|
DeZafra Ridge
The Cook Mountains is a group of mountains bounded by the Mulock Glacier, Mulock and Darwin Glacier (Antarctica), Darwin glaciers in Antarctica. Parts of the group were first viewed from the Ross Ice Shelf by the British National Antarctic Expedition (1901–04). Additional portions of these mountains were mapped by a New Zealand party of the Commonwealth Trans-Antarctic Expedition, CTAE (1956–58), and they were completely mapped by the United States Geological Survey, USGS from Tellurometer surveys and US Navy air photos, 1959–63. Named by the NZ-APC for Captain James Cook. Cook Mountains landforms include Bowling Green Col, Bowling Green Plateau, Bromwich Terrace, DeZafra Ridge, Soyuz-13 Rock, Schoonmaker Ridge, Wright Hill, and the Brown Hills. See also *Butcher Ridge, near the polar plateau in the west part of the Cook Mountains *Finn Spur, a rock spur northeast of Mount Ayres in the Cook Mountains *Gatson Ridge, a jagged ridge, long, that runs east from the southern pa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mountain
A mountain is an elevated portion of the Earth's crust, generally with steep sides that show significant exposed bedrock. Although definitions vary, a mountain may differ from a plateau in having a limited Summit (topography), summit area, and is usually higher than a hill, typically rising at least 300 metres (1,000 feet) above the surrounding land. A few mountains are Monadnock, isolated summits, but most occur in mountain ranges. Mountain formation, Mountains are formed through Tectonic plate, tectonic forces, erosion, or volcanism, which act on time scales of up to tens of millions of years. Once mountain building ceases, mountains are slowly leveled through the action of weathering, through Slump (geology), slumping and other forms of mass wasting, as well as through erosion by rivers and glaciers. High elevations on mountains produce Alpine climate, colder climates than at sea level at similar latitude. These colder climates strongly affect the Montane ecosystems, ecosys ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Schoonmaker Ridge
The Cook Mountains is a group of mountains bounded by the Mulock and Darwin glaciers in Antarctica. Parts of the group were first viewed from the Ross Ice Shelf by the British National Antarctic Expedition (1901–04). Additional portions of these mountains were mapped by a New Zealand party of the CTAE (1956–58), and they were completely mapped by the USGS from Tellurometer surveys and US Navy air photos, 1959–63. Named by the NZ-APC for Captain James Cook. Cook Mountains landforms include Bowling Green Col, Bowling Green Plateau, Bromwich Terrace, DeZafra Ridge, Soyuz-13 Rock, Schoonmaker Ridge, Wright Hill, and the Brown Hills. See also * Butcher Ridge, near the polar plateau in the west part of the Cook Mountains * Finn Spur, a rock spur northeast of Mount Ayres in the Cook Mountains * Gatson Ridge, a jagged ridge, long, that runs east from the southern part of Bowling Green Plateau Bowling Green Plateau () is a small but prominent ice-covered plateau at the n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mountain Ranges Of The Ross Dependency
A mountain is an elevated portion of the Earth's crust, generally with steep sides that show significant exposed bedrock. Although definitions vary, a mountain may differ from a plateau in having a limited summit area, and is usually higher than a hill, typically rising at least 300 metres (1,000 feet) above the surrounding land. A few mountains are isolated summits, but most occur in mountain ranges. Mountains are formed through tectonic forces, erosion, or volcanism, which act on time scales of up to tens of millions of years. Once mountain building ceases, mountains are slowly leveled through the action of weathering, through slumping and other forms of mass wasting, as well as through erosion by rivers and glaciers. High elevations on mountains produce colder climates than at sea level at similar latitude. These colder climates strongly affect the ecosystems of mountains: different elevations have different plants and animals. Because of the less hospitable terrain and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Soyuz-18 Rock
The Cook Mountains is a group of mountains bounded by the Mulock and Darwin glaciers in Antarctica. Parts of the group were first viewed from the Ross Ice Shelf by the British National Antarctic Expedition (1901–04). Additional portions of these mountains were mapped by a New Zealand party of the CTAE (1956–58), and they were completely mapped by the USGS from Tellurometer surveys and US Navy air photos, 1959–63. Named by the NZ-APC for Captain James Cook. Cook Mountains landforms include Bowling Green Col, Bowling Green Plateau, Bromwich Terrace, DeZafra Ridge, Soyuz-13 Rock, Schoonmaker Ridge, Wright Hill, and the Brown Hills. See also * Butcher Ridge, near the polar plateau in the west part of the Cook Mountains * Finn Spur, a rock spur northeast of Mount Ayres in the Cook Mountains * Gatson Ridge, a jagged ridge, long, that runs east from the southern part of Bowling Green Plateau Bowling Green Plateau () is a small but prominent ice-covered plateau at the no ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Finger Ridges
The Finger Ridges () are several mainly ice-free ridges and spurs extending over a distance of about , east–west, in the northwestern part of the Cook Mountains in Antarctica. The individual ridges are long and project northward from the higher main ridge. They were mapped by the United States Geological Survey from tellurometer surveys and Navy air photos, 1959–63, and named descriptively by the Advisory Committee on Antarctic Names. See also *Harper Ridge The Cook Mountains is a group of mountains bounded by the Mulock and Darwin glaciers in Antarctica. Parts of the group were first viewed from the Ross Ice Shelf by the British National Antarctic Expedition (1901–04). Additional portions of t ... References Ridges of Oates Land {{OatesLand-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Harper Ridge
The Cook Mountains is a group of mountains bounded by the Mulock and Darwin glaciers in Antarctica. Parts of the group were first viewed from the Ross Ice Shelf by the British National Antarctic Expedition (1901–04). Additional portions of these mountains were mapped by a New Zealand party of the CTAE (1956–58), and they were completely mapped by the USGS from Tellurometer surveys and US Navy air photos, 1959–63. Named by the NZ-APC for Captain James Cook. Cook Mountains landforms include Bowling Green Col, Bowling Green Plateau, Bromwich Terrace, DeZafra Ridge, Soyuz-13 Rock, Schoonmaker Ridge, Wright Hill, and the Brown Hills. See also * Butcher Ridge, near the polar plateau in the west part of the Cook Mountains * Finn Spur, a rock spur northeast of Mount Ayres in the Cook Mountains * Gatson Ridge, a jagged ridge, long, that runs east from the southern part of Bowling Green Plateau in the Cook Mountains * Gjelsvik Spur, a rock spur 2 nautical miles (4 km) north ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gjelsvik Spur
Butcher Ridge () is a large, mainly ice-free ridge near the polar plateau in the west part of the Cook Mountains. The ridge is in the form of an arc, extending northwest from Mount Ayres.Faure, G., and Mensing, T. M., 2010. ''The Transantarctic Mountains Rocks, Ice, Meteorites and Water.'' Germany, Heidelberg, Springer Dordrecht. 804 pp. The Ridge peaks at 2,003 meters (6,572 feet). It was named by the Advisory Committee on Antarctic Names for Commander H.K. Butcher, U.S. Navy, air operations officer on the Staff of the U.S. Naval Support Force, Antarctica, during U.S. Navy Operation Deepfreeze 1963 and 1964. Geology Butcher Ridge is a deeply eroded silicic igneous intrusion. It consists of a hypabyssal intrusion that contains rhythmically layered glassy rocks and plutonic rocks that vary in composition from basaltic andesite to rhyolite." U-Pb dating of baddeleyite from the Butcher Ridge yielded an age of about 182.4 Myr. This age confirms that this igneous complex was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gatson Ridge
Gatson Ridge () is a jagged ridge, long with an elevation of 1158m. It runs east from the southern part of Bowling Green Plateau in the Brown Hills of the Cook Mountains, Antarctica. It was named by the Advisory Committee on Antarctic Names after Karl W. Gatson of the United States Geological Survey (USGS), a topographic engineer on the joint 1975–76 USGS – British Antarctic Survey project to establish control points for Landsat mosaics of Palmer Land, and to establish geodetically tied independent survey nets in the Ellsworth Mountains and Antarctic Peninsula The Antarctic Peninsula, known as O'Higgins Land in Chile and Tierra de San Martín in Argentina, and originally as Graham Land in the United Kingdom and the Palmer Peninsula in the United States, is the northernmost part of mainland Antarctic ... into a worldwide reference system using Doppler satellite control. References External links * Ridges of Antarctica Oates Land {{OatesLand-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mount Ayres
The Cook Mountains is a group of mountains bounded by the Mulock and Darwin glaciers in Antarctica. Parts of the group were first viewed from the Ross Ice Shelf by the British National Antarctic Expedition (1901–04). Additional portions of these mountains were mapped by a New Zealand party of the CTAE (1956–58), and they were completely mapped by the USGS from Tellurometer surveys and US Navy air photos, 1959–63. Named by the NZ-APC for Captain James Cook. Cook Mountains landforms include Bowling Green Col, Bowling Green Plateau, Bromwich Terrace, DeZafra Ridge, Soyuz-13 Rock, Schoonmaker Ridge, Wright Hill, and the Brown Hills. See also * Butcher Ridge, near the polar plateau in the west part of the Cook Mountains * Finn Spur, a rock spur northeast of Mount Ayres in the Cook Mountains *Gatson Ridge, a jagged ridge, long, that runs east from the southern part of Bowling Green Plateau in the Cook Mountains *Gjelsvik Spur, a rock spur 2 nautical miles (4 km) northwe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Finn Spur
The Cook Mountains is a group of mountains bounded by the Mulock and Darwin glaciers in Antarctica. Parts of the group were first viewed from the Ross Ice Shelf by the British National Antarctic Expedition (1901–04). Additional portions of these mountains were mapped by a New Zealand party of the CTAE (1956–58), and they were completely mapped by the USGS from Tellurometer surveys and US Navy air photos, 1959–63. Named by the NZ-APC for Captain James Cook. Cook Mountains landforms include Bowling Green Col, Bowling Green Plateau, Bromwich Terrace, DeZafra Ridge, Soyuz-13 Rock, Schoonmaker Ridge, Wright Hill, and the Brown Hills. See also * Butcher Ridge, near the polar plateau in the west part of the Cook Mountains * Finn Spur, a rock spur northeast of Mount Ayres in the Cook Mountains * Gatson Ridge, a jagged ridge, long, that runs east from the southern part of Bowling Green Plateau Bowling Green Plateau () is a small but prominent ice-covered plateau at the n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Butcher Ridge
Butcher Ridge () is a large, mainly ice-free ridge near the polar plateau in the west part of the Cook Mountains. The ridge is in the form of an arc, extending northwest from Mount Ayres.Faure, G., and Mensing, T. M., 2010. ''The Transantarctic Mountains Rocks, Ice, Meteorites and Water.'' Germany, Heidelberg, Springer Dordrecht. 804 pp. The Ridge peaks at 2,003 meters (6,572 feet). It was named by the Advisory Committee on Antarctic Names for Commander H.K. Butcher, U.S. Navy, air operations officer on the Staff of the U.S. Naval Support Force, Antarctica, during U.S. Navy Operation Deepfreeze 1963 and 1964. Geology Butcher Ridge is a deeply eroded silicic igneous intrusion. It consists of a hypabyssal intrusion that contains rhythmically layered glassy rocks and plutonic rocks that vary in composition from basaltic andesite to rhyolite." U-Pb dating of baddeleyite from the Butcher Ridge yielded an age of about 182.4 Myr. This age confirms that this igneous complex was e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
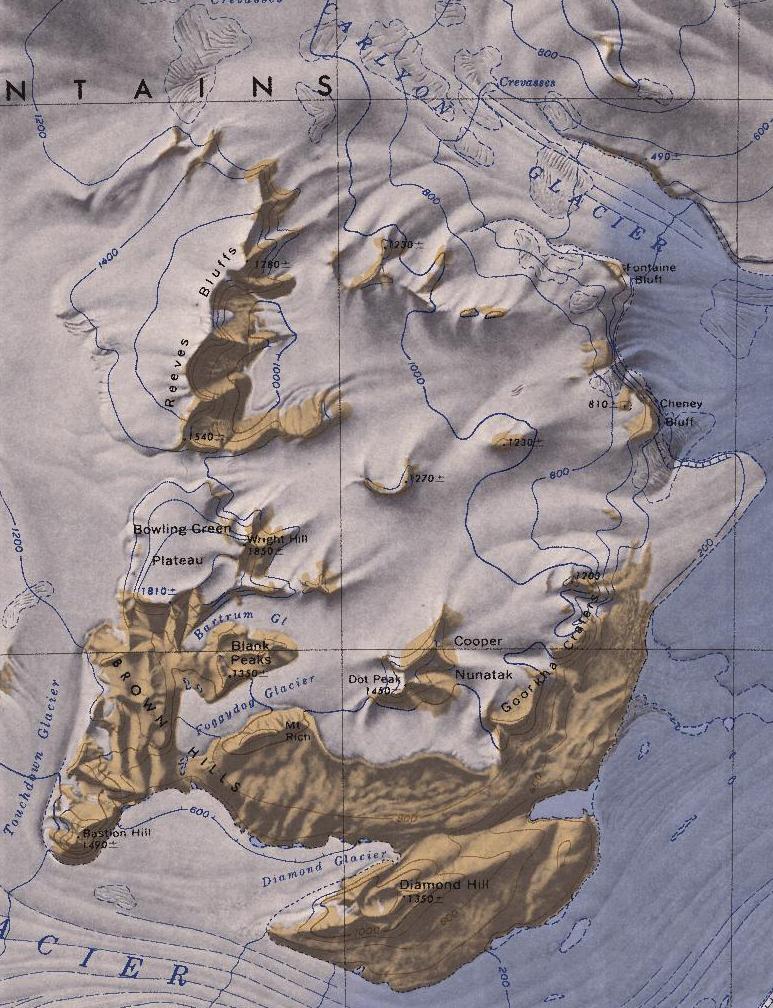
Brown Hills
The Brown Hills () are a group of mainly snow-free hills in the Cook Mountains of Antarctica. Location The Brown Hills lie north of the lower reaches of Darwin Glacier. They are north of Diamond Hill and are adjacent to Diamond Glacier, a distributary of the Darwin Glacier. To the east they are bordered by the Ross Ice Shelf. On the west side, the Touchdown Glacier flows south to the Darwin Glacier between Roadend Nunatak and the Brown Hills. Reeves Bluffs are to the north of the hills. The hills were named for their color by the Darwin Glacier Party of the Commonwealth Trans-Antarctic Expedition (1956–58). Geology During glacial periods, Diamond Glacier would probably have flowed over the Brown Hills to the Ross Ice Shelf. Exposure ages of five glacial erratics from the Brown Hills range from 7,000 to 205,000 years ago, which implies that until 7,000 years ago the Brown Hills saddle was ice-covered. Simpson 2002 proposes that the Darwin calcic suite, a K-series, I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |