to be one of the marvels of early wood-engraving." The book includes a total of 950 woodcut portraits. Many of the figures portrayed are of English origin. The images begin with Adam and Eve. In the preface, the publisher praises the work."''Abhandlungen Der Königlich Preussischen Akademie Der Wissenschaften, Philosophisch-H ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biblical Poetry
The ancient Hebrews identified poetical portions in their sacred texts, as shown by their entitling as "songs" or as " chants" passages such as Exodus 15:1-19 and Numbers 21:17-20; a song or chant () is, according to the primary meaning of the term, poetry. The question as to whether the poetical passages of the Old Testament show signs of regular rhythm or meter remains unsolved. Many of the features of Biblical poetry are lost when the poems are translated to English. Characteristics of Ancient Hebrew poetry Unusual forms The employment of unusual forms of language cannot be considered as a sign of ancient Hebrew poetry. In and elsewhere the form occurs. But this form, which represents partly and partly , has many counterparts in Hebrew grammar, as, for example, instead of ; or = "them"; or = "their"; or = "to them"—forms found in passages for which no claim to poetical expressions is made. Then there are found = "beast", = "tying", and = "salvation"—th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Barnabas Lindars
Barnabas Lindars (born Frederick Chevallier Lindars; 1923–1991) was an English New Testament scholar. Born 11 June 1923, Lindars was educated at Altrincham Grammar School and then studied at St John's College, Cambridge. He was ordained as an Anglican priest in 1949. After teaching at the University of Cambridge (where he was Dean of Jesus College), Lindars served as Rylands Professor of Biblical Criticism and Exegesis at the University of Manchester from 1978 to 1990. In 1988, ''It Is Written: Scripture Citing Scripture: Essays in Honour of Barnabas Lindars, SSF'' was published. It included contributions from C. K. Barrett, Richard Bauckham Richard John Bauckham (born 22 September 1946) is an English Anglican scholar in theology, historical theology and New Testament studies, specialising in New Testament Christology and the Gospel of John. He is a senior scholar at Ridley Hall, ..., G. K. Beale, D. A. Carson, R. E. Clements, and Morna D. Hoo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alberto Soggin
Jan Alberto Soggin (10 March 192627 October 2010) was a leading Italian biblical scholar. Early life Soggin was born on 10 March 1926. He took his first degrees in law at the Sapienza University of Rome and in theology at the Waldensian Theological Seminary in Rome. Academic career He became professor for Old Testament, Hebrew, and Greek at the University of Buenos Aires, the Hebrew University of Jerusalem and then until his retirement at the Waldensian Theological Seminary and at the Sapienza. Among other things he was a fellow at Princeton Theological Seminary, at St John's College, Cambridge and at the Hebrew University. He lectured widely and published various articles and books. He was a member of the editorial board of '' Henoch'', ''Vetus Testamentum'' and of '' Zeitschrift für die Alttestamentliche Wissenschaft''. In 2007, he was awarded the Burkitt Medal by the British Academy The British Academy is the United Kingdom's national academy for the humanities and th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hymn
A hymn is a type of song, and partially synonymous with devotional song, specifically written for the purpose of adoration or prayer, and typically addressed to a deity or deities, or to a prominent figure or personification. The word ''hymn'' derives from Greek (''hymnos''), which means "a song of praise". A writer of hymns is known as a hymnist. The singing or composition of hymns is called hymnody. Collections of hymns are known as hymnals or hymn books. Hymns may or may not include instrumental accompaniment. Although most familiar to speakers of English in the context of Christianity, hymns are also a fixture of other world religions, especially on the Indian subcontinent (''stotras''). Hymns also survive from antiquity, especially from Egyptian and Greek cultures. Some of the oldest surviving examples of notated music are hymns with Greek texts. Origins Ancient Eastern hymns include the Egyptian ''Great Hymn to the Aten'', composed by Pharaoh Akhenaten; the Hurrian ''Hy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jael
Jael or Yael ( he, יָעֵל ''Yāʿēl'') is the name of the heroine who delivered Israel from the army of King Jabin of Canaan in the Book of Judges of the Hebrew Bible. After Barak demurred at the behest of the prophetess Deborah, God turned Sisera over to Jael, who killed him by driving a tent peg through his skull after he entered her tent near the great tree in Zaanannim near Kedesh. Name The Hebrew ''ya'el'' means ibex, a nimble, sure-footed mountain goat native to that region. It literally translates to "he shall ascend or go up". As of 2016, ''Yael'' was one of the most common female first names in contemporary Israel. Family Jael has often been understood to be the wife of Heber the Kenite.Frymer-Kensky, Tikva. "Jael: ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Harosheth Haggoyim
Harosheth Haggoyim ( he, חרושת הגויים, lit. ''Smithy of the Nations'') is a fortress described in the Book of Judges as the fortress or cavalry base of Sisera, commander of the army of "Jabin, King of Canaan". Sisera is described as having had nine hundred iron chariots with which he fought the Israelites. In Judges 5, the mother of Sisera is poignantly described looking from a window, presumably in Harosheth Haggoyim, and asking ''"Why is his chariot so long in coming? Why is the clatter of his chariots delayed?"'' when he does not return from the battle where his army was defeated by the Israelites, and he was killed by the Biblical heroine Yael. Modern identifications Hariss in Lebanon In the late 19th century, Victor Guérin identified the southern Lebanese village of Hariss with Harosheth, a location with which the PEF's ''Survey of Western Palestine'' seems to agree.Conder and Kitchener, 1881, ''Survey of Western Palestine I'', pp96a116/ref> El-Ahwat in Isr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tel Hazor
Tel Hazor ( he, תל חצור), also Chatsôr ( he, חָצוֹר), translated in LXX as Hasōr ( grc, Άσώρ), identified at Tell Waqqas / Tell Qedah el-Gul ( ar, تل القدح, Tell el-Qedah), is an archaeological tell at the site of ancient Hazor, located in Israel, Upper Galilee, north of the Sea of Galilee, in the northern Korazim Plateau. In the Middle Bronze Age (around 1750 BCE) and the Israelite period (ninth century BCE), Hazor was the largest fortified city in the country and one of the most important in the Fertile Crescent. It maintained commercial ties with Babylon and Syria, and imported large quantities of tin for the bronze industry. In the Book of Joshua, Hazor is described as “the head of all those kingdoms” (Josh. 11:10). Though some scholars do not consider the Book of Joshua to be historically accurate,Killebrew, Ann E., (2005)Biblical Peoples and Ethnicity: An Archaeological Study of Egyptians, Canaanites, and Early Israel, 1300-1100 B.C.E. So ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
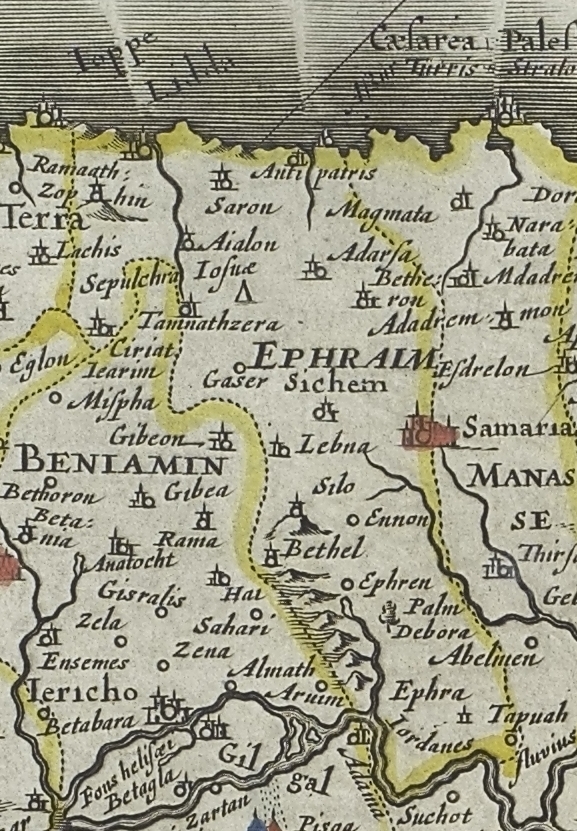
Tribe Of Ephraim
According to the Hebrew Bible, the Tribe of Ephraim ( he, אֶפְרַיִם, ''ʾEp̄rayīm,'' in pausa: אֶפְרָיִם, ''ʾEp̄rāyīm'') was one of the tribes of Israel. The Tribe of Manasseh together with Ephraim formed the ''House of Joseph''. It is one of the ten lost tribes. The etymology of the name is disputed.For the etymology, see Ephraim as portrayed in biblical narrative According to the Bible, the Tribe of Ephraim is descended from a man named Ephraim, who is recorded as the son of Joseph, the son of Jacob, and Asenath, the daughter of Potiphera. The descendants of Joseph formed two of the tribes of Israel, whereas the other sons of Jacob were the founders of one tribe each. The Bible records that the Tribe of Ephraim entered the land of Canaan during its conquest by Joshua, a descendant of Ephraim himself. However, many archeologists have abandoned the idea that Joshua carried out a conquest of Canaan similar to that described in the Book of Joshua, seein ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bethel
Bethel ( he, בֵּית אֵל, translit=Bēṯ 'Ēl, "House of El" or "House of God",Bleeker and Widegren, 1988, p. 257. also transliterated ''Beth El'', ''Beth-El'', ''Beit El''; el, Βαιθήλ; la, Bethel) was an ancient Israelite sanctuary frequently mentioned in the Hebrew Bible. Bethel is first referred to in the bible as being near where Abram pitched his tent. Later, Bethel is mentioned as the location where Jacob dreams of a ladder leading to heaven, and which he therefore named Bethel, "House of God". The name is further used for a border city located between the territory of the Israelite tribe of Benjamin and that of the tribe of Ephraim, which first belonged to the Benjaminites and was later conquered by the Ephraimites. In the 4th century CE, Eusebius of Caesarea and Jerome described Bethel as a small village that lay 12 Roman miles north of Jerusalem, to the right or east of the road leading to Neapolis.Robinson and Smith, 1856, pp. 449–450. Most schola ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ramah In Benjamin
Ramah (from Hebrew: "height") was, according to the Hebrew Bible, a city in ancient Israel in the land allocated to the tribe of Benjamin. It was located near Gibeon and Mizpah to the West, Gibeah to the South, and Geba to the East. It has been identified with modern Er-Ram, about north of Jerusalem. Biblical accounts The city is first mentioned in , near Gibeah of Benjamin. In the Book of Judges, a Levite came traveling to Gibeah, with Ramah just ahead (). Ramathaim-zophim is the town that was home to Samuel's mother Hannah and his father Elkanah, from which they journeyed to the sanctuary at Shiloh, where Hannah prayed to God to end her barrenness and give her a child (). Ramah is mentioned in in reference to a meeting place during Samuel's rule. Ramah was later fortified by Baasha, king of the northern kingdom, in order to control access to Jerusalem (; ). Asa, king of the southern kingdom of Judah, employed Ben-Hadad I, the Syrian king, successfully to attack Ba ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
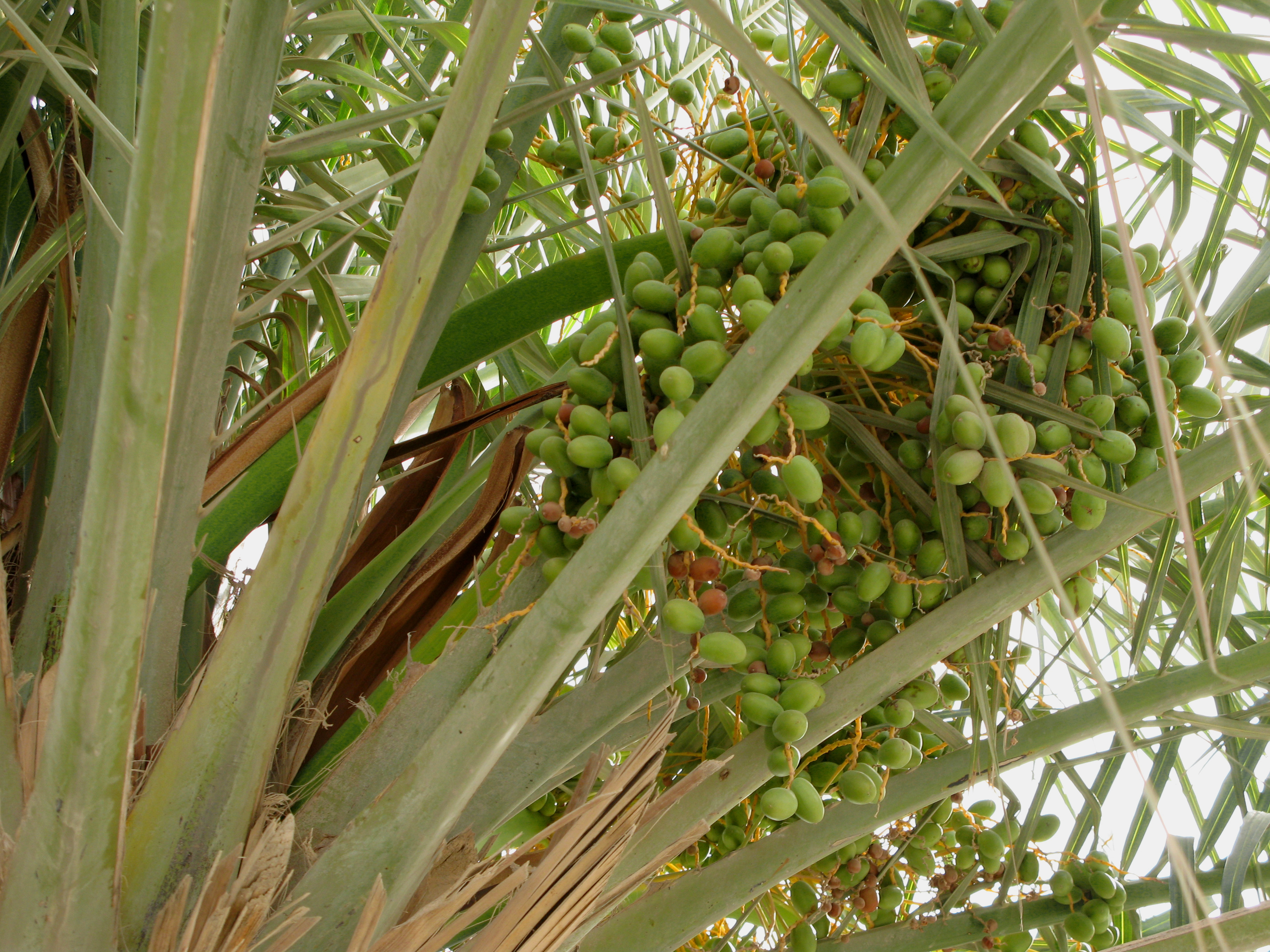
Date Palm
''Phoenix dactylifera'', commonly known as date or date palm, is a flowering plant species in the palm family, Arecaceae, cultivated for its edible sweet fruit called dates. The species is widely cultivated across northern Africa, the Middle East, and South Asia, and is naturalized in many tropical and subtropical regions worldwide. ''P. dactylifera'' is the type species of genus ''Phoenix'', which contains 12–19 species of wild date palms. Date trees reach up to in height, growing singly or forming a clump with several stems from a single root system. Slow-growing, they can reach over 100 years of age when maintained properly. Date fruits (dates) are oval-cylindrical, long, and about in diameter, with colour ranging from dark brown to bright red or yellow, depending on variety. Containing 61–68 percent sugar by mass when dried, dates are very sweet and are enjoyed as desserts on their own or within confections. Dates have been cultivated in the Middle East and the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |