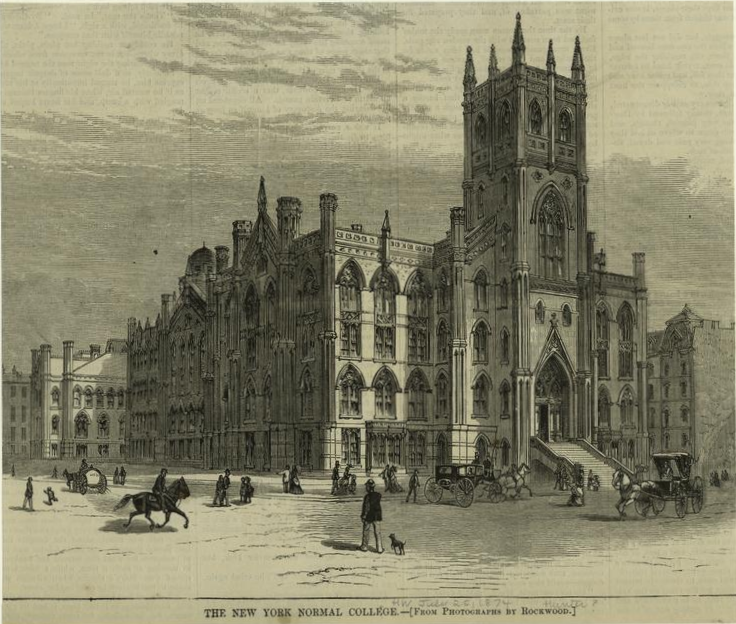|
David B. Zilberman
David Beniaminovich Zilberman (Russian language, Russian: Дави́д Бениами́нович Зильберма́н; May 25, 1938, Odessa – July 25, 1977, Boston) was a Russian-American philosopher and sociologist, scholar of Indian philosophy and culture. He was well-versed in the study of languages and knew Russian, Sanskrit, English, Slavic languages, Ancient Greek, French, and German. Life and work USSR David Zilberman was born in Odessa, Ukraine on May 25, 1938, to Benjamin Zilberman, an engineer-economist, and Riva Timaner, a medical doctor. He graduated from high school in 1955. In 1962, Zilberman was awarded an engineering and meteorology degree from The Odessa State College of Meteorology. From 1962 until 1966, Zilberman was employed as a meteorologist at the local airport in Ashgabat, Turkmenistan, in Central Asia. Zilberman began his Indological studies in 1962. He met and became friends with the academician :ru:Смирнов, Борис Леонидович, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Western Philosophy
Western philosophy encompasses the philosophical thought and work of the Western world. Historically, the term refers to the philosophical thinking of Western culture, beginning with the ancient Greek philosophy of the pre-Socratics. The word ''philosophy'' itself originated from the Ancient Greek (φιλοσοφία), literally, "the love of wisdom" grc, φιλεῖν , "to love" and σοφία '' sophía'', "wisdom"). History Ancient The scope of ancient Western philosophy included the problems of philosophy as they are understood today; but it also included many other disciplines, such as pure mathematics and natural sciences such as physics, astronomy, and biology (Aristotle, for example, wrote on all of these topics). Pre-Socratics The pre-Socratic philosophers were interested in cosmology; the nature and origin of the universe, while rejecting mythical answers to such questions. They were specifically interested in the (the cause or first principle) of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vijnanavada Buddhism
Yogachara ( sa, योगाचार, IAST: '; literally "yoga practice"; "one whose practice is yoga") is an influential tradition of Buddhist philosophy and psychology emphasizing the study of cognition, perception, and consciousness through the interior lens of meditative and yogic practices. It is also variously termed ''Vijñānavāda'' (the doctrine of consciousness), ''Vijñaptivāda'' (the doctrine of ideas or percepts) or ''Vijñaptimātratā-vāda'' (the doctrine of 'mere representation'), which is also the name given to its major epistemic theory. There are several interpretations of this main theory; while often regarded as a kind of Idealism, critical scholars argue that it is closer to a kind of phenomenology or representationalism, aimed at deconstructing the reification of our perceptions. According to Dan Lusthaus, this tradition developed "an elaborate psychological therapeutic system that mapped out the problems in cognition along with the antidotes to co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of Chicago
The University of Chicago (UChicago, Chicago, U of C, or UChi) is a private research university in Chicago, Illinois. Its main campus is located in Chicago's Hyde Park neighborhood. The University of Chicago is consistently ranked among the best universities in the world and it is among the most selective in the United States. The university is composed of an undergraduate college and five graduate research divisions, which contain all of the university's graduate programs and interdisciplinary committees. Chicago has eight professional schools: the Law School, the Booth School of Business, the Pritzker School of Medicine, the Crown Family School of Social Work, Policy, and Practice, the Harris School of Public Policy, the Divinity School, the Graham School of Continuing Liberal and Professional Studies, and the Pritzker School of Molecular Engineering. The university has additional campuses and centers in London, Paris, Beijing, Delhi, and Hong Kong, as well as in downtown ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hunter College
Hunter College is a public university in New York City. It is one of the constituent colleges of the City University of New York and offers studies in more than one hundred undergraduate and postgraduate fields across five schools. It also administers Hunter College High School and Hunter College Elementary School. Hunter was founded in 1870 as a women's college; it first admitted male freshmen in 1946. The main campus has been located on Park Avenue since 1873. In 1943, Eleanor Roosevelt dedicated Franklin Delano Roosevelt's and her former townhouse to the college; the building was reopened in 2010 as the Roosevelt House Public Policy Institute at Hunter College. The institution has an 57% undergraduate graduation rate within six years. History Founding Hunter College has its origins in the 19th-century movement for normal school training which swept across the United States. Hunter descends from the Female Normal and High School (later renamed the Normal College of the C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iron Curtain
The Iron Curtain was the political boundary dividing Europe into two separate areas from the end of World War II in 1945 until the end of the Cold War in 1991. The term symbolizes the efforts by the Soviet Union (USSR) to block itself and its satellite states from open contact with the West, its allies and neutral states. On the east side of the Iron Curtain were the countries that were connected to or influenced by the Soviet Union, while on the west side were the countries that were NATO members, or connected to or influenced by the United States; or nominally neutral. Separate international economic and military alliances were developed on each side of the Iron Curtain. It later became a term for the physical barrier of fences, walls, minefields, and watchtowers that divided the "east" and "west". The Berlin Wall was also part of this physical barrier. The nations to the east of the Iron Curtain were Poland, East Germany, Czechoslovakia, Hungary, Romania, Bulgaria, Albania, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tattvachintamani
Tattvachintamani is a treatise in Sanskrit authored by 14th-century CE Indian logician and philosopher Gangesa (fl. c. 1325). The title may be translated into English as "A Thought-jewel of Truth." The treatise is also known as Pramāṇa-chintāmaṇi ("A Thought-jewel of Valid Knowledge"). The treatise introduced a new era in the history of Indian logic. Satis Chandra Vidyabhusana in his authoritative 681-page history of Indian logic divided the millennia long history of Indian logic into three sometimes-overlapping periods: Ancient period (650 BCE100 CE), Medieval period (1001200 CE) and Modern period (from 900 CE). He also identified certain standard work as typical representative of each of these periods. Tattvachintamani of Gangesa is the text identified as the standard work of the Modern period in the history of Indian logic, the standard works for the earlier periods being Nyāya Sūtra by Akshapāda Gautama (Ancient period) and Pramāṇa-samuccaya by Dignāga Dign� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Boris Grushin
Boris Andreevich Grushin (russian: Бори́с Андре́евич Гру́шин; 2 August 1929, in Moscow – 18 September 2007, in Moscow) was a well-known Soviet and Russian philosopher, sociologist and historical and sociological scientist. He is generally seen as the pioneer of public opinion polling in the Soviet Union more than thirty years before its breakup. Prominent American novelist Olga Grushin is his daughter. Life and scientific activity Grushin graduated from the Faculty of Philosophy of the Lomonosov Moscow State University in 1952 with a dissertation on ''The Logical and Historical Problem in Marx's Capital''. In 1957 he completed his postgraduate study in the same place, with a thesis on ''Receptions and Ways of Reproducing the Thoughts of Historical Development''. At the same time in 1952 Grushin was one of the founders of the Moscow Logic Circle. Other members who entered the circle included Aleksandr Zinovyev, Merab Mamardashvili and Georgy Schedrovitsky ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Merab Mamardashvili
Merab Mamardashvili ( ka, მერაბ მამარდაშვილი, russian: Мера́б Константи́нович Мамардашви́ли; September 15, 1930 – November 25, 1990) was a Georgian philosopher. Biography He was born in Gori (Eastern Georgia). In 1955 he graduated from the Faculty of Philosophy of the Moscow State University. From 1968 to 1987 he was a deputy editor of the scientific journal "Voprosi Filosofii" ("Questions of Philosophy"). He became a professor of the Moscow State University and a senior research fellow of the Moscow Institute of Philosophy of the Russian Academy of Science. From 1987-1990 Mamardashvili was head of the Department of the Tsereteli Institute of Philosophy of the Georgian Academy of Sciences and Professor of the Tbilisi State University. In his life only a few books were published, his lectures (for his style of lecturing he and others called them "dialogues" or "conversations" and he was called "Russian (or Geor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Georgy Shchedrovitsky
Georgy Petrovich Shchedrovitsky (russian: Георгий Петрович Щедровицкий) (23 February 1929 – 3 February 1994) was a Russian philosopher and methodologist, public and cultural figure. The creator of the system-thinking methodology, the founder and leader of the Moscow methodological circle, the ideological inspirer of the "methodological movement." Early years Georgy Shchedrovitsky was born in Moscow in the family of the engineer and organizer of the Soviet aviation industry Pyotr Georgievich Shchedrovitsky (1899-1972) and the microbiologist Kapitolina Nikolaevna Shchedrovitskaya (née Bayukova, 1904-1994). He was great-nephew of Aaron Soltz. In 1937 he entered the second grade of Moscow secondary school No. 2, in which he studied before the evacuation of his family in the city of Kuibyshev. There, in parallel with his studies at a local school, he worked as a hospital orderly and a grinder at a military factory. In 1943, the family returned to Moscow, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Odessa State Environmental University
Odesa State Environmental University ( uk, Одеський державний екологічний університет) is a university in Odesa, Ukraine. History The university was founded on May 1, 1932 in Kharkiv as the Kharkiv Institute of Hydrometeorological Engineering. In the beginning of World War II the institute was evacuated to Ashgabat until August 1944. On July 4, 1944, it was relocated from Ashgabat to Odesa and renamed the Odesa Hydrometeorological Institute (OHMI). In 2001, the Odesa Hydrometeorological Institute received a new name - Odessa State Environmental University. Education at the school Institutes and faculties * Hydrometeorological Institute; * Faculty of Ecology and Economics; * Faculty of Conservation; * Faculty of Computer Science; * Faculty of Master's and Postgraduate Studies; * Correspondence department. Colleges * Odesa College of Computer Technology (formerly Odesa Machine Building College); * Kharkiv Hydrometeorological College ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |