|
Deadband
A deadband or dead-band (also known as a dead zone or a neutral zone) is a band of input values in the domain of a transfer function in a control system or signal processing system where the output is zero (the output is 'dead' - no action occurs). Deadband regions can be used in control systems such as servoamplifiers to prevent oscillation or repeated activation-deactivation cycles (called 'hunting' in proportional control systems). A form of deadband that occurs in mechanical systems, compound machines such as gear trains is backlash. Voltage regulators In some power substations there are regulators that keep the voltage within certain predetermined limits, but there is a range of voltage in-between during which no changes are made, such as between 112 and 118 volts (the deadband is 6 volts), or between 215 to 225 volts (deadband is 10 volts). Backlash Gear teeth with slop (''backlash'') exhibit deadband. There is no drive from the input to the output shaft in either di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deadband
A deadband or dead-band (also known as a dead zone or a neutral zone) is a band of input values in the domain of a transfer function in a control system or signal processing system where the output is zero (the output is 'dead' - no action occurs). Deadband regions can be used in control systems such as servoamplifiers to prevent oscillation or repeated activation-deactivation cycles (called 'hunting' in proportional control systems). A form of deadband that occurs in mechanical systems, compound machines such as gear trains is backlash. Voltage regulators In some power substations there are regulators that keep the voltage within certain predetermined limits, but there is a range of voltage in-between during which no changes are made, such as between 112 and 118 volts (the deadband is 6 volts), or between 215 to 225 volts (deadband is 10 volts). Backlash Gear teeth with slop (''backlash'') exhibit deadband. There is no drive from the input to the output shaft in either di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deadband Plot
A deadband or dead-band (also known as a dead zone or a neutral zone) is a band of input values in the domain of a transfer function in a control system or signal processing system where the output is zero (the output is 'dead' - no action occurs). Deadband regions can be used in control systems such as servoamplifiers to prevent oscillation or repeated activation-deactivation cycles (called 'hunting' in proportional control systems). A form of deadband that occurs in mechanical systems, compound machines such as gear trains is backlash. Voltage regulators In some power substations there are regulators that keep the voltage within certain predetermined limits, but there is a range of voltage in-between during which no changes are made, such as between 112 and 118 volts (the deadband is 6 volts), or between 215 to 225 volts (deadband is 10 volts). Backlash Gear teeth with slop (''backlash'') exhibit deadband. There is no drive from the input to the output shaft in either di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hysteresis
Hysteresis is the dependence of the state of a system on its history. For example, a magnet may have more than one possible magnetic moment in a given magnetic field, depending on how the field changed in the past. Plots of a single component of the moment often form a loop or hysteresis curve, where there are different values of one variable depending on the direction of change of another variable. This history dependence is the basis of memory in a hard disk drive and the remanence that retains a record of the Earth's magnetic field magnitude in the past. Hysteresis occurs in ferromagnetic and ferroelectric materials, as well as in the deformation of rubber bands and shape-memory alloys and many other natural phenomena. In natural systems it is often associated with irreversible thermodynamic change such as phase transitions and with internal friction; and dissipation is a common side effect. Hysteresis can be found in physics, chemistry, engineering, biology, and economics. I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thermostat
A thermostat is a regulating device component which senses the temperature of a physical system and performs actions so that the system's temperature is maintained near a desired setpoint. Thermostats are used in any device or system that heats or cools to a setpoint temperature. Examples include building heating, central heating, air conditioners, HVAC systems, water heaters, as well as kitchen equipment including ovens and refrigerators and medical and scientific incubators. In scientific literature, these devices are often broadly classified as thermostatically controlled loads (TCLs). Thermostatically controlled loads comprise roughly 50% of the overall electricity demand in the United States. A thermostat operates as a "closed loop" control device, as it seeks to reduce the error between the desired and measured temperatures. Sometimes a thermostat combines both the sensing and control action elements of a controlled system, such as in an automotive thermostat. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leadscrews
A leadscrew (or lead screw), also known as a power screw or translation screw,Bhandari, p. 202. is a screw used as a linkage in a machine, to translate turning motion into linear motion. Because of the large area of sliding contact between their male and female members, screw threads have larger frictional energy losses compared to other linkages. They are not typically used to carry high power, but more for intermittent use in low power actuator and positioner mechanisms. Leadscrews are commonly used in linear actuators, machine slides (such as in machine tools), vises, presses, and jacks.Shigley, p. 400. Leadscrews are a common component in electric linear actuators. Leadscrews are manufactured in the same way as other thread forms (they may be rolled, cut, or ground). A lead screw is sometimes used with a split nut (also called half nut) which allows the nut to be disengaged from the threads and moved axially, independently of the screw's rotation, when needed (such a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Backlash
Backlash may refer to: Literature * '' Backlash: The Undeclared War Against American Women'', a 1991 book by Susan Faludi * ''Backlash'' (Star Wars novel), a 2010 novel by Aaron Allston * Backlash (Marc Slayton), comic book character * ''Backlash'' (alternative title to: ''A Plague on Both Your Causes''), a novel by John Brunner Music * ''Backlash'' (Bad English album), 1991 * ''Backlash'' (Freddie Hubbard album), 1967 * ''Backlash'', an album by Nina Simone *"Backlash", a 1991 song by Joan Jett from the album '' Notorious'' * "Backlash" (song), by 10 Years Film * ''Backlash'' (1947 film), an American film noir starring Jean Rogers * ''Backlash'' (1956 film), an American Western starring Richard Widmark * ''Backlash'' (1986 film), an Australian drama directed by Bill Bennett * ''Backlash'' (1994 film), an American film starring Sunny Doench Other media * WWE Backlash, an annual World Wrestling Entertainment event * Backlash, a Demolition Vehicle in the video game ' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Voltage
Voltage, also known as electric pressure, electric tension, or (electric) potential difference, is the difference in electric potential between two points. In a static electric field, it corresponds to the work needed per unit of charge to move a test charge between the two points. In the International System of Units, the derived unit for voltage is named ''volt''. The voltage between points can be caused by the build-up of electric charge (e.g., a capacitor), and from an electromotive force (e.g., electromagnetic induction in generator, inductors, and transformers). On a macroscopic scale, a potential difference can be caused by electrochemical processes (e.g., cells and batteries), the pressure-induced piezoelectric effect, and the thermoelectric effect. A voltmeter can be used to measure the voltage between two points in a system. Often a common reference potential such as the ground of the system is used as one of the points. A voltage can represent either a source ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Voltage Regulator
A voltage regulator is a system designed to automatically maintain a constant voltage. A voltage regulator may use a simple feed-forward design or may include negative feedback. It may use an electromechanical mechanism, or electronic components. Depending on the design, it may be used to regulate one or more AC or DC voltages. Electronic voltage regulators are found in devices such as computer power supplies where they stabilize the DC voltages used by the processor and other elements. In automobile alternators and central power station generator plants, voltage regulators control the output of the plant. In an electric power distribution system, voltage regulators may be installed at a substation or along distribution lines so that all customers receive steady voltage independent of how much power is drawn from the line. Electronic voltage regulators A simple voltage/current regulator can be made from a resistor in series with a diode (or series of diodes). Due to the loga ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Backlash (engineering)
In mechanical engineering, backlash, sometimes called lash, play, or slop, is a clearance or lost motion in a mechanism caused by gaps between the parts. It can be defined as "the maximum distance or angle through which any part of a mechanical system may be moved in one direction without applying appreciable force or motion to the next part in mechanical sequence."p. 1-8 An example, in the context of gears and gear trains, is the amount of clearance between mated gear teeth. It can be seen when the direction of movement is reversed and the slack or lost motion is taken up before the reversal of motion is complete. It can be heard from the railway couplings when a train reverses direction. Another example is in a valve train with mechanical tappets, where a certain range of lash is necessary for the valves to work properly. Depending on the application, backlash may or may not be desirable. Some amount of backlash is unavoidable in nearly all reversing mechanical couplings, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Domain Of A Function
In mathematics, the domain of a function is the set of inputs accepted by the function. It is sometimes denoted by \operatorname(f) or \operatornamef, where is the function. More precisely, given a function f\colon X\to Y, the domain of is . Note that in modern mathematical language, the domain is part of the definition of a function rather than a property of it. In the special case that and are both subsets of \R, the function can be graphed in the Cartesian coordinate system. In this case, the domain is represented on the -axis of the graph, as the projection of the graph of the function onto the -axis. For a function f\colon X\to Y, the set is called the codomain, and the set of values attained by the function (which is a subset of ) is called its range or image. Any function can be restricted to a subset of its domain. The restriction of f \colon X \to Y to A, where A\subseteq X, is written as \left. f \_A \colon A \to Y. Natural domain If a real function is giv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gear Train
A gear train is a mechanical system formed by mounting gears on a frame so the teeth of the gears engage. Gear teeth are designed to ensure the pitch circles of engaging gears roll on each other without slipping, providing a smooth transmission of rotation from one gear to the next. Features of gears and gear trains include: * The gear ratio of the pitch circles of mating gears defines the speed ratio and the mechanical advantage of the gear set. * A planetary gear train provides high gear reduction in a compact package. * It is possible to design gear teeth for gears that are non-circular, yet still transmit torque smoothly. * The speed ratios of chain and belt drives are computed in the same way as gear ratios. See bicycle gearing. The transmission of rotation between contacting toothed wheels can be traced back to the Antikythera mechanism of Greece and the south-pointing chariot of China. Illustrations by the Renaissance scientist Georgius Agricola show gear trains with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
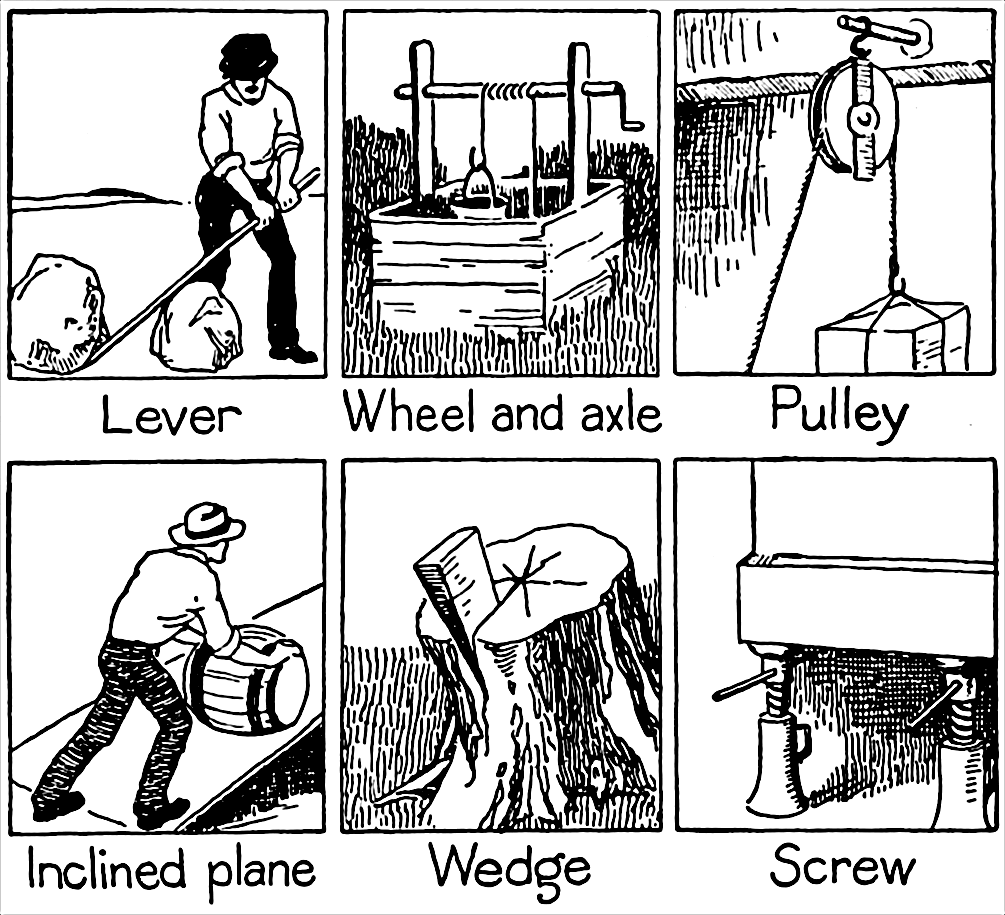
Simple Machine
A simple machine is a mechanical device that changes the direction or magnitude of a force. In general, they can be defined as the simplest mechanisms that use mechanical advantage (also called leverage) to multiply force. Usually the term refers to the six classical simple machines that were defined by Renaissance scientists: * Lever * Wheel and axle * Pulley * Inclined plane * Wedge * Screw A simple machine uses a single applied force to do work against a single load force. Ignoring friction losses, the work done on the load is equal to the work done by the applied force. The machine can increase the amount of the output force, at the cost of a proportional decrease in the distance moved by the load. The ratio of the output to the applied force is called the ''mechanical advantage''. Simple machines can be regarded as the elementary "building blocks" of which all more complicated machines (sometimes called "compound machines") are composed. For example, wheels, levers, and pu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |