|
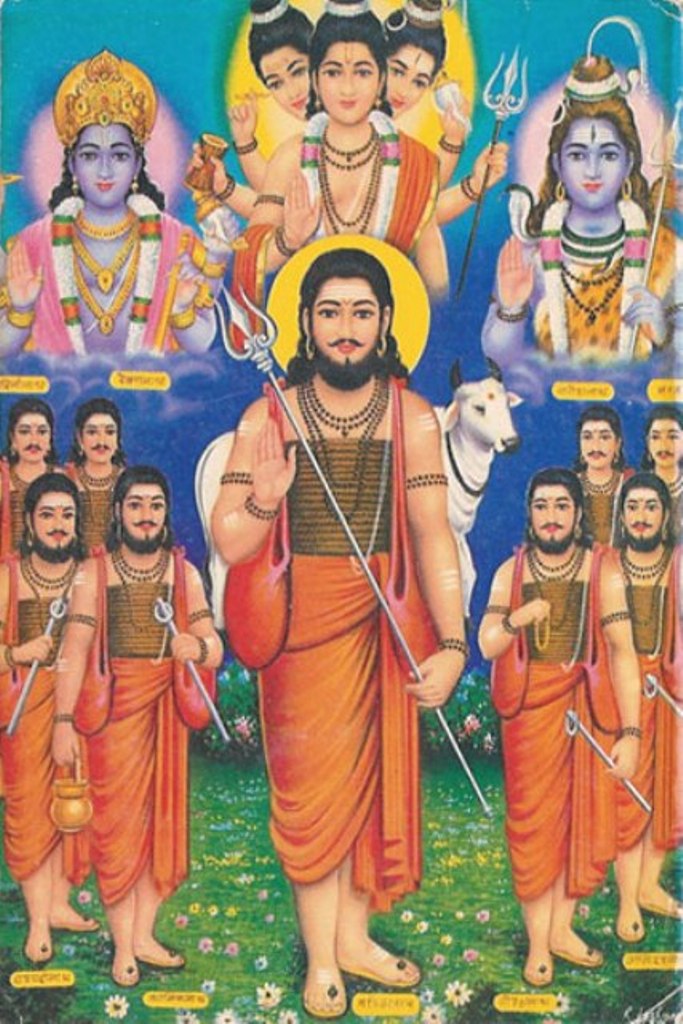
Dasbodh
''Dāsbodh'', loosely meaning "advice to the disciple" in Marathi, is a 17th-century bhakti (devotion) and jnana (insight) spiritual text. It was orally narrated by the saint Samarth Ramdas to his disciple, Kalyan Swami. The ''Dāsbodh'' provides readers with spiritual guidance on matters such as devotion and acquiring knowledge. Besides this, it also helps in answering queries related to day-to-day life and how to find solutions to it. Background The ''Dāsbodha'' was written in 1654 by Samarth Ramdas Swāmi (1608-1681), a satguru, a Hindu saint from Maharashtra, in the local Marathi language. It is a comprehensive volume in verse form providing instructions on the religious life, presented in the format of a conversation between a Guru and disciple. The narration is believed to have taken place in a cave called Shivthar Ghal (pronounced shiv-ther-gaal) in the Raigad district of Maharashtra. Style ''Dāsbodh'' is written in the verse form known as ''owi'' (''ōvyā'') in Mar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Samarth Ramdas
Samarth Ramdas (c. 1608 - c. 1681), also known as Sant Ramdas or Ramdas Swami, was an Indian Hindu saint, philosopher, poet, writer and spiritual master. He was a devotee of the Hindu deities Rama and Hanuman. Early life Ramdas or previously Narayan was born at Jamb, a village in present-day Jalna district, Maharashtra on the occasion of Rama Navami, probably in 1608. He was born into a Marathi Deshastha Rigvedi Brahmin family to Suryajipanta and Ranubai Thosar. His father was a devotee of Surya, the Vedic solar deity. Ramdas had an elder brother named Gangadhar. His father died when Narayan was around seven years of age. Narayan turned into an introvert after the demise of his father and was often noticed to be engrossed in thoughts about the divine. According to legend, Narayan fled his wedding ceremony upon hearing a pundit chant the word 'Saavdhan' (Beware!) during a customary Hindu wedding ritual. Then at the age of twelve, he is believed to have walked to Panchavati, a H ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Siddharameshwar Maharaj
Sri Siddharameshwar Maharaj (1888–1936) was a guru in the Inchagiri Sampradaya founded by his guru Bhausaheb Maharaj, a branch of the Navnath Sampradaya, the 'Nine Masters' tradition in India. His disciples included Nath teachers Nisargadatta Maharaj, Ranjit Maharaj, Kaadsiddheshwar, and Ganapatrao Maharaj Kannur. Biography Siddharameshwar was born in 1888 in the village Pathri, Solapur, India. Since his childhood, he was very intelligent and had very sharp imbibe abilities. In 1906, he was initiated by his guru 'Shri Bhausaheb Maharaj' in Inchagiri in Karnataka India, who taught mantra meditation as the way to reach Final Reality. He was one of the contemporaries of Sri Ramana Maharshi. In 1920, Siddharameshwar started to set out on "the Bird's Path", the fast way to attain realization, six years after Bhauhaseb maharaj had died. His fellow-students opposed, but eventually he succeeded by himself. Siddharameshwar died on 9 November 1936 (Ekadashi, 11th day in the later h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inchegeri Sampradaya
The Inchagiri Sampradaya, also known as Nimbargi Sampradaya, is a lineage of Hindu Navnath and Lingayat teachers from Maharashtra which was started by Bhausaheb Maharaj. It is inspired by Sant Mat teachers as Namdev, Raidas and Kabir. The Inchagiri Sampradaya has become well known throughout the western world due to the popularity of Nisargadatta Maharaj. History Navnath Dattatreya The mythological origins of the Inchagiri Sampradaya are ascribed to Adiguru Shri Dattatreya. He initiated the Navanaths, the Holy Nine Gurus, and the Navanath Sampraday. Revananath – Siddhagiri Math (Kaneri Math) One of those Navnaths was Revanath, the 7th or 8th Navnath. Revanath settled on the Siddhgiri hill for ascetic practice, living on whatever the jungle, gave him. He became famous as Kaadhsiddheshwar, "the one who attained supreme realization in a forest". Revananath is considered to have established the Kaadsiddheshwar temple and math, also called ''Kaadsiddheshwar Peeth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shivthar Ghal
Shivthar Ghal, also known as Sundarmath, (Sundarmath means Beautiful Monastery), is a cave, about 34 km from Mahad, near Barasgaon, Maharashtra, India. Shivthar Ghal is located in Varandha Ghat in the Sahyadris on the Bhor-Mahad road. In monsoons, a waterfall falls in front of the cave. Samarth Ramdas dictated Dasbodh to Kalyan Swami. Samarth Ramdas lived here for about 22 years. It is believed that this is where the first meeting between Maratha king Chatrapati Shivaji Maharaj and Samarth Ramdas took place. The cave was discovered by Shankarrao Deo of Dhule in 1930. The cave and surrounding area was renovated after Samarth Seva Mandal was formed in 1950. The campus includes the actual cave under the waterfall, Ramdas Swami temple, dining hall and accommodation. Between 12:00 pm and 1:30 pm, the visitors can have the prasad 200px, Prasad thaal offered to Swaminarayan temple in Ahmedabad ">Shri Swaminarayan Mandir, Ahmedabad">Swaminarayan temple in Ahmedabad Prasada ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Samarth Ramdas Swami , Indian filmmaker
{{Disambiguation ...
Samarth may refer to: *Samarth-class offshore patrol vessel *Mukherjee-Samarth family *Swami Samarth, Indian guru *Ravikumar Samarth, Indian cricketer *Nitin Samarth, American physicist *Shobhna Samarth, Indian actress *Tanuja Samarth, Indian actress *Shri Samarth High School, Amravati, Indian high school *Samarth Ramdas, Indian saint *Samarth Vyas, Indian cricketer *Kumarsen Samarth Kumarsen Samarth ( mr, कुमारसेन समर्थ) was an Indian film director. He belonged to a Marathi CKP family. His inclination towards the Marathi language led him to direct some great Marathi/Hindi movies such as ''Nal Damyan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marathi-language Literature
Marathi (; ''Marāṭhī'', ) is an Indo-Aryan language predominantly spoken by Marathi people in the Indian state of Maharashtra. It is the official language of Maharashtra, and additional official language in the state of Goa. It is one of the 22 scheduled languages of India, with 83 million speakers as of 2011. Marathi ranks 11th in the list of languages with most native speakers in the world. Marathi has the third largest number of native speakers in India, after Hindi and Bengali. The language has some of the oldest literature of all modern Indian languages. The major dialects of Marathi are Standard Marathi and the Varhadi dialect. Marathi distinguishes inclusive and exclusive forms of 'we' and possesses a three-way gender system, that features the neuter in addition to the masculine and the feminine. In its phonology, it contrasts apico-alveolar with alveopalatal affricates and alveolar with retroflex laterals ( and (Marathi letters and respectively). History ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Advaita
''Advaita Vedanta'' (; sa, अद्वैत वेदान्त, ) is a Hindu sādhanā, a path of spiritual discipline and experience, and the oldest extant tradition of the orthodox Hindu school Vedānta. The term ''Advaita'' (literally "non-secondness", but usually rendered as "nondualism", and often equated with monism) refers to the idea that ''Brahman'' alone is ultimately real, while the transient phenomenal world is an illusory appearance (''maya'') of Brahman. In this view, (''jiv) Ātman'', the experiencing self, and ''Ātman-Brahman'', the highest Self and Absolute Reality, is non-different. The ''jivatman'' or individual self is a mere reflection or limitation of singular ''Ātman'' in a multitude of apparent individual bodies. In the Advaita tradition, ''moksha'' (liberation from suffering and rebirth) is attained through recognizing this illusoriness of the phenomenal world and disidentification from the body-mind complex and the notion of 'doership' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Advait Mat
Advait Mat or Paramhans Advait Mat is a cluster of panths (groups of disciples) in northern India. It was founded by Shri Swami Advaitanand Ji Maharaj (1846-1919) who is also known as Paramhans Dyal Ji Maharaj. He declared Swami Swarupanand Ji Maharaj ( also known as Shri Nangli Niwasi Bhagwan Ji) as his spiritual successor. Swami Swarupanand Ji Maharaj founded more than 300 ashrams with the purpose of disseminating his master's teachings. Swami Swarupanand Ji Maharaj had initiated more than thousand of his disciples into the sanyas. Many of his disciples went on to establish spiritual institutions to spread the same knowledge. The ashrams founded by Shri Paramahans Dyal Ji were called Krishna Dwaras. The ashrams with the name Adwait-Swarup Ashram, Paramhans Satyarthi Dham, Shri Anandpur Satsang Ashram are also related to him and Shri Paramhans Advait Mat. Reportedly, they perceive themselves to be originating from Totapuri in the 18th century, who was the guru of Ramakrishna ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
17th-century Indian Books
The 17th century lasted from January 1, 1601 ( MDCI), to December 31, 1700 ( MDCC). It falls into the early modern period of Europe and in that continent (whose impact on the world was increasing) was characterized by the Baroque cultural movement, the latter part of the Spanish Golden Age, the Dutch Golden Age, the French ''Grand Siècle'' dominated by Louis XIV, the Scientific Revolution, the world's first public company and megacorporation known as the Dutch East India Company, and according to some historians, the General Crisis. From the mid-17th century, European politics were increasingly dominated by the Kingdom of France of Louis XIV, where royal power was solidified domestically in the civil war of the Fronde. The semi-feudal territorial French nobility was weakened and subjugated to the power of an absolute monarchy through the reinvention of the Palace of Versailles from a hunting lodge to a gilded prison, in which a greatly expanded royal court could be more easily k ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1654 Books
Events January–March * January 6– In India, Jaswant Singh of Marwar (in what is now the state of Rajasthan) is elevated to the title of Maharaja by Emperor Shah Jahan. * January 11– In the Battle of Río Bueno in southern Chile during the Arauco War, the indigenous Huilliche warriors rout Spanish troops from Fort Nacimiento who are attempting to cross the Bueno River. * January 26– Portugal recaptures the South American city of Recife from the Netherlands after a siege of more than two years during the Dutch-Portuguese War, bringing an end to Dutch rule of what is now Brazil. The Dutch West India Company had held the city (which they called Mauritsstad) for more than 23 years. * February 9– Spanish troops led by Don Gabriel de Rojas y Figueroa successfully attack the Fort de Rocher, a pirate-controlled base on the Caribbean island of Tortuga. * February 10– The Battle of Tullich takes place in Aberdeenshire in Scotland during Gle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hindu Texts
Hindu texts are manuscripts and voluminous historical literature which are related to any of the diverse traditions within Hinduism. A few of these texts are shared across these traditions and they are broadly considered Hindu scriptures. These include the Puranas, Itihasa and Vedas. Scholars hesitate in defining the term "Hindu scriptures" given the diverse nature of Hinduism,Dominic Goodall (1996), Hindu Scriptures, University of California Press, , page ix-xliii but many list the Bhagavad Gita and the Agamas as Hindu scriptures,Klaus Klostermaier (2007), A Survey of Hinduism: Third Edition, State University of New York Press, , pages 46–52, 76–77 and Dominic Goodall includes Bhagavata Purana and Yajnavalkya Smriti in the list of Hindu scriptures as well. History There are two historic classifications of Hindu texts: ''Śruti'' – that which is heard, and ''Smriti'' – that which is remembered. The ''Shruti'' refers to the body of most authoritative, ancient religious ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |