|
Daurentius
Daurentius ( gr, Δαυρέντιος), Dauritas ( gr, Δαυρίτας), or Dobreta ( sr, Добрета) was a South Slavic (''Sclaveni'') chieftain. He seems to have been the supreme chief, having lesser ones subordinated to him. His realm was situated in the basin of the Zala river, roughly in the territory of the old Roman province of Pannonia Prima, in present-day Hungary. Daurentius is the first Slavic chieftain to be recorded by name, by the Byzantine historian Menander Protector, who reported that the Avar khagan Bayan I Bayan I reigned as the first khagan of the Avar Khaganate between 562 and 602. As the Göktürk Empire expanded westwards on the Eurasian Steppe during the 6th century, peoples such as the Avars (also known as the ''Pseudo-Avars'', ''Obri'' ... sent an embassy, asking Daurentius and his Slavs to accept Avar suzerainty and pay tribute, because the Avars knew that the Slavs had amassed great wealth after repeatedly plundering the Byzantine Balkan p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
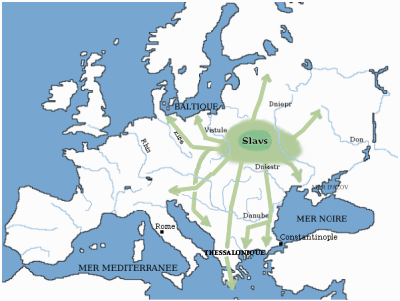
Sclaveni
The ' (in Latin) or ' (various forms in Greek, see below) were early Slavic tribes that raided, invaded and settled the Balkans in the Early Middle Ages and eventually became the progenitors of modern South Slavs. They were mentioned by early Byzantine chroniclers as barbarians having appeared at the Byzantine borders along with the Antes (East Slavs), another Slavic group. The Sclaveni were differentiated from the Antes and Wends (West Slavs); however, they were described as kin. Eventually, most South Slavic tribes accepted Byzantine or Frankish suzerainty, and came under their cultural influences and Chalcedonian Christianity. The term was widely used as general catch-all term until the emergence of separate tribal names by the 10th century. Customs The Sclaveni had similar if not identical customs and culture as the Antes. They were carefully described by chroniclers such as Procopius and Maurice, whose works contribute greatly to our understanding of these two Early Slavi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Slavic Mythology
Slavic mythology or Slavic religion is the religious beliefs, myths, and ritual practices of the Slavs before Christianisation, which occurred at various stages between the 8th and the 13th century. The South Slavs, who likely settled in the Balkan Peninsula during the 6th–7th centuries AD, bordering with the Byzantine Empire to the south, came under the sphere of influence of Eastern Christianity, beginning with the creation of writing systems for Slavic languages (first Glagolitic, and then Cyrillic script) in 855 by the brothers Saints Cyril and Methodius and the adoption of Christianity in Bulgaria in 863. The East Slavs followed with the official adoption in 988 by Vladimir the Great of Kievan Rus'. The West Slavs' process of Christianization was more gradual and complicated. The Moravians accepted Christianity as early as 831, the Bohemian dukes followed in 845, Slovaks accepted Christianity somewhere between the years 828 and 863, but the Poles accepted it much later ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zala River
The Zala is a river in south-western Hungary. Its source is in the hills northwest of Szalafő near the borders with Austria and Slovenia. Its length is and drains water from . Several smaller rivers feed into it, including the Felső-Válicka, Szentmihályfalvai patak (brook), Szévíz csatorna (channel), Foglár csatorna on the right bank, and Szentjakabi patak, Sárvíz (Zala) patak, Széplaki patak, Csörgető patak and Nádas patak on the left bank. It flows through the city of Zalaegerszeg before flowing into Lake Balaton near Keszthely. The River Zala flows through the Hungarian counties of Vas and Zala. See also Watermills on Zala River For centuries, the watermills on the Zala river (Zala County, Western Transdanubia, Hungary Hungary ( hu, Magyarország ) is a landlocked country in Central Europe. Spanning of the Pannonian Basin, Carpathian Basin, it is bordered by ... References External links Rivers of Hungary Geography of Vas Count ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman Province
The Roman provinces (Latin: ''provincia'', pl. ''provinciae'') were the administrative regions of Ancient Rome outside Roman Italy that were controlled by the Romans under the Roman Republic and later the Roman Empire. Each province was ruled by a Roman appointed as governor. For centuries it was the largest administrative unit of the foreign possessions of ancient Rome. With the administrative reform initiated by Diocletian, it became a third level administrative subdivision of the Roman Empire, or rather a subdivision of the imperial dioceses (in turn subdivisions of the imperial prefectures). Terminology The English word ''province'' comes from the Latin word ''provincia''. In early Republican times, the term was used as a common designation for any task or set of responsibilities assigned by the Roman Senate to an individual who held ''imperium'' (right of command), which was often a military command within a specified theatre of operations. In time, the term became t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pannonia Prima
Pannonia Prima was an ancient Roman province. It was formed in the year 296, during the reign of Emperor Diocletian. Previously, it was a part of the province of Pannonia Superior, which, along with Pannonia Inferior, was gradually divided into four administrative units: Pannonia Prima, Pannonia Secunda, Valeria, and Savia. This transition was completed by the time of Constantine. According to the Notitia Dignitatum, Pannonia Prima was governed by a . Geography Pannonia Prima included parts of present-day Hungary, Austria, Croatia, Slovenia, and Slovakia. Its capital was Savaria (modern Szombathely), a city built during the reign of Claudius. This city was located on an important junction between the Amber Road connecting Italy with Hungary and the road between Treveris and Sirmium. Other important cities were Vindobona (modern Vienna; in German), and Scarbantia (modern Sopron). The city of Sirmium in Pannonia Secunda had administrative oversight over all of the newly created ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hungary
Hungary ( hu, Magyarország ) is a landlocked country in Central Europe. Spanning of the Carpathian Basin, it is bordered by Slovakia to the north, Ukraine to the northeast, Romania to the east and southeast, Serbia to the south, Croatia and Slovenia to the southwest, and Austria to the west. Hungary has a population of nearly 9 million, mostly ethnic Hungarians and a significant Romani minority. Hungarian, the official language, is the world's most widely spoken Uralic language and among the few non-Indo-European languages widely spoken in Europe. Budapest is the country's capital and largest city; other major urban areas include Debrecen, Szeged, Miskolc, Pécs, and Győr. The territory of present-day Hungary has for centuries been a crossroads for various peoples, including Celts, Romans, Germanic tribes, Huns, West Slavs and the Avars. The foundation of the Hungarian state was established in the late 9th century AD with the conquest of the Carpathian Basin by Hungar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Byzantine
The Byzantine Empire, also referred to as the Eastern Roman Empire or Byzantium, was the continuation of the Roman Empire primarily in its eastern provinces during Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, when its capital city was Constantinople. It survived the fragmentation and fall of the Western Roman Empire in the 5th century AD and continued to exist for an additional thousand years until the fall of Constantinople to the Ottoman Empire in 1453. During most of its existence, the empire remained the most powerful economic, cultural, and military force in Europe. The terms "Byzantine Empire" and "Eastern Roman Empire" were coined after the end of the realm; its citizens continued to refer to their empire as the Roman Empire, and to themselves as Romans—a term which Greeks continued to use for themselves into Ottoman times. Although the Roman state continued and its traditions were maintained, modern historians prefer to differentiate the Byzantine Empire from Ancient Rome a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Menander Protector
Menander Protector (Menander the Guardsman, Menander the Byzantian; el, Μένανδρος Προτήκτωρ or Προτέκτωρ), Byzantine historian, was born in Constantinople in the middle of the 6th century AD. The little that is known of his life is contained in the account of himself quoted in the '' Suda'' (Mu, 591: Μένανδρος). Menander mentions his father Euphratas, who came from Byzantium, and his brother Herodotus. He at first took up the study of law, but abandoned it for a life of pleasure. When his fortunes were low, the patronage accorded to literature by the Emperor Maurice, at whose court he was a military officer (hence the epithet ''Protector'', which denotes his military function), encouraged him to try writing history. Menander took as his model Agathias who like him had been a jurist, and his history begins at the point where Agathias leaves off. It embraces the period from the arrival of the Kutrigurs in Thrace during the reign of Justinian in 558 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Avars (Carpathians)
The Pannonian Avars () were an alliance of several groups of Eurasian nomads of various origins. The peoples were also known as the Obri in chronicles of Rus, the Abaroi or Varchonitai ( el, Βαρχονίτες, Varchonítes), or Pseudo-Avars in Byzantine sources, and the Apar ( otk, 𐰯𐰺) to the Göktürks (). They established the Avar Khaganate, which spanned the Pannonian Basin and considerable areas of Central and Eastern Europe from the late 6th to the early 9th century. The name Pannonian Avars (after the area in which they settled) is used to distinguish them from the Avars of the Caucasus, a separate people with whom the Pannonian Avars might or might not have had links. Although the name ''Avar'' first appeared in the mid-5th century, the Pannonian Avars entered the historical scene in the mid-6th century, on the Pontic–Caspian steppe as a people who wished to escape the rule of the Göktürks. They are probably best known for their invasions and destruction in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Khagan
Khagan or Qaghan (Mongolian:; or ''Khagan''; otk, 𐰴𐰍𐰣 ), or , tr, Kağan or ; ug, قاغان, Qaghan, Mongolian Script: ; or ; fa, خاقان ''Khāqān'', alternatively spelled Kağan, Kagan, Khaghan, Kaghan, Khakan, Khakhan, Khaqan, Xagahn, Qaghan, Chagan, Қан, or Kha'an is a title of imperial rank in the Turkic, Mongolic and some other languages, equal to the status of emperor and someone who rules a khaganate (empire). The female equivalent is Khatun. It may also be translated as " Khan of Khans", equivalent to King of Kings. In Bulgarian, the title became known as ''Khan'', while in modern Turkic, the title became ''Khaan'' with the ''g'' sound becoming almost silent or non-existent; the ''ğ'' in modern Turkish ''Kağan'' is also silent. Since the division of the Mongol Empire, monarchs of the Yuan dynasty and the Northern Yuan held the title of ''Khagan''. ''Kağan, Hakan'' and ''Kaan'', Turkish equivalents of the title are common Turkish names ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bayan I
Bayan I reigned as the first khagan of the Avar Khaganate between 562 and 602. As the Göktürk Empire expanded westwards on the Eurasian Steppe during the 6th century, peoples such as the Avars (also known as the ''Pseudo-Avars'', ''Obri'', ''Abaroi'' and ''Varchonites'') and the Bulgars migrated into Central Europe and the Balkans. Bayan I led the Avars (along with some Bulgars) into Pannonia, where they established their khaganate from 568. Raids against the Franks and Lombards By 562, the Avars and Bulgars had reached the Lower Danube: it was most likely in that year that Bayan became their supreme Khagan, as his predecessor, the Kutrigur khan Zabergan had died. As allies of the Byzantine Empire (ruled at time by Justinian I), the Avars had obtained a grant of gold to crush other nomads — the Sabirs, Utigurs, Kutrigurs and Saragurs - in the lands later known as Ukraine, a task they accomplished to the emperor's satisfaction. Bayan's Avars now exacted the renewal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
South Slavic History
South is one of the cardinal directions or compass points. The direction is the opposite of north and is perpendicular to both east and west. Etymology The word ''south'' comes from Old English ''sūþ'', from earlier Proto-Germanic ''*sunþaz'' ("south"), possibly related to the same Proto-Indo-European root that the word ''sun'' derived from. Some languages describe south in the same way, from the fact that it is the direction of the sun at noon (in the Northern Hemisphere), like Latin meridies 'noon, south' (from medius 'middle' + dies 'day', cf English meridional), while others describe south as the right-hand side of the rising sun, like Biblical Hebrew תֵּימָן teiman 'south' from יָמִין yamin 'right', Aramaic תַּימנַא taymna from יָמִין yamin 'right' and Syriac ܬܰܝܡܢܳܐ taymna from ܝܰܡܝܺܢܳܐ yamina (hence the name of Yemen, the land to the south/right of the Levant). Navigation By convention, the ''bottom or down-facing side'' of a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |