|
Deansgrange
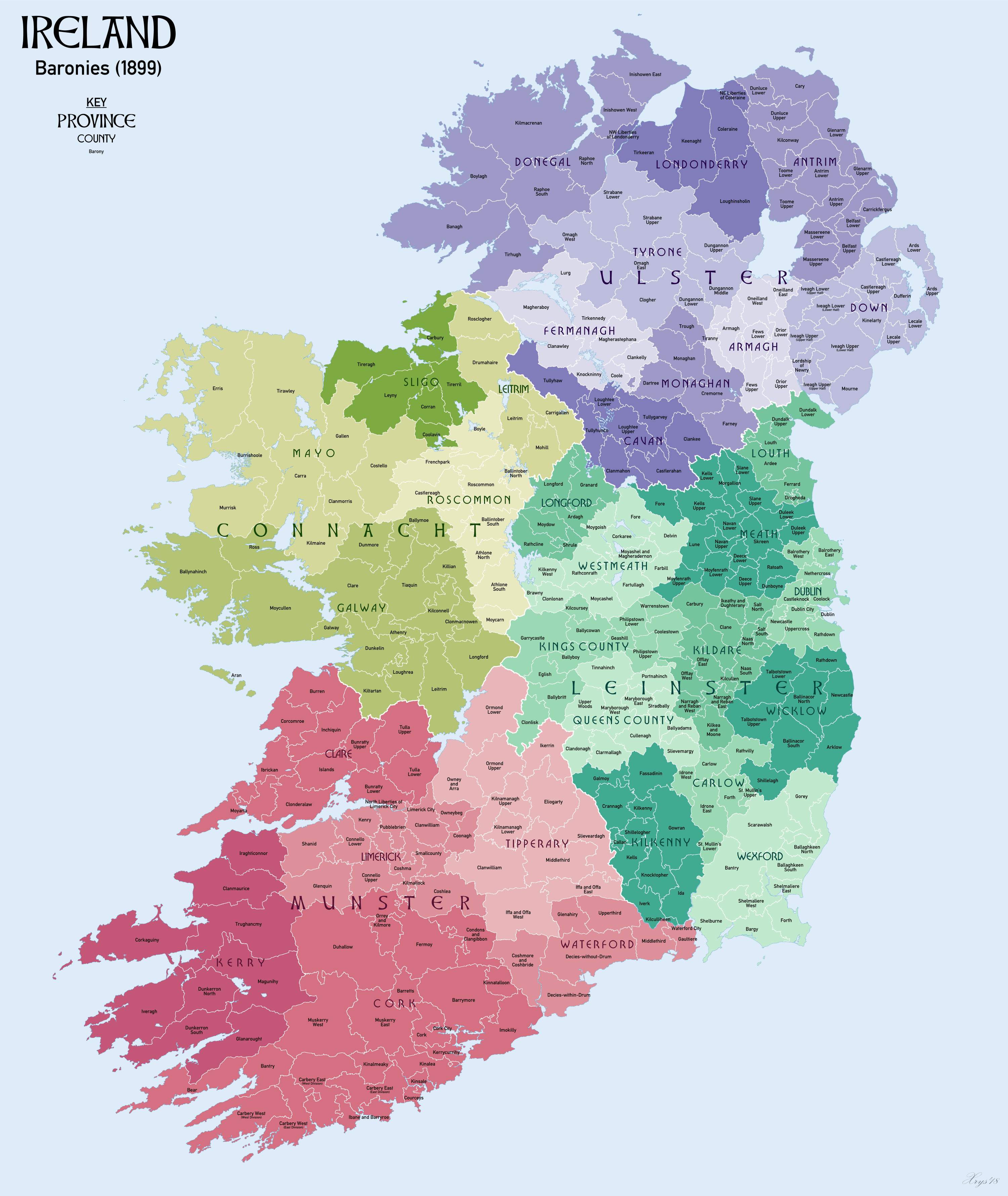
Deansgrange () is a southern suburb of Dublin, centred on the crossroads of Clonkeen Road and Kill Lane. The area shares the name Clonkeen () with the area further east, known as Kill of the Grange (i.e. "Church of the Grange of ": referring to Grange Church (now in ruins)). History and etymology Since early medieval times the area was owned by the Augustinians, and used as a grange, giving rise to the medieval civil parish of Kill, in the half-barony of Rathdown. The Ordnance Survey Ireland map 1837–1842 shows a "Grange Church" (now in ruins, the modern housing estate surrounding it is called ''Kill Abbey''), "Kill Abbey" (still existing), "Grange House" (demolished with the building of the ''South Park'' estate), and "Glebe House" (still existing). Deansgrange was a townland of Kill Parish. Presumably the dean of the grange lived in ''Grange House'', and so the area became known as "the Dean's Grange", and then simply, Deansgrange. Geography The crossroads are the comme ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deans Grange Cemetery
Deans Grange Cemetery (; also spelled ''Deansgrange'') is situated in the suburban area of Deansgrange in the Dún Laoghaire–Rathdown part of the former County Dublin, Ireland. Since it first opened in 1865, over 150,000 people have been buried there. It is, together with Glasnevin and Mount Jerome, one of the largest cemeteries in the Dublin area, occupying . History The Burial Act of 1855 resulted in the closure of many of the older churchyards in Dublin and its environs due to overcrowding. This drove the need to find new lands for cemeteries.Igoe, Vivien (2001). "Dublin Burial Grounds & Graveyards", Wolfhound Press, p76, The initial cemetery consisted of just bought by the Rathdown Union from Rev. John Beatty. The price agreed was £200 which Rev. Beatty set as being equivalent to twenty years rent. A committee was formed to run the new cemetery and on 20 November 1861 Sir George Hobson, chairman of the ''Guardians of the Rural Districts of the Union'', signed the dee ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cabinteely GAA, Cabinteely
Cabinteely () is a suburb of Dublin's southside. It is in Dún Laoghaire–Rathdown, County Dublin, Ireland. Geography Cabinteely lies around the crossroads of Johnstown Road / Brennanstown Road and the Old Bray Road, and on either side of the ''Stillorgan Dual Carriageway'' ( N11), which is parallel to the Old Bray Road. The R827 road runs from Blackrock and terminates in Cabinteely. Much of Cabinteely is parkland (Cabinteely Park and Kilbogget Park) or open countryside (around Laughanstown and Brennanstown). Cabinteely borders Ballybrack, Carrickmines, Cherrywood, Cornelscourt, Deansgrange, Foxrock, Johnstown, Killiney and Loughlinstown. History and monuments The area has seen human activity since prehistoric times - there is a tomb known as Brennanstown Portal Tomb, Glendruid cromlech/dolmen, or The Druids’ Altar near Cabinteely. Excavations between 1957 and 1999 some 700m southeast of Cabinteely suggest that the area was of "considerable status and importance" from t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cabinteely
Cabinteely () is a suburb of Dublin's southside. It is in Dún Laoghaire–Rathdown, County Dublin, Ireland. Geography Cabinteely lies around the crossroads of Johnstown Road / Brennanstown Road and the Old Bray Road, and on either side of the ''Stillorgan Dual Carriageway'' ( N11), which is parallel to the Old Bray Road. The R827 road runs from Blackrock and terminates in Cabinteely. Much of Cabinteely is parkland (Cabinteely Park and Kilbogget Park) or open countryside (around Laughanstown and Brennanstown). Cabinteely borders Ballybrack, Carrickmines, Cherrywood, Cornelscourt, Deansgrange, Foxrock, Johnstown, Killiney and Loughlinstown. History and monuments The area has seen human activity since prehistoric times - there is a tomb known as Brennanstown Portal Tomb, Glendruid cromlech/dolmen, or The Druids’ Altar near Cabinteely. Excavations between 1957 and 1999 some 700m southeast of Cabinteely suggest that the area was of "considerable status and importance" from th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kill Of The Grange
Kill of the Grange, often Kill o' the Grange, is an ancient parish in the half Barony of Rathdown, which contains an early religious site, within County Dublin, Ireland; the ancient site is a National Monument. The area, part of broader Deansgrange, within the jurisdiction of Dun Laoghaire-Rathdown, is 5 miles southeast of Dublin. Location Kill of the Grange lies inland, on the south side of Dublin Bay. In modern times it is surrounded by housing developments and is located within Deansgrange, in the traditional County Dublin. Structures The early church is associated with St Finnian of Clonard and dates from the 11th century. Parts may date to the 6th century as they are similar to remains found at Glendalough. The church was originally a simple oblong (now the nave) and a chancel and belfry were later added. Originally known as Clonkeen (), it is now known as Kill of the Grange, meaning "church of the monastic grange." There is also a bullaun (about across) and holy w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dún Laoghaire–Rathdown
Dún Laoghaire–Rathdown ( ga, Dún Laoghaire–Ráth an Dúin) is a Counties of Ireland, county in Republic of Ireland, Ireland. It is part of the Provinces of Ireland, province of Leinster and the Eastern and Midland Region. It is one of three successor counties to County Dublin, which was disestablished in 1994. It is named after the former borough of Dún Laoghaire and the Barony (Ireland), barony of Rathdown, County Dublin, Rathdown. Dún Laoghaire–Rathdown County Council is the Local government in the Republic of Ireland, local authority for the county. The population of the county was 218,018 at the time of the 2016 census. Geography and subdivisions Dún Laoghaire–Rathdown is bordered to the east by the Irish Sea, to the north by the city of Dublin, to the west by the county of South Dublin, and to the south by County Wicklow. With the city of Dublin, Fingal and South Dublin, it is one of four local government areas in the old County Dublin. Located to the south-east o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Foxrock
Foxrock () is an affluent suburb of Dublin, Ireland. It is within the county of Dún Laoghaire–Rathdown, in the postal district of Dublin 18 and in the Roman Catholic parish of Foxrock. History The suburb of Foxrock was developed by William and John Bentley and Edward and Anthony Fox, who, in 1859, leased the lands of the Foxrock Estate from the Ecclesiastical Commissioners and Richard Whately, the Church of Ireland Archbishop of Dublin, with the aim of creating an affluent garden suburb. The development was facilitated by the existence of the Harcourt Street railway line, built in 1854, that put Dublin city within commuting distance. The developers donated a site to the Dublin Wicklow and Wexford Railway Company for Foxrock railway station, which opened in 1861. In 1862, the following advertisement was placed in ''The Irish Times'': Beautiful building sites for mansions and pretty villas – Foxrock estate. The improvements recently made on this property, and still progress ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
R827 Road
The R827 road is a Regional road (Ireland), regional road in Dún Laoghaire–Rathdown, Dublin, Republic of Ireland, Ireland connecting Blackrock, Dublin, Blackrock and Monkstown, County Dublin, Monkstown with the N11 road (Ireland), N11 (Stillorgan Road). The official definition of the R827 from the ''Roads Act 1993 (Classification of Regional Roads) Order 2012'' states:Statutory Instrument 54 of 2012 — Roads Act 1993 (Classification of Regional Roads) Order 2012 ''Irish Statute Book''. Retrieved 2012-08-09. :R827: Blackrock - Cornelscourt, County Dublin :Between its junction with R113 at Newtownpark Avenue and its junction with N11 at Cabinteely Bypass via Stradbrook Road, Deansgrange Road and Clonkeen Road all in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blackrock, Dublin
Blackrock () is a suburb of Dublin, Ireland, northwest of Dún Laoghaire. Location and access Blackrock covers a large but not precisely defined area, rising from sea level on the coast to at White's Cross on the N11 national primary road. Blackrock is bordered by Booterstown, Mount Merrion, Stillorgan, Foxrock, Deansgrange and Monkstown. Transport Blackrock has a station on the Dublin Area Rapid Transit (DART) line, which is 15 minutes away by train from the city centre. The DART runs on the same track that was built in 1834 for the Dublin and Kingstown Railway. Blackrock railway station, on both the DART and the mainline South Eastern Commuter railway line, opened on 17 December 1834. Bus services operated by Dublin Bus and Go-Ahead Ireland also serve the area with multiple bus routes. These are routes 4, 7/A/D, 17/C/D, 46E, 84/A, 114 and 7N. The Aircoach services to Dublin Airport from Dalkey and Greystones call at Blackrock en route to the airport. The Blackrock b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dublin
Dublin (; , or ) is the capital and largest city of Republic of Ireland, Ireland. On a bay at the mouth of the River Liffey, it is in the Provinces of Ireland, province of Leinster, bordered on the south by the Dublin Mountains, a part of the Wicklow Mountains range. At the 2016 census of Ireland, 2016 census it had a population of 1,173,179, while the preliminary results of the 2022 census of Ireland, 2022 census recorded that County Dublin as a whole had a population of 1,450,701, and that the population of the Greater Dublin Area was over 2 million, or roughly 40% of the Republic of Ireland's total population. A settlement was established in the area by the Gaels during or before the 7th century, followed by the Vikings. As the Kings of Dublin, Kingdom of Dublin grew, it became Ireland's principal settlement by the 12th century Anglo-Norman invasion of Ireland. The city expanded rapidly from the 17th century and was briefly the second largest in the British Empire and sixt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Barony (Ireland)
In Ireland, a barony ( ga, barúntacht, plural ) is a historical subdivision of a county, analogous to the hundreds into which the counties of England were divided. Baronies were created during the Tudor reconquest of Ireland, replacing the earlier cantreds formed after the original Norman invasion.Mac Cotter 2005, pp.327–330 Some early baronies were later subdivided into half baronies with the same standing as full baronies. Baronies were mainly cadastral rather than administrative units. They acquired modest local taxation and spending functions in the 19th century before being superseded by the Local Government (Ireland) Act 1898. Subsequent adjustments of county boundaries mean that some baronies now straddle two counties. The final catalogue of baronies numbered 331, with an average area of ; therefore, each county was divided, on average, into 10 or 11 baronies. Creation The island of Ireland was "shired" into counties in two distinct periods: the east and south duri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bank Of Ireland
Bank of Ireland Group plc ( ga, Banc na hÉireann) is a commercial bank operation in Ireland and one of the traditional Big Four Irish banks. Historically the premier banking organisation in Ireland, the Bank occupies a unique position in Irish banking history. At the core of the modern-day group is the old Governor and Company of the Bank of Ireland, the ancient institution established by Royal Charter in 1783. History Bank of Ireland is the oldest bank in continuous operation (apart from closures due to bank strikes in 1950, 1966, 1970, and 1976) in Ireland. In 1781, the Bank of Ireland Act was passed by the Parliament of Ireland, establishing Bank of Ireland. On 25 June 1783, Bank of Ireland opened for business at Mary's Abbey in a private house previously owned by one Charles Blakeney. On 6 June 1808, Bank of Ireland moved to 2 College Green. In 1864, Bank of Ireland paid its first interest on deposits. In 1926, Bank of Ireland took control of the National Land Bank. I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Foxrock–Cabinteely GAA
Foxrock–Cabinteely GAA is a Gaelic Athletic Association club based in the Foxrock, Cabinteely, Johnstown and Cornelscourt areas of Dún Laoghaire–Rathdown. The club was founded in 2005, following the merger of Foxrock Girls Gaelic Club and Cabinteely GAA. The club specialises in ladies' Gaelic football. During the 2010s Foxrock–Cabinteely have won both the Dublin Ladies' Senior Football Championship and the Leinster Ladies' Senior Club Football Championship. They have also played in All-Ireland Ladies' Club Football Championship finals. History In 2005 Cabinteely GAA Ladies' merged with Foxrock Girls Gaelic Club to become Foxrock–Cabinteely GAA. The founding members of the club, including Pat Ring and Philip McAnenly, decided that the new club should specialise in ladies' Gaelic football. They also established partnerships with local national schools, including St. Patrick's and Hollypark in Foxrock, St. Brigid's in Cabinteely, Our Lady of Good Counsel in Johnstown and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
_-_geograph.org.uk_-_530691.jpg)