|
Deadliest Enemy
''Deadliest Enemy: Our War Against Killer Germs'' is a non-fiction book by epidemiologist Michael T. Osterholm and writer Mark Olshaker, that explores public health emergencies including antimicrobial resistance, emerging infectious disease, and the threat of an influenza pandemic. It proposes a nine-point "battle plan for survival" for dealing with these threats, including solutions to antimicrobial drug resistance. The book also focuses on the epidemiology of HIV/AIDS, severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS), Middle East respiratory syndrome (MERS), toxic shock syndrome, Zika, Ebola, bioterrorism, influenza research, and the antivaccine movement. The book was first published in March 2017 by Little, Brown and Company. Synopsis Michael Osterholm describes his book as "part history, part current affairs, and part blueprint for the future". Top of his concerns are influenza pandemics, antibiotic resistance and bioterrorism, combined with "no clear international gov ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Michael T
Michael may refer to: People * Michael (given name), a given name * Michael (surname), including a list of people with the surname Michael Given name "Michael" * Michael (archangel), ''first'' of God's archangels in the Jewish, Christian and Islamic religions * Michael (bishop elect), English 13th-century Bishop of Hereford elect * Michael (Khoroshy) (1885–1977), cleric of the Ukrainian Orthodox Church of Canada * Michael Donnellan (1915–1985), Irish-born London fashion designer, often referred to simply as "Michael" * Michael (footballer, born 1982), Brazilian footballer * Michael (footballer, born 1983), Brazilian footballer * Michael (footballer, born 1993), Brazilian footballer * Michael (footballer, born February 1996), Brazilian footballer * Michael (footballer, born March 1996), Brazilian footballer * Michael (footballer, born 1999), Brazilian footballer Rulers =Byzantine emperors= *Michael I Rangabe (d. 844), married the daughter of Emperor Nikephoros I *Mic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
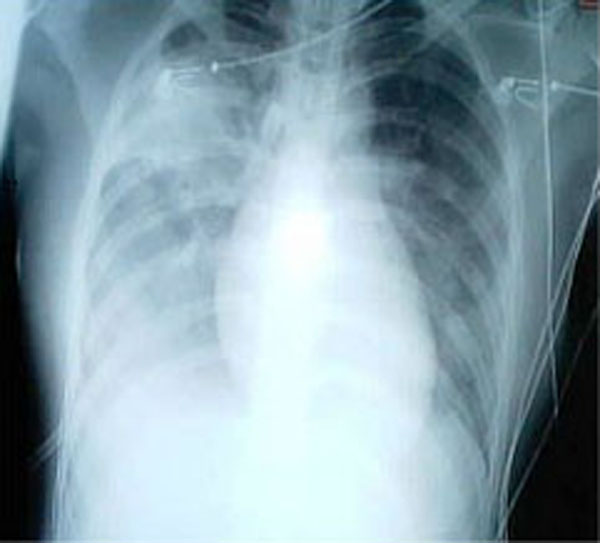
SARS
Severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS) is a viral respiratory disease of zoonotic origin caused by the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus (SARS-CoV or SARS-CoV-1), the first identified strain of the SARS coronavirus species, ''severe acute respiratory syndrome–related coronavirus'' (SARSr-CoV). The first known cases occurred in November 2002, and the syndrome caused the 2002–2004 SARS outbreak. In the 2010s, Chinese scientists traced the virus through the intermediary of Asian palm civets to cave-dwelling horseshoe bats in Xiyang Yi Ethnic Township, Yunnan.The locality was referred to be "a cave in Kunming" in earlier sources because the Xiyang Yi Ethnic Township is administratively part of Kunming, though 70 km apart. Xiyang was identified on * For an earlier interview of the researchers about the locality of the caves, see: SARS was a relatively rare disease; at the end of the epidemic in June 2003, the incidence was 8,469 cases with a case fatality rate (CFR ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Richard Preston
Richard Preston (born August 5, 1954) is a writer for ''The New Yorker'' and bestselling author who has written books about infectious disease, bioterrorism, redwoods and other subjects, as well as fiction. Biography Preston was born in Cambridge, Massachusetts. He graduated Wellesley High School in Massachusetts in 1972 and attended Pomona College in Claremont, California. He earned a Ph.D. in English from Princeton University in 1983. His 1992 ''New Yorker'' article "Crisis in the Hot Zone" was expanded into his breakout book, ''The Hot Zone'' (1994). It is classified as a "non-fiction thriller" about ebolaviruses. He learned of ebola through such contacts as U.S. Army researchers Drs. C.J. Peters and Nancy Jaax. His fascination began during a visit to Africa where he was an eyewitness to epidemics. The book served as the (very loose) basis of the Hollywood movie ''Outbreak'' (1995) about military machinations surrounding a fictional "Motaba virus". Preston's novel '' The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nature (journal)
''Nature'' is a British weekly scientific journal founded and based in London, England. As a multidisciplinary publication, ''Nature'' features peer-reviewed research from a variety of academic disciplines, mainly in science and technology. It has core editorial offices across the United States, continental Europe, and Asia under the international scientific publishing company Springer Nature. ''Nature'' was one of the world's most cited scientific journals by the Science Edition of the 2019 ''Journal Citation Reports'' (with an ascribed impact factor of 42.778), making it one of the world's most-read and most prestigious academic journals. , it claimed an online readership of about three million unique readers per month. Founded in autumn 1869, ''Nature'' was first circulated by Norman Lockyer and Alexander Macmillan as a public forum for scientific innovations. The mid-20th century facilitated an editorial expansion for the journal; ''Nature'' redoubled its efforts in exp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
La Crosse Encephalitis
La Crosse encephalitis is an encephalitis caused by an arbovirus (the La Crosse virus) which has a mosquito vector (''Ochlerotatus triseriatus'' synonym ''Aedes'' ''triseriatus''). La Crosse encephalitis virus (LACV) is one of a group of mosquito-transmitted viruses that can cause encephalitis, or inflammation of the brain. LAC encephalitis is rare; in the United States, about 80–100 LACV disease cases are reported each year, although it is believed to be under-reported due to minimal symptoms experienced by many of those affected. Signs and symptoms It takes 5 to 15 days after the bite of an infected mosquito to develop symptoms of LACV disease. Symptoms include nausea, headache, vomiting in milder cases and seizures, coma, paralysis and permanent brain damage in severe cases. LAC encephalitis initially presents as a nonspecific summertime illness with fever, headache, nausea, vomiting and lethargy. Severe disease occurs most commonly in children under the age of 16 and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Institute Of Health
The National Institutes of Health, commonly referred to as NIH (with each letter pronounced individually), is the primary agency of the United States government responsible for biomedical and public health research. It was founded in the late 1880s and is now part of the United States Department of Health and Human Services. The majority of NIH facilities are located in Bethesda, Maryland, and other nearby suburbs of the Washington metropolitan area, with other primary facilities in the Research Triangle Park in North Carolina and smaller satellite facilities located around the United States. The NIH conducts its own scientific research through the NIH Intramural Research Program (IRP) and provides major biomedical research funding to non-NIH research facilities through its Extramural Research Program. , the IRP had 1,200 principal investigators and more than 4,000 postdoctoral fellows in basic, translational, and clinical research, being the largest biomedical research institut ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biotechnology Risk
Biotechnology risk is a form of existential risk that could come from biological sources, such as genetically engineered biological agents. The origin of such a high-consequence pathogen could be a deliberate release (in the form of bioterrorism or biological weapons), an accidental release, or a naturally occurring event. A chapter on biotechnology and biosecurity was published in Nick Bostrom's 2008 anthology ''Global Catastrophic Risks'', which covered risks including as viral agents. Since then, new technologies like CRISPR and gene drives have been introduced. While the ability to deliberately engineer pathogens has been constrained to high-end labs run by top researchers, the technology to achieve this (and other astonishing feats of bioengineering) is rapidly becoming cheaper and more widespread. Such examples include the diminishing cost of sequencing the human genome (from $10 million to $1,000), the accumulation of large datasets of genetic information, the discovery ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dual-use Technology
In politics, diplomacy and export control, dual-use items refers to goods, software and technology that can be used for both civilian and military applications.''Exporting dual-use goods.'' European Commission (accessed Aug 2022) More generally speaking, dual-use can also refer to any goods or technology which can satisfy more than one goal at any given time. Thus, expensive technologies that would otherwise benefit only civilian commercial interests can also be used to serve military purposes if they are not otherwise engaged, such as the . The "dual-use dilemma" was first noted with the discovery of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Endemic (epidemiology)
In epidemiology, an infection is said to be endemic in a specific population or populated place when that infection is constantly maintained at a baseline level without extra infections being brought into the group as a result of travel or similar means. An endemic disease always has a steady, predictable number of people getting sick, but that number can be high (''hyperendemic'') or low (''hypoendemic''), and the disease can be severe or mild. Also, a disease that is usually endemic can become epidemic. For example, chickenpox is endemic (steady state) in the United Kingdom, but malaria is not. Every year, there are a few cases of malaria reported in the UK, but these do not lead to sustained transmission in the population due to the lack of a suitable vector (mosquitoes of the genus ''Anopheles''). Consequently, the number of people infected by malaria is too variable to be called endemic. However, the number of people who get chickenpox in the UK varies little from year ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pathogens
In biology, a pathogen ( el, πάθος, "suffering", "passion" and , "producer of") in the oldest and broadest sense, is any organism or agent that can produce disease. A pathogen may also be referred to as an infectious agent, or simply a germ. The term ''pathogen'' came into use in the 1880s. Typically, the term ''pathogen'' is used to describe an ''infectious'' microorganism or agent, such as a virus, bacterium, protozoan, prion, viroid, or fungus. Small animals, such as helminths and insects, can also cause or transmit disease. However, these animals are usually referred to as parasites rather than pathogens. The scientific study of microscopic organisms, including microscopic pathogenic organisms, is called microbiology, while parasitology refers to the scientific study of parasites and the organisms that host them. There are several pathways through which pathogens can invade a host. The principal pathways have different episodic time frames, but soil has the longest ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gain-of-function Research
Gain-of-function research (GoF research or GoFR) is medical research that genetically alters an organism in a way that may enhance the biological functions of gene products. This may include an altered pathogenesis, transmissibility, or host range, i.e. the types of hosts that a microorganism can infect. This research is intended to reveal targets to better predict emerging infectious diseases and to develop vaccines and therapeutics. For example, influenza B can infect only humans and harbor seals. Introducing a mutation that would allow influenza B to infect rabbits in a controlled laboratory situation would be considered a gain-of-function experiment, as the virus did not previously have that function. That type of experiment could then help reveal which parts of the virus's genome correspond to the species that it can infect, enabling the creation of antiviral medicines which block this function. In virology, gain-of-function research is usually employed with the intention ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of Minnesota School Of Public Health
The University of Minnesota School of Public Health, located in Minneapolis, Minnesota, is a professional school of the University of Minnesota. The school offers 16 masters programs and four doctoral programs, which culminate in one of the following degrees: Master of Public Health (M.P.H.), Master of Healthcare Administration (M.H.A.), Master of Science (M.S.), or Doctoral (Ph.D.). There are also many dual degree programs, such as those with the Law School, the School of Nursing, the Hubert H. Humphrey Institute of Public Affairs and School of Social Work. The School of Public Health was founded in 1944, although public health courses have been offered at the University of Minnesota since its inception in 1874. The School's faculty coordinated the pioneering Seven Countries Study directed by Professors Ancel Keys and Henry Blackburn.U.S. News & World Reportconsistently ranks the UMN School of Public Health among the top 10 schools of public health in the country. Most recently ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


_Virus_PHIL_1878_lores.jpg)
