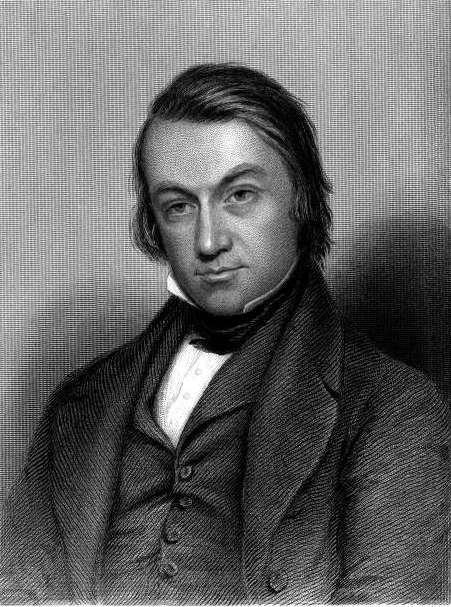|
David Robertson (bookseller)
David Robertson (1795–1854) was a Scottish bookseller, now known for his publication of the early ''Whistle Binkie'' anthologies. Life The son of a farmer, Robertson was born in the parish of Kippen, Perthshire. He received an education in his native district, and in 1810 was apprenticed to William Turnbull, bookseller in Trongate, Glasgow. In 1821 appeared a pseudonymous work ''Three Nights in Perthshire'' by Percy Yorke Jr., written by Robertson's friend Thomas Atkinson. The pair had made a visit to Perthshire, the historical county: they went to the Trossachs, now in the Stirling council area, as is Kippen. The younger Atkinson, a Glaswegian, at this point was working for Brash & Reid, booksellers, where he had been an apprentice. The book is a fictionalised account of their visit to Loch Ard and the farm Ledard there, run by the Macfarlane family, who included Donald Macfarlan(e) MD of Ledard (died 1857). On the death of Turnbull in 1823, Robertson carried on the business ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Whistle Binkie
''Whistle-Binkie, or, The piper of the party: Being a collection of songs for the social circle'' was a Scottish poetry and song anthology first appearing in 1832. There were later volumes under the same title, at least four more anthologies, and collected editions appearing from 1853. The style of verse typically was in imitation of Robert Burns. The series was enduringly popular, and the final ''Whistle Binkie'' anthology appeared in 1890. While the intention at the time was to publish Scottish writers, later critics such as Edwin Morgan have attacked the series on grounds of taste. Alexander Laing saw in it "sentiment, mild pathos and sly humour" writing in 1857; by a century later Hugh MacDiarmid could regard it as opening the way for children to be given "sentimental trash". First edition ''Whistle Binkie'' was published in 1832 by David Robertson, a bookseller in Trongate, Glasgow. The editor was John Donald Carrick, who also contributed to the collection. Notes Extern ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Motherwell
William Motherwell (13 October 1797, Glasgow – 1 November 1835, Glasgow) was a Scottish poet, antiquary and journalist. Life Motherwell was born at Glasgow, the son of Willan and Jane Motherwell. His father was an ironmonger. He was sent to school and at the age of fifteen he was apprenticed in the office of the sheriff-clerk at Paisley. He studied classics for a winter term at Glasgow University between 1818 and 1819.Hamish Whyte, ‘Motherwell, William (1797–1835)’, Oxford Dictionary of National Biography, Oxford University Press, 200accessed 4 April 2017/ref> He and appointed sheriff-clerk depute there in 1819. He spent his leisure in collecting materials for a volume of local ballads which he published in 1819 under the title of ''The Harp of Renfrewshire''. In 1827 he published a further instalment in ''Minstrelsy Ancient and Modern'', prefaced by an excellent historical introduction. This work was to provide evidence of the work of notable women like Agnes Ly ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bank Of Scotland
The Bank of Scotland plc (Scottish Gaelic: ''Banca na h-Alba'') is a commercial and clearing bank based in Scotland and is part of the Lloyds Banking Group, following the Bank of Scotland's implosion in 2008. The bank was established by the Parliament of Scotland in 1695 to develop Scotland's trade with other countries, and aimed to create a stable banking system in the Kingdom of Scotland. With a history dating to the end of the 17th century, it is the fifth-oldest extant bank in the United Kingdom (the Bank of England having been established one year earlier), and is the only commercial institution created by the Parliament of Scotland to remain in existence. It was one of the first banks in Europe to print its own banknotes, and it continues to print its own sterling banknotes under legal arrangements that allow Scottish banks to issue currency. In June 2006, the HBOS Group Reorganisation Act 2006 was passed by the Parliament of the United Kingdom, allowing the bank' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
James MacGregor (moderator)
James MacGregor FRSE (1832–1910) was a Scottish minister and philanthropist. He was Moderator of the General Assembly of the Church of Scotland in 1891. In 1886 he was made Chaplain in Ordinary to Queen Victoria, in 1901 Chaplain to King Edward VII, and in 1910 to King George V, serving three monarchs in all. Life He was born on 11 July 1832 at Brownhill Farm near Scone, Perthshire, the son of James MacGregor, farmer, and his wife, Margaret MacDougall. He was educated at Scone Parish School, then Perth Academy. He then studied divinity at St Andrews University 1848 to 1855. He was licensed to preach by the Presbytery of Perth in May 1855 and then served in a series of illustrious churches: Paisley High Church (1855-1862); Monimail Church in Fife (1862-1864), Tron Church in Glasgow (1864-1868); Tron Kirk in Edinburgh (1868-1873); and finally St Cuthbert's Church, Edinburgh (1873-1910). During his ministry of St Cuthberts, he oversaw the total reconstruction of the chur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oliver And Boyd
Oliver and Boyd was a British publishing and printing firm that traded from 1807 or 1808 until 1990.British Museum: Term Details - Oliver & Boyd (Biographical details) britishmuseum.org. Retrieved 24 June 2018. The firm has been described as a "stalwart in Scottish publishing".David Finkelstein "Publishing 18 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kyle, Ayrshire
Kyle (or Coila poetically; gd, Cuil) is a former comital district of Scotland which stretched across parts of modern-day East Ayrshire and South Ayrshire. It is supposedly named after Coel Hen, a legendary king of the Britons, who is said to be buried under a mound at Coylton. Geographical extent The area is bordered by the historical districts of Cunninghame to the north, Clydesdale to the east and by Carrick to the south. The Firth of Clyde lies to the west. Kyle was the central of the three districts in the sheriffdom of Ayr ( Ayrshire), which was divided naturally by its three primary rivers all running in a generally westward direction to flow into the firth of Clyde. The River Irvine forms the northern boundary of Kyle with Cunninghame; the River Doon established its southern boundary with Carrick. Additionally, Kyle itself was sub-divided into two parts. To the north of the River Ayr was "Kyle Stewart" (sometimes called "Stewart Kyle" or "Walter's Kyle"), lands held ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clan Logan
Clan Logan is a Scottish clan. Two distinct branches of Clan Logan exist: the Highland branch; and the Lowland branch (which descends from Sir Robert Logan of Restalrig who married Katherine Stewart, a daughter of the future Robert II () and, in 1400, became Lord High Admiral of Scotland). The clan does not have a chief recognised by Lord Lyon King of Arms, and therefore can be considered an armigerous clan. Today, some regard Clan MacLennan as a variant of the Highland Logan clan. History The surname ''Logan'' is a territorial name, likely derived from the lands of Logan in present Ayrshire, Scotland. The earliest record of the surname is of Robert Logan who is recorded as witnessing the resignation of the lands of Ingilbristoun in 1204. The name is variously recorded throughout the 13th century. Several Logans are recorded as paying homage to Edward I of England within the Ragman Rolls of 1296. These are Phelippe de Logyn (burgess from Montrose), Thurbrandus de Logyn (from D ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Albert, Prince Consort
Prince Albert of Saxe-Coburg and Gotha (Franz August Karl Albert Emanuel; 26 August 1819 – 14 December 1861) was the consort of Queen Victoria from their marriage on 10 February 1840 until his death in 1861. Albert was born in the Saxon duchy of Saxe-Coburg-Saalfeld to a family connected to many of Europe's ruling monarchs. At the age of twenty, he married his first cousin Victoria; they had nine children. Initially he felt constrained by his role as consort, which did not afford him power or responsibilities. He gradually developed a reputation for supporting public causes, such as educational reform and the abolition of slavery worldwide, and was entrusted with running the Queen's household, office, and estates. He was heavily involved with the organisation of the Great Exhibition of 1851, which was a resounding success. Victoria came to depend more and more on Albert's support and guidance. He aided the development of Britain's constitutional monarchy by persuading his w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lord Jeffrey
Francis Jeffrey, Lord Jeffrey (23 October 1773 – 26 January 1850) was a Scottish judge and literary critic. Life He was born at 7 Charles Street near Potterow in south Edinburgh, the son of George Jeffrey, a clerk in the Court of Session (first clerk to Robert Sinclair, advocate). After attending the Royal High School for six years, he studied at the University of Glasgow from 1787 to May 1789, and at Queen's College, Oxford, from September 1791 to June 1792. He had begun the study of law at Edinburgh before going to Oxford, and returned to it afterwards. He became a member of the Speculative Society, where he measured himself in debate with Sir Walter Scott, Lord Brougham, Francis Horner, the Marquess of Lansdowne, Lord Kinnaird and others. He was admitted to the Scottish bar in December 1794, but, having abandoned the Tory principles in which he had been educated, he found that his Whig politics hampered his legal prospects. In consequence of his lack of success a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charles Mackay (author)
Charles Mackay (27 March 1814 – 24 December 1889) was a Scottish poet, journalist, author, anthologist, novelist, and songwriter, remembered mainly for his book ''Extraordinary Popular Delusions and the Madness of Crowds''. Early life Charles Mackay was born in Perth, Scotland. His father, George Mackay, was a bombardier in the Royal Artillery, and his mother Amelia Cargill died shortly after his birth. Mackay was educated at the Caledonian Asylum, in London. In 1828 he was placed by his father at a school in Brussels, on the Boulevard de Namur, shortly taken over by William James Joseph Drury; and studied languages. In 1830 he was engaged as a private secretary to William Cockerill, the ironmaster, near Liège, began writing in French in the ''Courrier Belge'', and sent English poems to a local newspaper called ''The Telegraph''. In the summer of 1830 he visited Paris, and he spent 1831 with Cockerill at Aix-la-Chapelle. In May 1832 his father brought him back to London ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glasgow Royal Infirmary
The Glasgow Royal Infirmary (GRI) is a large teaching hospital. With a capacity of around 1,000 beds, the hospital campus covers an area of around , and straddles the Townhead and Dennistoun districts on the north-eastern fringe of the city centre of Glasgow, Scotland. It is managed by NHS Greater Glasgow and Clyde. It was originally opened in 1794, with the present main building dating from 1914. History Founding of the infirmary A Royal Charter was obtained in 1791 granting the Crown-owned land to the hospital. The infirmary was built beside Glasgow Cathedral on land that held the ruins of the Bishop's Castle, which dated from at least the 13th century but had been allowed to fall into disrepair. George Jardine, Professor of Logic, was appointed the first manager in January 1793. Designed by Robert and James Adam, the original Royal Infirmary building was opened in December 1794. The original Adams building had five floors (one underground) holding eight wards (giving the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.png)