|
De Interpretatione
''De Interpretatione'' or ''On Interpretation'' (Greek: Περὶ Ἑρμηνείας, ''Peri Hermeneias'') is the second text from Aristotle's ''Organon'' and is among the earliest surviving philosophical works in the Western tradition to deal with the relationship between language and logic in a comprehensive, explicit, and formal way. The work is usually known by its Latin title. The work begins by analyzing simple ''categoric'' propositions, and draws a series of basic conclusions on the routine issues of classifying and defining basic linguistic forms, such as ''simple terms'' and ''propositions'', nouns and verbs, negation, the ''quantity'' of simple propositions (primitive roots of the quantifiers in modern symbolic logic), investigations on the ''excluded middle'' (which to Aristotle is not applicable to future tense propositions—the problem of future contingents), and on modal propositions. The first five chapters deal with the terms that form propositions. Chapter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ancient Greek
Ancient Greek includes the forms of the Greek language used in ancient Greece and the ancient world from around 1500 BC to 300 BC. It is often roughly divided into the following periods: Mycenaean Greek (), Dark Ages (), the Archaic period (), and the Classical period (). Ancient Greek was the language of Homer and of fifth-century Athenian historians, playwrights, and philosophers. It has contributed many words to English vocabulary and has been a standard subject of study in educational institutions of the Western world since the Renaissance. This article primarily contains information about the Epic and Classical periods of the language. From the Hellenistic period (), Ancient Greek was followed by Koine Greek, which is regarded as a separate historical stage, although its earliest form closely resembles Attic Greek and its latest form approaches Medieval Greek. There were several regional dialects of Ancient Greek, of which Attic Greek developed into Koi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
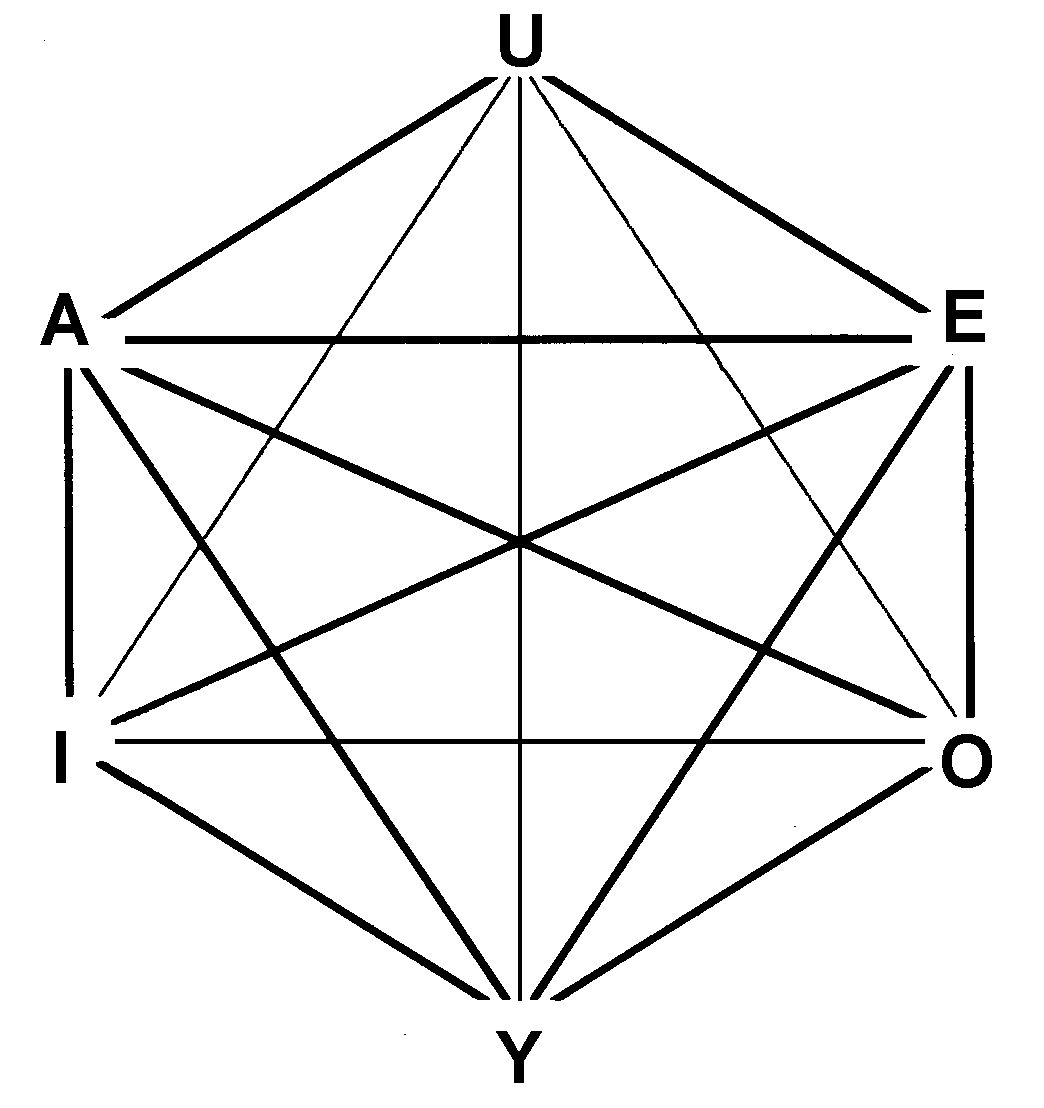
Robert Blanché
__NOTOC__ Robert Blanché (1898–1975) was an associate professor of philosophy at the University of Toulouse. He wrote many books addressing the philosophy of mathematics. About ''Structures intellectuelles'' Robert Blanché died in 1975. Nine years before, in 1966, he published with Vrin: ''Structures intellectuelles''. Therein, he deals with the logical hexagon. Whereas the logical square or square of Apuleius represents four values: A,E,I,O , the logical hexagon represents six, that is to say, not only A,E,I,O but also two new values: Y and U. It is advisable to read the article: logical hexagon as well what concerns Indian logic The development of Indian logic dates back to the '' anviksiki'' of Medhatithi Gautama (c. 6th century BCE); the Sanskrit grammar rules of Pāṇini (c. 5th century BCE); the Vaisheshika school's analysis of atomism (c. 6th century BCE to 2nd cen .... In ''La Logique et son histoire d' Aristote à Russell'', published with Armand Colin in 19 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jules Vuillemin
Jules Vuillemin (; ; 15 February 1920 – 16 January 2001) was a French philosopher, Professor of Philosophy of Knowledge at the prestigious Collège de France, in Paris, from 1962 to 1990, succeeding Maurice Merleau-Ponty, and Professor emeritus from 1991 to 2001. He was an Invited Professor at the Institute for Advanced Study, in Princeton, New Jersey (1968). At the Collège de France, Vuillemin introduced analytical philosophy to France. Vuillemin’s thought had a major influence on Jacques Bouveresse's works. Vuillemin himself vindicated the legacy of Martial Gueroult. A friend of Michel Foucault, he supported his election at the Collège de France, and was also close to Michel Serres. Biography After studying at the Ecole Normale Supérieure, he completed his agrégation in 1943, being received ''premier ex aequo'' alongside Tran Duc Thao. A student of French historical epistemologists Gaston Bachelard and Jean Cavaillès, he was however at first influenced by ph ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ella Mary Edghill
Ella Mary Edghill (born 13 November 1881 at Aldershot; died 24 January 1964 at St Mary's Hospital, Bristol) was a British translator known primarily for her translation of '' Categories'' which appeared in Volume 1 (1928) of '' The Works of Aristotle'' series, edited by W. D. Ross and J. A. Smith and for her translation of On Interpretation by Aristotle. She was the daughter of Rev. John Cox Edghill, DD, Chaplain General to British Armed Forces, and Mary Nesfield. She was educated at Bedford High School and Newnham College, Cambridge, where she took the Classical Tripos. She then achieved an MA and education diploma at London University. Following training at Notting Hill High school she became the senior classics mistress at Bedford High School. In November 1913 she was appointed headmistress of the King's High School for girls in Warwick. Towards the end of 1920 she was appointed headmistress of Redland High School for Girls. The Clarendon Press edition of 1928 describes E ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Susanne Bobzien
Susanne Bobzien (born 1960) is a German-born philosopherWho'sWho in America 2012, 64th Edition whose research interests focus on philosophy of logic and language, determinism and freedom, and ancient philosophy. She currently is senior research fellow at All Souls College, Oxford and professor of philosophy at the University of Oxford. Early life Bobzien was born in Hamburg, Germany, in 1960. She graduated in 1985 with an M.A. at Bonn University, and in 1993 with a doctorate in philosophy (D.Phil.) at Oxford University, where from 1987–1989 she was affiliated with Somerville College. Academic career Bobzien currently holds the position of senior research fellow at All Souls College, Oxford and is professor of philosophy at Oxford University. She was appointed to a senior professorship in philosophy at Yale in 2001 [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sign Relation
A sign relation is the basic construct in the theory of signs, also known as semiotics, as developed by Charles Sanders Peirce. Anthesis Thus, if a sunflower, in turning towards the sun, becomes by that very act fully capable, without further condition, of reproducing a sunflower which turns in precisely corresponding ways toward the sun, and of doing so with the same reproductive power, the sunflower would become a Representamen of the sun. (C.S. Peirce, "Syllabus" (''c''. 1902), ''Collected Papers'', CP 2.274). In his picturesque illustration of a sign relation, along with his tracing of a corresponding sign process, or ''semiosis'', Peirce uses the technical term ''representamen'' for his concept of a sign, but the shorter word is precise enough, so long as one recognizes that its meaning in a particular theory of signs is given by a specific definition of what it means to be a sign. Definition One of Peirce's clearest and most complete definitions of a sign is one that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sign (semiotics)
In semiotics, a sign is anything that communicates a meaning that is not the sign itself to the interpreter of the sign. The meaning can be intentional, as when a word is uttered with a specific meaning, or unintentional, as when a symptom is taken as a sign of a particular medical condition. Signs can communicate through any of the senses, visual, auditory, tactile, olfactory, or taste. Two major theories describe the way signs acquire the ability to transfer information. Both theories understand the defining property of the sign as a relation between a number of elements. In the tradition of semiotics developed by Ferdinand de Saussure (referred to as semiology) the sign relation is dyadic, consisting only of a form of the sign (the signifier) and its meaning (the signified). Saussure saw this relation as being essentially arbitrary (the principle of semiotic arbitrariness), motivated only by social convention. Saussure's theory has been particularly influential in the study ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Semiotics
Semiotics (also called semiotic studies) is the systematic study of sign processes (semiosis) and meaning making. Semiosis is any activity, conduct, or process that involves signs, where a sign is defined as anything that communicates something, usually called a meaning, to the sign's interpreter. The meaning can be intentional such as a word uttered with a specific meaning, or unintentional, such as a symptom being a sign of a particular medical condition. Signs can also communicate feelings (which are usually not considered meanings) and may communicate internally (through thought itself) or through any of the senses: visual, auditory, tactile, olfactory, or gustatory (taste). Contemporary semiotics is a branch of science that studies meaning-making and various types of knowledge. The semiotic tradition explores the study of signs and symbols as a significant part of communications. Unlike linguistics, semiotics also studies non-linguistic sign systems. Semiotics includes the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Semiosis
Semiosis (, ), or sign process, is any form of activity, conduct, or process that involves signs, including the production of meaning. A sign is anything that communicates a meaning, that is not the sign itself, to the interpreter of the sign. The meaning can be intentional such as a word uttered with a specific meaning, or unintentional, such as a symptom being a sign of a particular medical condition. Signs can communicate through any of the senses, visual, auditory, tactile, olfactory, or taste. The term was introduced by Charles Sanders Peirce (1839–1914) to describe a process that interprets signs as referring to their objects, as described in his theory of sign relations, or semiotics. Other theories of sign processes are sometimes carried out under the heading of semiology, following on the work of Ferdinand de Saussure (1857–1913). Overview Peirce was interested primarily in logic, while Saussure was interested primarily in linguistics, which examines the functio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Interpretation (logic)
An interpretation is an assignment of meaning to the symbols of a formal language. Many formal languages used in mathematics, logic, and theoretical computer science are defined in solely syntactic terms, and as such do not have any meaning until they are given some interpretation. The general study of interpretations of formal languages is called formal semantics. The most commonly studied formal logics are propositional logic, predicate logic and their modal analogs, and for these there are standard ways of presenting an interpretation. In these contexts an interpretation is a function that provides the extension of symbols and strings of symbols of an object language. For example, an interpretation function could take the predicate ''T'' (for "tall") and assign it the extension (for "Abraham Lincoln"). Note that all our interpretation does is assign the extension to the non-logical constant ''T'', and does not make a claim about whether ''T'' is to stand for tall and ' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hermeneutics
Hermeneutics () is the theory and methodology of interpretation, especially the interpretation of Biblical hermeneutics, biblical texts, wisdom literature, and Philosophy, philosophical texts. Hermeneutics is more than interpretative principles or methods used when immediate comprehension fails and includes the art of understanding and communication. #Modern hermeneutics, Modern hermeneutics includes both verbal and non-verbal communication''The Routledge Companion to Philosophy in Organization Studies'', Routledge, 2015, p. 113.Joann McNamara, ''From Dance to Text and Back to Dance: A Hermeneutics of Dance Interpretive Discourse'', PhD thesis, Texas Woman's University, 1994. as well as semiotics, presuppositions, and pre-understandings. Hermeneutics has been broadly applied in the humanities, especially in law, history and theology. Hermeneutics was initially applied to the interpretation, or exegesis, of Religious texts, scripture, and has been later broadened to questions of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Boethius
Anicius Manlius Severinus Boethius, commonly known as Boethius (; Latin: ''Boetius''; 480 – 524 AD), was a Roman senator, consul, '' magister officiorum'', historian, and philosopher of the Early Middle Ages. He was a central figure in the translation of the Greek classics into Latin, a precursor to the Scholastic movement, and, along with Cassiodorus, one of the two leading Christian scholars of the 6th century. The local cult of Boethius in the Diocese of Pavia was sanctioned by the Sacred Congregation of Rites in 1883, confirming the diocese's custom of honouring him on the 23 October. Boethius was born in Rome a few years after the collapse of the Western Roman Empire. A member of the Anicii family, he was orphaned following the family's sudden decline and was raised by Quintus Aurelius Memmius Symmachus, a later consul. After mastering both Latin and Greek in his youth, Boethius rose to prominence as a statesman during the Ostrogothic Kingdom: becoming a senator ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |