|
David Nelligan
David Neligan (14 October 1899 – 1983), known by his soubriquet "The Spy in the Castle", was a crucial figure involved in the Irish War of Independence (1919–21) and subsequently became Director of Intelligence for the Irish Army after the Irish Civil War (1922–23). Early life David Neligan was born 14 October 1899 at Templeglantine, Limerick where his parents, David and Elizabeth Neligan (née Mullan), were primary school teachers. He was an accomplished hurler with his local Templeglantine GAA Club. In 1917 Neligan joined the military organisation established in 1913 by Irish nationalists - the Irish Volunteers. Dublin Metropolitan Police & MI5 Against his father's wishes, Neligan joined the Dublin Metropolitan Police (DMP) - also in 1917. Picking up travel documentation from the local Royal Irish Constabulary barracks he declined a suggestion that he enlist in this armed rural force. After service as a uniformed constable with the DMP, Neligan was promoted to Dete ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
David Neligan
David Neligan (14 October 1899 – 1983), known by his soubriquet "The Spy in the Castle", was a crucial figure involved in the Irish War of Independence (1919–21) and subsequently became Director of Intelligence for the Irish Army after the Irish Civil War (1922–23). Early life David Neligan was born 14 October 1899 at Templeglantine, Limerick where his parents, David and Elizabeth Neligan (née Mullan), were primary school teachers. He was an accomplished hurler with his local Templeglantine GAA Club. In 1917 Neligan joined the military organisation established in 1913 by Irish nationalists - the Irish Volunteers. Dublin Metropolitan Police & MI5 Against his father's wishes, Neligan joined the Dublin Metropolitan Police (DMP) - also in 1917. Picking up travel documentation from the local Royal Irish Constabulary barracks he declined a suggestion that he enlist in this armed rural force. After service as a uniformed constable with the DMP, Neligan was promoted to Detecti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eamon Broy
Eamon Broy (also called ''Edward Broy''; 22 December 1887 – 22 January 1972) was successively a member of the Dublin Metropolitan Police, the Irish Republican Army, the National Army, and the Garda Síochána of the Irish Free State. He served as Commissioner of the Gardaí from February 1933 to June 1938. He later served as president of the Olympic Council of Ireland for fifteen years. Career RIC / pre-independence Broy joined the Royal Irish Constabulary on 2 August 1910, and the Dublin Metropolitan Police (DMP) on 20 January 1911. Broy was a double agent within the DMP, with the rank of Detective Sergeant (DS). He worked as a clerk inside G Division, the intelligence branch of the DMP. While there, he copied sensitive files for IRA leader Michael Collins and passed many of these files on to Collins through Thomas Gay, the librarian at Capel Street Library. On 7 April 1919, Broy smuggled Collins into G Division's archives in Great Brunswick Street (now Pearse Street), enab ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diarmuid O'Hegarty
Diarmuid O'Hegarty (Irish: ''Ó hÉigeartaigh''; 1892–1958) was an Irish revolutionary and civil servant. He was a member of the Irish Volunteer executive (June 1916 – November 1921), IRA Director of Communications (July 1918 – March 1920) and Director of Organisation (March 1920 – April 1921). O’Hegarty was an extremely self-effacing man whom Frank Pakenham called the "civil servant of the revolution". Early life Diarmuid O'Hegarty (Ó hÉigeartuigh) (26 December 1892–14 March 1958) was born Jeremiah Stephen Hegarty on 26 December 1892 in Lowertown, Schull, Co Cork, the eldest of seven children (four sons and three daughters). Both his father, Jeremiah Hegarty (1856–1934), and his mother, Eileen (née Barry), were teachers. Diarmuid's father was also known as Diarmuid Ó hÉigeartuigh, and was a member of the Gaelic League. He collected stories and folklore from his grandmother later published as Is uasal ceird (1968) (edited by Stiofán Ó hAnnracháin); he also ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ernie O'Malley
Ernest Bernard Malley ( ga, Earnán Ó Máille; 26 May 1897 – 25 March 1957) was an IRA officer during the Irish War of Independence. Subsequently, he became assistant chief of staff of the Anti-Treaty IRA during the Irish Civil War. O'Malley was an active revolutionary who displayed courage in battle and was wounded a number of times. He wrote two memoirs, ''On Another Man's Wound'' and ''The Singing Flame'', and two histories, ''Raids and Rallies'' and ''Rising Out: Seán Connolly of Longford, 1890–1921''. The memoirs cover his early life, the War of Independence and the Civil War period. Although he was elected to Dáil Éireann in 1923 while in prison, O'Malley largely eschewed politics, seeing himself primarily as a soldier who had "fought and killed the enemies of our nation". Early life O'Malley was born in Castlebar, County Mayo, on 26 May 1897. His was a lower-middle class Catholic family in which he was the second of eleven children born to local man Luke Malley an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ballyseedy Massacre
The executions during the Irish Civil War took place during the guerrilla phase of the Irish Civil War (June 1922 – May 1923). This phase of the war was bitter, and both sides, the government forces of the Irish Free State and the anti-Treaty Irish Republican Army (IRA) insurgents, used executions and terror in what developed into a cycle of atrocities. From November 1922, the Free State government embarked on a policy of executing Republican prisoners in order to bring the war to an end. Many of those killed had previously been allies, and in some cases close friends (during the Irish War of Independence 1919–1921), of those who ordered their deaths in the civil war. In addition, government troops summarily executed prisoners in the field on several occasions. The executions of prisoners left a lasting legacy of bitterness in Irish politics. The use of execution by the Irish Free State in the Civil War was relatively harsh compared to the recent British record. In contr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Executions During The Irish Civil War
The executions during the Irish Civil War took place during the guerrilla phase of the Irish Civil War (June 1922 – May 1923). This phase of the war was bitter, and both sides, the government forces of the Irish Free State and the anti-Treaty Irish Republican Army (IRA) insurgents, used executions and terror in what developed into a cycle of atrocities. From November 1922, the Free State government embarked on a policy of executing Republican prisoners in order to bring the war to an end. Many of those killed had previously been allies, and in some cases close friends (during the Irish War of Independence 1919–1921), of those who ordered their deaths in the civil war. In addition, government troops summarily executed prisoners in the field on several occasions. The executions of prisoners left a lasting legacy of bitterness in Irish politics. The use of execution by the Irish Free State in the Civil War was relatively harsh compared to the recent British record. In contr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
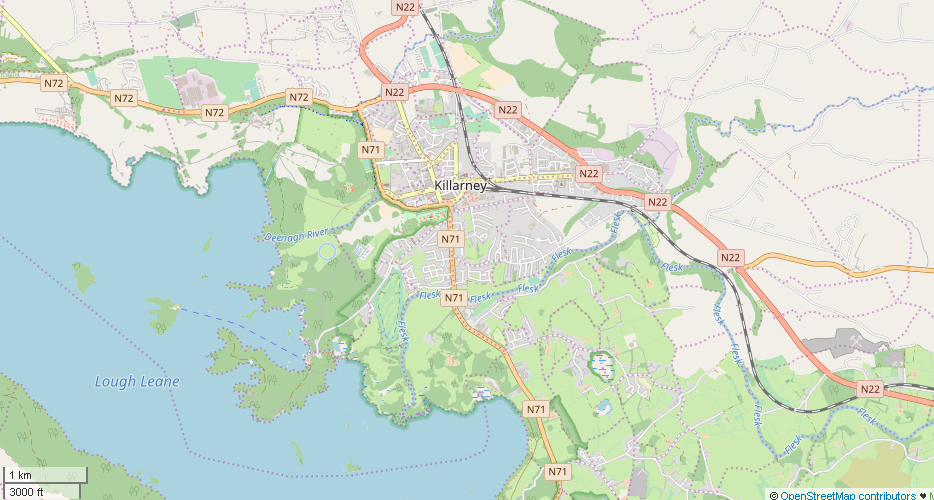
Killarney
Killarney ( ; ga, Cill Airne , meaning 'church of sloes') is a town in County Kerry, southwestern Ireland. The town is on the northeastern shore of Lough Leane, part of Killarney National Park, and is home to St Mary's Cathedral, Ross Castle, Muckross House and Abbey, the Lakes of Killarney, MacGillycuddy's Reeks, Purple Mountain, Mangerton Mountain, Paps Mountain, the Gap of Dunloe and Torc Waterfall. Its natural heritage, history and location on the Ring of Kerry make Killarney a popular tourist destination. Killarney won the Best Kept Town award in 2007, in a cross-border competition jointly organised by the Department of the Environment and the Northern Ireland Amenity Council. In 2011, it was named Ireland's tidiest town and the cleanest town in the country by Irish Business Against Litter. History Early history and development Killarney featured prominently in early Irish history, with religious settlements playing an important part of its recorded history. Its fi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tralee
Tralee ( ; ga, Trá Lí, ; formerly , meaning 'strand of the Lee River') is the county town of County Kerry in the south-west of Ireland. The town is on the northern side of the neck of the Dingle Peninsula, and is the largest town in County Kerry. The town's population (including suburbs) was 23,691 census, thus making it the eighth largest town, and List of urban areas in the Republic of Ireland by population, 14th largest urban settlement, in Ireland. Tralee is well known for the Rose of Tralee (festival), Rose of Tralee International Festival, which has been held annually in August since 1959. History Situated at the confluence of some small rivers and adjacent to marshy ground at the head of Tralee Bay, Tralee is located at the base of an ancient roadway that heads south over the Slieve Mish Mountains. On this old track is located a large boulder sometimes called Scotia's Grave, reputedly the burial place of an Egyptian Pharaoh's daughter. Anglo-Normans founded the to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ballymullen Barracks
Ballymullen Barracks () is an Defence Forces (Ireland), Irish military installation at Tralee, County Kerry in Ireland. History The barracks were built for local militia units between 1810 and 1815. In 1873 a system of recruiting areas based on counties was instituted under the Cardwell Reforms and the barracks became the Regimental depot, depot for the 101st Regiment of Foot (Royal Bengal Fusiliers) and 104th Regiment of Foot (Bengal Fusiliers). Following the Childers Reforms, the 101st and 104th regiments amalgamated to form the Royal Munster Fusiliers with its depot in the barracks in 1881. The Royal Munster Fusiliers were disbanded at the time at the establishment of the Irish Free State in 1922. The barracks were taken over by the Irish Republican Army in February 1922 and then secured by the forces of the Free State in August 1922. The barracks continued to be used by the Irish Army and a newly refurbished headquarters block was opened at the barracks in April 2002. The si ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Military Intelligence
Military intelligence is a military discipline that uses information collection and analysis approaches to provide guidance and direction to assist commanders in their decisions. This aim is achieved by providing an assessment of data from a range of sources, directed towards the commanders' mission requirements or responding to questions as part of operational or campaign planning. To provide an analysis, the commander's information requirements are first identified, which are then incorporated into intelligence collection, analysis, and dissemination. Areas of study may include the operational environment, hostile, friendly and neutral forces, the civilian population in an area of combat operations, and other broader areas of interest. Intelligence activities are conducted at all levels, from tactical to strategic, in peacetime, the period of transition to war, and during a war itself. Most governments maintain a military intelligence capability to provide analytical and i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fenit
Fenit () is a small village in County Kerry, Ireland, located on north side of Tralee Bay about west of Tralee town, just south of the Shannon Estuary. The bay is enclosed from the Atlantic by the Maharee spit which extends northwards from the Dingle peninsula. Fenit harbour is a mixed function sea port, where fishing, freight import and export, and a 136 berth marina are the main forms of business. As of the 2016 CSO census of Ireland, Fenit had a population of 538 people. History Saint Brendan, the navigator, was probably born north west of the village on Fenit Island in close proximity to what is now Fenit harbour around 484, and is honoured by a large bronze monument in the harbour area. It has been suggested that Brendan arrived in the Americas prior to Christopher Columbus but this has not been proven. Though Tim Severin demonstrated it is possible that a leather-clad boat such as the one described in the ''Navigatio'' could have potentially reached North America. In 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dublin Guard
The Dublin Guard was a unit of the Irish Republican Army during the Irish War of Independence and then of the Irish National Army in the ensuing Civil War. Foundation In May 1921 the Active Service Unit of the Irish Republican Army's Dublin Brigade and the "Squad" assassination unit were amalgamated. The Guard was created due to the heavy losses sustained by the Dublin Brigade in their burning of the Custom House on May 25, 1921. Five IRA volunteers were killed in the operation and eighty-three captured. Paddy Daly, previously head of the Squad, was put in command of the new unit. The Guard became part of the new National Army of the Irish Free State in January 1922. They were supportive of the Anglo-Irish Treaty which split the IRA, in large part because of their personal loyalty to Michael Collins. At this time, its numbers were greatly expanded from a core of IRA veterans to a battalion-sized unit, and eventually a brigade. The Dublin Guard provided most of the ceremonial parti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




_(cropped).jpg)
