|
Death-inducing Signaling Complex
The death-inducing signaling complex (DISC) is a multiprotein complex formed by members of the death receptor family of apoptosis-inducing cellular receptors. A typical example is FasR, which forms the DISC upon trimerization as a result of its ligand ( FasL) binding. The DISC is composed of the death receptor, FADD, and caspase 8. It transduces a downstream signal cascade resulting in apoptosis. Description The Fas ligands, or cytotoxicity-dependent APO-1-associated proteins, physically associate with APO-1 (also known as the Fas receptor, or CD95), a tumor necrosis factor containing a functional death domain. This association leads to the formation of the DISC, thereby inducing apoptosis. The entire process is initiated when the cell registers the presence of CD95L, the cognate ligand for APO-1. Upon binding, the CAP proteins and procaspase-8 (composed of FLICE, MACH, and Mch5) bind to CD95 through death domain and death effector domain interactions. Procaspase-8 activa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fas Signaling
Fas or FAS may refer to: Places * Fez, Morocco, alternate spelling * Poti, Georgia, a port city in Georgia Businesses * Federation Air Service, a former Malaysian regional airliner * Fiat Automobili Srbija, Serbian automobile manufacturer * Film Authors' Studio, Croatia Organizations In research and academia * Faculty of Arts and Sciences (other), of several universities * Federation of American Scientists * Federation of Astronomical Societies (mainly UK) In sport * Football Association of Singapore * Club Deportivo FAS, a Salvadoran football club Other organizations * Federal Antimonopoly Service, Russia * '' Femmes Africa Solidarité'', an NGO founded in 1996 * ''FÁS'' former training and employment authority of Ireland * Foreign Agricultural Service, US * Salvadoran Air Force (Spanish: ''Fuerza Aérea Salvadoreña'') In science and technology In biology and medicine * Fas receptor or CD95, a receptor protein * Fatty acid synthase, an enzyme * Fetal alcohol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
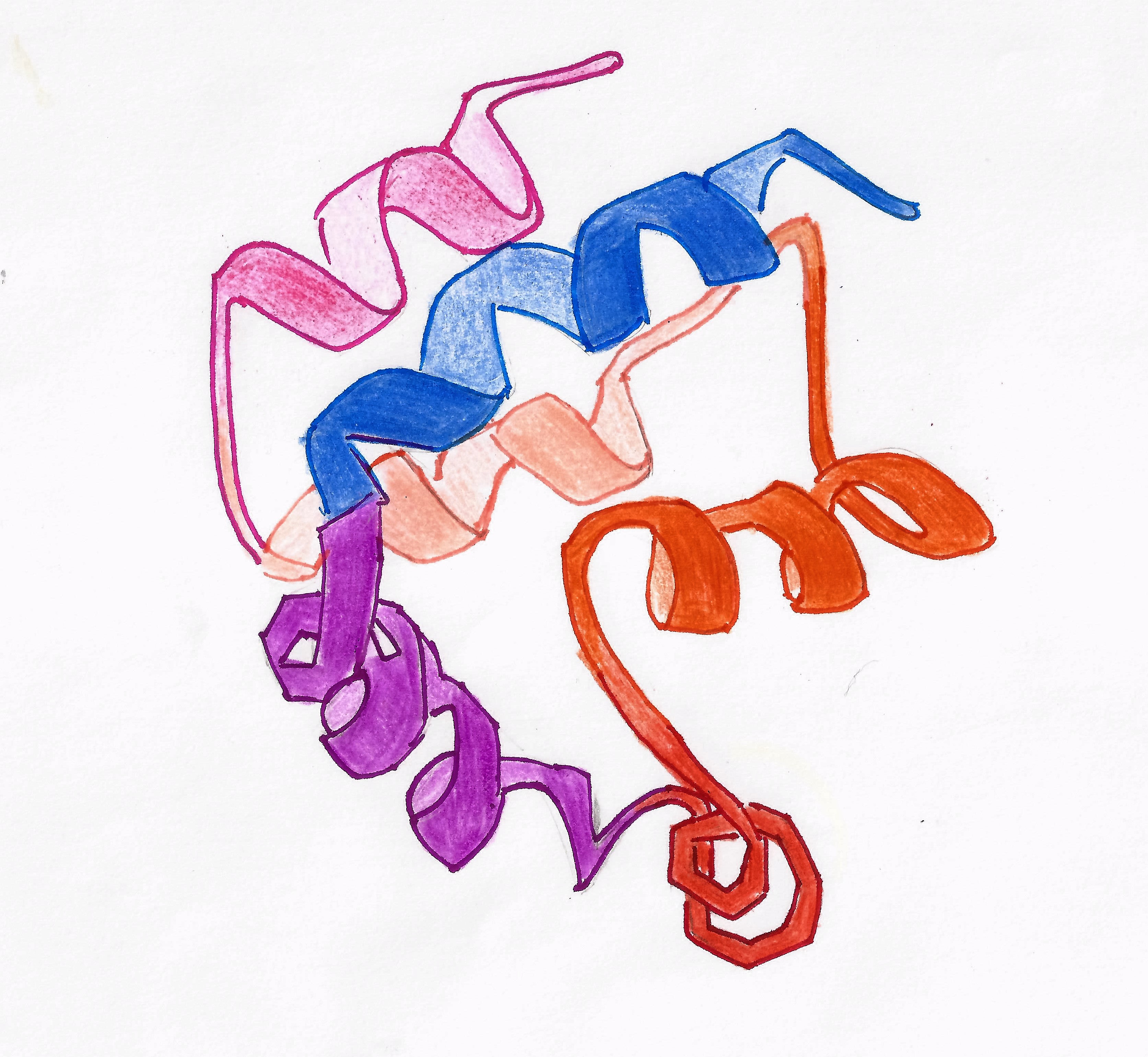
Death Effector Domain
The death-effector domain (DED) is a protein interaction domain found only in eukaryotes that regulates a variety of cellular signalling pathways. The DED domain is found in inactive procaspases (cysteine proteases) and proteins that regulate caspase activation in the apoptosis cascade such as FAS-associating death domain-containing protein (FADD). FADD recruits procaspase 8 and procaspase 10 into a death induced signaling complex (DISC). This recruitment is mediated by a homotypic interaction between the procaspase DED and a second DED that is death effector domain in an Signal transducing adaptor protein, adaptor protein that is directly associated with activated TNF receptors. Complex formation allows proteolytic activation of procaspase into the active caspase form which results in the initiation of apoptosis (cell death). Structurally the DED domain are a subclass of protein motif known as the death fold and contains 6 alpha helices, that closely resemble the structure of the D ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Death Receptor 5
Death receptor 5 (DR5), also known as TRAIL receptor 2 (TRAILR2) and tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily member 10B (TNFRSF10B), is a cell surface receptor of the TNF-receptor superfamily that binds TRAIL and mediates apoptosis. Function The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the TNF-receptor superfamily, and contains an intracellular death domain. This receptor can be activated by tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis inducing ligand (TNFSF10/TRAIL/APO-2L), and transduces apoptosis signal. Mice have a homologous gene, tnfrsf10b, that has been essential in the elucidation of the function of this gene in humans. Studies with FADD-deficient mice suggested that FADD, a death domain containing adaptor protein, is required for the apoptosis mediated by this protein. Interactions DR5 has been shown to interact with: * Caspase 8, * Caspase 10, * FADD, and * TRAIL. Cancer therapy Monoclonal antibodies targeting DR5 have been developed and are currently unde ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Death Receptor 4
Death receptor 4 (DR4), also known as TRAIL receptor 1 (TRAILR1) and tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily member 10A (TNFRSF10A), is a cell surface receptor of the TNF-receptor superfamily that binds TRAIL and mediates apoptosis. Function The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the TNF-receptor superfamily. This receptor is activated by tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis inducing ligand (TNFSF10/TRAIL), and thus transduces cell death signal and induces cell apoptosis. Studies with FADD-deficient mice suggested that FADD FAS-associated death domain protein, also called MORT1, is encoded by the ''FADD'' gene on the 11q13.3 region of chromosome 11 in humans. FADD is an Signal transducing adaptor protein, adaptor protein that bridges members of the Tumor necrosi ..., a death domain containing adaptor protein, is required for the apoptosis mediated by this protein. Interactions TNFRSF10A has been shown to interact with DAP3. References Further readin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
TRAIL
A trail, also known as a path or track, is an unpaved lane or a small paved road (though it can also be a route along a navigable waterways) generally not intended for usage by motorized vehicles, usually passing through a natural area. However, it is sometimes applied to highways in North America. In the United Kingdom and Ireland, a path or footpath is the preferred term for a pedestrian or hiking trail. In the US, the term was historically used for a route into or through wild territory used by explorers and migrants (e.g. the Oregon Trail). In the United States, "trace" is a synonym for trail, as in Natchez Trace. Some trails are restricted to use by only walkers, or cyclists, or equestrians, or for snowshoeing, or cross-country skiing, others, for example bridleways in the UK, are shared, and can be used by walkers, cyclists and equestrians. Although most ban motorized use, there are unpaved trails used by dirt bikes, quad bikes and other off-road vehicles, u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DNA-PKcs
DNA-dependent protein kinase catalytic subunit, also known as DNA-PKcs, is an enzyme that plays a crucial role in repairing DNA double-strand breaks and has a number of other DNA housekeeping functions. In humans it is encoded by the gene designated as ''PRKDC'' or ''XRCC7''. DNA-PKcs belongs to the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase-related kinase protein family. The DNA-Pkcs protein is a serine/threonine protein kinase consisting of a single polypeptide chain of 4,128 amino acids. Function DNA-PKcs is the catalytic subunit of a nuclear DNA-dependent serine/threonine protein kinase called DNA-PK. The second component is the autoimmune antigen Ku. On its own, DNA-PKcs is inactive and relies on Ku to direct it to DNA ends and trigger its kinase activity. DNA-PKcs is required for the non-homologous end joining (NHEJ) pathway of DNA repair, which rejoins double-strand breaks. It is also required for V(D)J recombination, a process that utilizes NHEJ to promote immune system diversit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CrmA
{{disambig ...
CRMA may refer to: * Critical Raw Materials Act * City and Regional Magazine Association * Chulachomklao Royal Military Academy * Civil Rights Movement Archive * Canadian Radio Music Awards The Canadian Radio Music Awards is an annual series of awards presented by the Canadian Association of Broadcasters that was part of Canadian Music Week The Departure Festival + Conference, formerly known as Canadian Music Week, is an industr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
FLICE
Caspase-8 is a caspase protein, encoded by the ''CASP8'' gene. It most likely acts upon caspase-3. ''CASP8'' orthologs have been identified in numerous mammals for which complete genome data are available. These unique orthologs are also present in birds. Function The ''CASP8'' gene encodes a member of the cysteine-aspartic acid protease (caspase) family. Sequential activation of caspases plays a central role in the execution-phase of cell apoptosis. Caspases exist as inactive proenzymes composed of a prodomain, a large protease subunit, and a small protease subunit. Activation of caspases requires proteolytic processing at conserved internal aspartic residues to generate a heterodimeric enzyme consisting of the large and small subunits. This protein is involved in the programmed cell death induced by Fas and various apoptotic stimuli. The N-terminal FADD-like death effector domain of this protein suggests that it may interact with Fas-interacting protein FADD. This protein ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cysteine Protease
Cysteine proteases, also known as thiol proteases, are hydrolase enzymes that degrade proteins. These proteases share a common catalytic mechanism that involves a nucleophilic cysteine thiol in a catalytic triad or dyad. Discovered by Gopal Chunder Roy in 1873, the first cysteine protease to be isolated and characterized was papain, obtained from ''Carica papaya''. Cysteine proteases are commonly encountered in fruits including the papaya, pineapple, fig and kiwifruit. The proportion of protease tends to be higher when the fruit is unripe. In fact, the latex of dozens of different plant families are known to contain cysteine proteases. Cysteine proteases are used as an ingredient in meat tenderizers. Classification The MEROPS protease classification system counts 14 superfamilies plus several currently unassigned families (as of 2013) each containing many families. Each superfamily uses the catalytic triad or dyad in a different protein fold and so represent convergent evo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oligomer
In chemistry and biochemistry, an oligomer () is a molecule that consists of a few repeating units which could be derived, actually or conceptually, from smaller molecules, monomers.Quote: ''Oligomer molecule: A molecule of intermediate relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises a small plurality of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of lower relative molecular mass.'' The name is composed of Greek elements '' oligo-'', "a few" and '' -mer'', "parts". An adjective form is ''oligomeric''. The oligomer concept is contrasted to that of a polymer, which is usually understood to have a large number of units, possibly thousands or millions. However, there is no sharp distinction between these two concepts. One proposed criterion is whether the molecule's properties vary significantly with the removal of one or a few of the units. An oligomer with a specific number of units is referred to by the Greek prefix denoting that number, w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dimer (chemistry)
In chemistry, dimerization is the process of joining two identical or similar Molecular entity, molecular entities by Chemical bond, bonds. The resulting bonds can be either strong or weak. Many symmetrical chemical species are described as dimers, even when the monomer is unknown or highly unstable. The term ''homodimer'' is used when the two subunits are identical (e.g. A–A) and ''heterodimer'' when they are not (e.g. A–B). The reverse of dimerization is often called Dissociation (chemistry), dissociation. When two oppositely-charged ions associate into dimers, they are referred to as ''Bjerrum pairs'', after Danish chemist Niels Bjerrum. Noncovalent dimers Anhydrous carboxylic acids form dimers by hydrogen bonding of the acidic hydrogen and the carbonyl oxygen. For example, acetic acid forms a dimer in the gas phase, where the monomer units are held together by hydrogen bonds. Many OH-containing molecules form dimers, e.g. the water dimer. Dimers that form based on w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Death Domain
The death domain (DD) is a protein interaction module composed of a bundle of six alpha helix, alpha-helices. DD is a subclass of protein structural motif , motif known as the death fold and is related in sequence and structure to the death effector domain (death effector domain, DED) and the caspase recruitment domain (CARD domain, CARD), which work in similar pathways and show similar interaction properties. DD bind each other forming oligomers. Mammals have numerous and diverse DD-containing proteins. Within these proteins, the DD domains can be found in combination with other domains, including: CARDs, DEDs, ankyrin repeats, caspase-like folds, kinase domains, leucine zippers, leucine-rich repeats (LRR), TIR domains, and ZU5 domains. Some DD-containing proteins are involved in the regulation of apoptosis and inflammation through their activation of caspases and NF-κB, which typically involves interactions with tumor necrosis factor, TNF (tumour necrosis factor) cytokine recepto ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |