|
Dawn Probe
''Dawn'' is a retired space probe that was launched by NASA in September 2007 with the mission of studying two of the three known protoplanets of the asteroid belt: Vesta and Ceres. In the fulfillment of that mission—the ninth in NASA's Discovery Program—''Dawn'' entered orbit around Vesta on July 16, 2011, and completed a 14-month survey mission before leaving for Ceres in late 2012. It entered orbit around Ceres on March 6, 2015. In 2017, NASA announced that the planned nine-year mission would be extended until the probe's hydrazine fuel supply was depleted. On November 1, 2018, NASA announced that ''Dawn'' had depleted its hydrazine, and the mission was ended. The spacecraft is currently in a derelict, but stable, orbit around Ceres. ''Dawn'' is the first spacecraft to orbit two extraterrestrial bodies, the first spacecraft to visit either Vesta or Ceres, and the first to orbit a dwarf planet. The ''Dawn'' mission was managed by NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory, with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orbiter
A spacecraft is a vehicle or machine designed to fly in outer space. A type of artificial satellite, spacecraft are used for a variety of purposes, including communications, Earth observation, meteorology, navigation, space colonization, planetary exploration, and transportation of humans and cargo. All spacecraft except single-stage-to-orbit vehicles cannot get into space on their own, and require a launch vehicle (carrier rocket). On a sub-orbital spaceflight, a space vehicle enters space and then returns to the surface without having gained sufficient energy or velocity to make a full Earth orbit. For orbital spaceflights, spacecraft enter closed orbits around the Earth or around other celestial bodies. Spacecraft used for human spaceflight carry people on board as crew or passengers from start or on orbit (space stations) only, whereas those used for robotic space missions operate either autonomously or telerobotically. Robotic spacecraft used to support scientific ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mission Patch
A mission patch is a cloth reproduction of a spaceflight mission emblem worn by astronauts and other personnel affiliated with that mission. It is usually executed as an embroidered patch. The term ''space patch'' is mostly applied to an emblem designed for a crewed space mission. Traditionally, the patch is worn on the space suit that astronauts and cosmonauts wear when launched into space. Mission patches have been adopted by the crew and personnel of many other space ventures, public and private. Origins The first space patch was flown by Soviet cosmonaut Valentina Tereshkova on the Vostok 6 mission in 1963; however, that was hidden from public view by the bright orange coverall that was part of the space suit at the time. At the start of the human spaceflight space age, as a rule, astronauts were pilots from a military background. These pilots took the tradition of military shoulder patches with them; most US space missions have had dedicated designs, and since the mid-1980s m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glenn Research Center
NASA John H. Glenn Research Center at Lewis Field is a NASA center within the cities of Brook Park and Cleveland between Cleveland Hopkins International Airport and the Rocky River Reservation of Cleveland Metroparks, with a subsidiary facility in Sandusky, Ohio. Its acting director is James A. Kenyon. Glenn Research Center is one of ten major NASA facilities, whose primary mission is to develop science and technology for use in aeronautics and space. , it employed about 1,650 civil servants and 1,850 support contractors on or near its site. In 2010, the formerly on-site NASA Visitors Center moved to the Great Lakes Science Center in the North Coast Harbor area of downtown Cleveland. History The installation was established in 1942 as part of the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics (NACA) and was later incorporated into the National Aeronautics and Space Administration as a laboratory for aircraft engine research. It was first named the Aircraft Engine Research L ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Harold R
Harold may refer to: People * Harold (given name), including a list of persons and fictional characters with the name * Harold (surname), surname in the English language * András Arató, known in meme culture as "Hide the Pain Harold" Arts and entertainment * ''Harold'' (film), a 2008 comedy film * ''Harold'', an 1876 poem by Alfred, Lord Tennyson * ''Harold, the Last of the Saxons'', an 1848 book by Edward Bulwer-Lytton, 1st Baron Lytton * ''Harold or the Norman Conquest'', an opera by Frederic Cowen * ''Harold'', an 1885 opera by Eduard Nápravník * Harold, a character from the cartoon ''The Grim Adventures of Billy & Mandy'' *Harold & Kumar, a US movie; Harold/Harry is the main actor in the show. Places ;In the United States * Alpine, Los Angeles County, California, an erstwhile settlement that was also known as Harold * Harold, Florida Harold is an unincorporated community and census-designated place in Santa Rosa County, in the U.S. state of Florida. Its populati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SERT-1 Spacecraft
SERT-1 (Space Electric Rocket Test) was a NASA probe used to test electrostatic ion thruster design and was built by NASA's Lewis Research Center (now NASA Glenn). SERT-1 was the first spacecraft to utilize ion engine design. It was launched on July 20, 1964 on a Scout rocket. It carried two electric propulsion engines; of the two, the first, an electron-bombardment ion engine ("Kaufman ion thruster") was run for a total of 31 minutes and 16 seconds. This was the first time that an ion engine of any type had been operated in space, and demonstrated that the neutralizer worked as predicted. (A second thruster, of a different type, failed to operate.) The test was followed by the SERT-II probe, launched into a 1000-km-high polar orbit on February 3, 1970, page at Astronautix (Accessed July 1, 2010) which demonstrated two |
Planetary Flyby
A planetary flyby is the act of sending a space probe past a planet or a dwarf planet close enough to record scientific data. This is a subset of the overall concept of a flyby in spaceflight. The first flyby of another planet with a functioning spacecraft took place on December 14, 1962, when Mariner 2 zoomed by the planet Venus. Planetary flybys are commonly used as gravity assist maneuvers to "slingshot" a space probe toward its primary target without expending fuel, but in some cases (such as with New Horizons), flybys are the primary objectives of a mission in of themselves. A relatively recent example of a flyby spacecraft is ''New Horizons,'' which performed flyby maneuvers of Jupiter, Pluto and its moons in the 21st century. The flyby of Jupiter, used as a gravity assist, allowed the craft to reach Pluto at high velocity without the complications of slowing down, after which it proceeded further into the Kuiper Belt on an escape trajectory out of the Solar System. Li ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
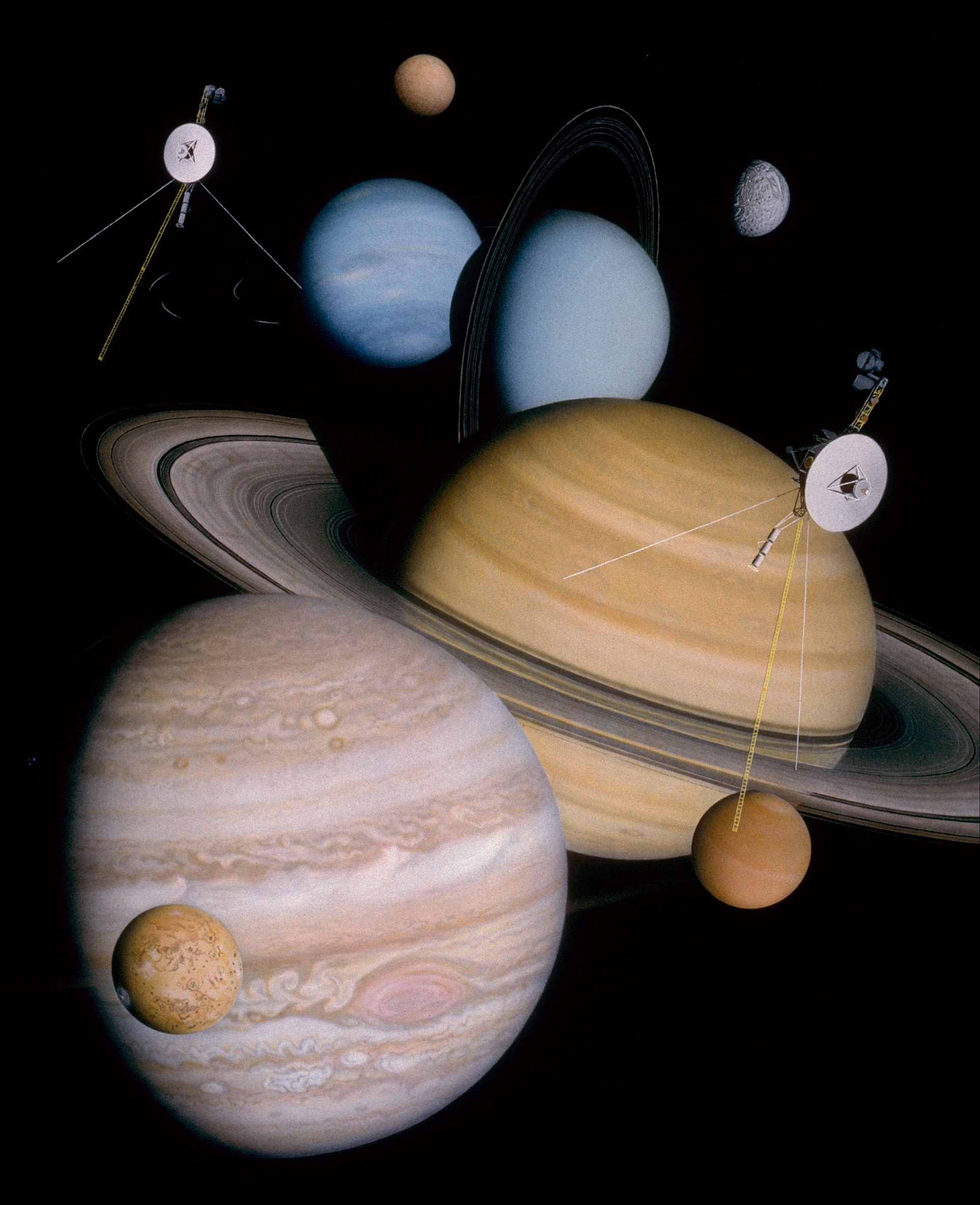
Voyager Program
The Voyager program is an American scientific program that employs two robotic interstellar probes, ''Voyager 1'' and ''Voyager 2''. They were launched in 1977 to take advantage of a favorable alignment of Jupiter and Saturn, to Flyby (spaceflight), fly near them while collecting data for transmission back to Earth. After launch the decision was taken to send ''Voyager 2'' near Uranus and Neptune to collect data for transmission back to Earth. As of 2022, the Voyagers are still in operation past the outer boundary of the heliosphere in interstellar space. They collect and transmit useful data to Earth. , ''Voyager 1'' was moving with a velocity of , or 17 km/s, relative to the Sun, and was from the Sun reaching a distance of from Earth as of February 10, 2022. On 25 August 2012, data from ''Voyager 1'' indicated that it had entered interstellar space. , ''Voyager 2'' was moving with a velocity of , or 15 km/s, relative to the Sun, and was from the Sun reaching a distan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |