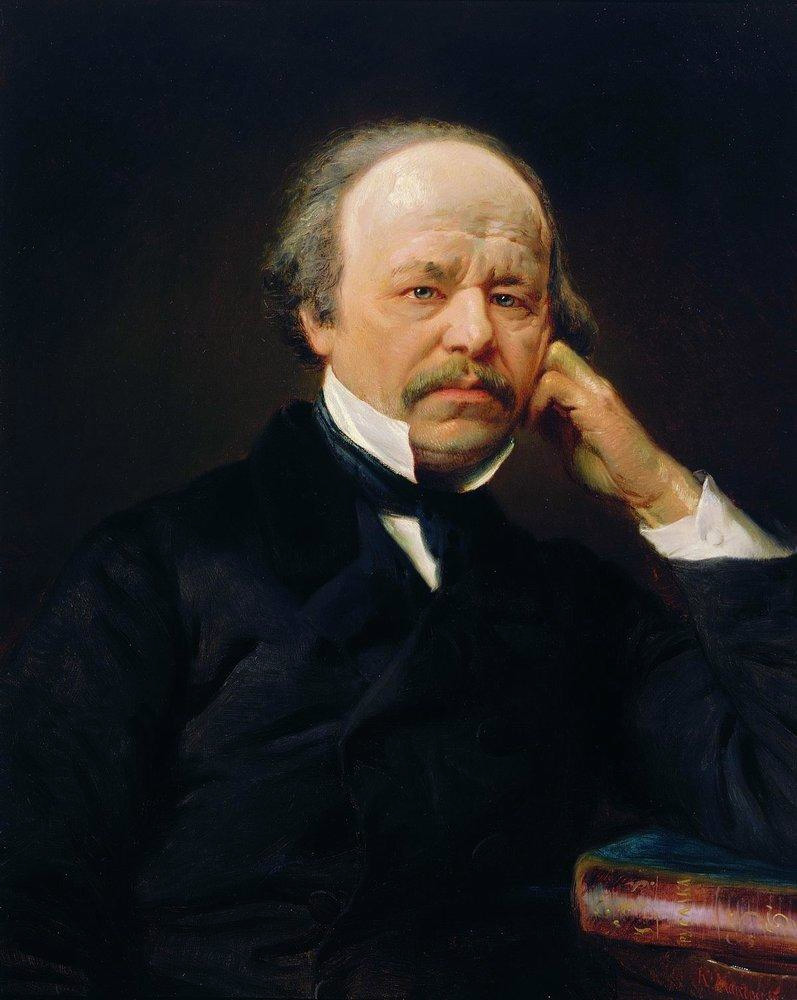|
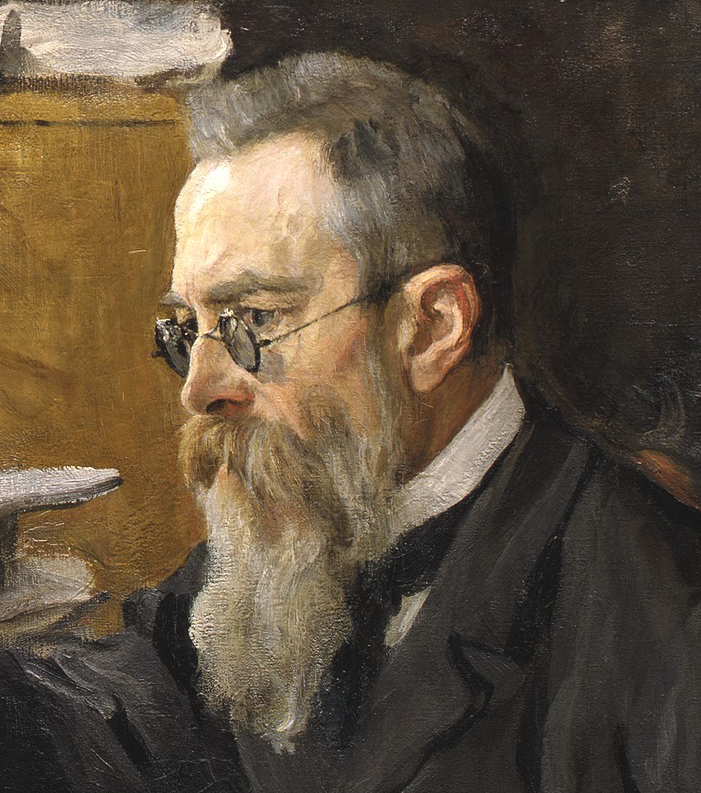
Dargomyzhsky
Alexander Sergeyevich Dargomyzhsky ( rus, link=no, Александр Сергеевич Даргомыжский, Aleksandr Sergeyevich Dargomyzhskiy., ɐlʲɪkˈsandr sʲɪrˈɡʲe(j)ɪvʲɪdʑ dərɡɐˈmɨʂskʲɪj, Ru-Aleksandr-Sergeevich-Dargomyzhsky.ogg; ) was a 19th-century Russian composer. He bridged the gap in Russian opera composition between Mikhail Glinka and the later generation of The Five and Pyotr Ilyich Tchaikovsky. Biography Dargomyzhsky was born in village Troitskoye, Belyov uyezd, Tula Governorate (now Arsenyevsky District, Tula Oblast), and educated in Saint Petersburg. He was already known as a talented musical amateur when in 1833 he met Mikhail Glinka and was encouraged to devote himself to composition. His opera '' Esmeralda'' (libretto by composer, based on Victor Hugo's ''The Hunchback of Notre Dame'') was composed in 1839 (performed 1847), and his ''Rusalka'' was performed in 1856; but he had little success or recognition either at home or abroad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Stone Guest (Dargomyzhsky)
''The Stone Guest'' (''Каменный гость'' in Cyrillic script, Cyrillic, ''Kamennyj gost' '' in transliteration) is an opera in three acts by Alexander Dargomyzhsky from a libretto taken almost verbatim from Alexander Pushkin's 1830 The Stone Guest (play), play of the same name which had been written in blank verse and which forms part of his collection ''Little Tragedies''. It was first performed at the Mariinsky Theatre, Saint Petersburg, 16 February 1872 (Old Style and New Style dates, Old Style). According to the composer's wishes, the last few lines of tableau 1 were composed by César Cui, and the whole was orchestrated by Nikolai Rimsky-Korsakov. Many years later, Rimsky-Korsakov revised his own orchestration of the opera, rewrote a few of Dargomyzhsky's own original passages, and added an orchestral prelude. This version, completed in 1903 and first performed in 1907 at the Bolshoi Theatre, is now considered the standard version. Performance History The Austrian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rusalka (Dargomyzhsky)
''Rusalka'' ( rus, Русалка, Rusálka ) is an opera in four acts, six tableaux, by Alexander Dargomyzhsky, composed during 1848-1855. The Russian libretto was adapted by the composer from Aleksandr Pushkin's incomplete dramatic poem of the same name. It premiered on 4 May 1856 (Old Style) at the Theatre-circus, conducted by Konstantin Lyadov (father of Anatoly Lyadov), choreographed by Marius Petipa and Nikolay Goltz, but was badly received predominantly by the aristocracy. In 1859, the opera was again presented at the Bolshoi Theatre in Moscow, but it was not until 1865, when it was staged at the Mariinsky Theatre, that it was finally well received. The conductor was Eduard Nápravník; the Prince was sung by Fyodor Petrovich Komissarzhevsky, the Princess by Darya Leonova, Miller by Osip Petrov, and Natasha by Yulya Platonova. Although much of Dargomyzhsky's ''Rusalka'' is fairly conventional in musical form and style, its singular innovation for the history of Russia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nikolai Rimsky-Korsakov
Nikolai Andreyevich Rimsky-Korsakov . At the time, his name was spelled Николай Андреевичъ Римскій-Корсаковъ. la, Nicolaus Andreae filius Rimskij-Korsakov. The composer romanized his name as ''Nicolas Rimsky-Korsakow''.The BGN/PCGN transliteration of Russian is used for his name here. ALA-LC system: Nikolaĭ Andrevich Rimskiĭ-Korsakov, ISO 9 system: Nikolaj Andreevič Rimskij-Korsakov. (18 March 1844 – 21 June 1908) was a Russian composer, a member of the group of composers known as The Five. He was a master of orchestration. His best-known orchestral compositions—'' Capriccio Espagnol'', the ''Russian Easter Festival Overture'', and the symphonic suite ''Scheherazade''—are staples of the classical music repertoire, along with suites and excerpts from some of his 15 operas. ''Scheherazade'' is an example of his frequent use of fairy-tale and folk subjects. Rimsky-Korsakov believed in developing a nationalistic style of classical ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alexander Pushkin
Alexander Sergeyevich Pushkin (; rus, links=no, Александр Сергеевич ПушкинIn pre-Revolutionary script, his name was written ., r=Aleksandr Sergeyevich Pushkin, p=ɐlʲɪkˈsandr sʲɪrˈɡʲe(j)ɪvʲɪtɕ ˈpuʂkʲɪn, a=ru-Pushkin.ogg; ) was a Russian poet, playwright, and novelist of the Romantic era.Basker, Michael. Pushkin and Romanticism. In Ferber, Michael, ed., ''A Companion to European Romanticism''. Oxford: Blackwell, 2005. He is considered by many to be the greatest Russian poetShort biography from University of Virginia . Retrieved 24 November 2006.Allan Rei ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Five (composers)
The Five ( rus, link=no, Могучая кучка, lit. ''Mighty Bunch''), also known as the Mighty Handful, The Mighty Five, and the New Russian School, were five prominent 19th-century Russian composers who worked together to create a distinct national style of classical music: Mily Balakirev (the leader), César Cui, Modest Mussorgsky, Nikolai Rimsky-Korsakov and Alexander Borodin. They lived in Saint Petersburg, and collaborated from 1856 to 1870. History Name In May 1867 the critic Vladimir Stasov wrote an article, titled ''Mr. Balakirev's Slavic Concert'', covering a concert that had been performed for visiting Slav delegations at the "All-Russian Ethnographical Exhibition" in Moscow. The four Russian composers whose works were played at the concert were Mikhail Glinka, Alexander Dargomyzhsky, Mily Balakirev, and Nikolai Rimsky-Korsakov. The article ended with the following statement: The expression "mighty handful" (russian: Могучая кучка, ''Moguchaya ku ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Esmeralda (Dargomyzhsky)
Esmeralda may refer to: Places * Esmeralda, Queensland, a locality in the Shire of Croydon, Australia * Esmeralda Municipality, Oruro Department, Bolivia * Esmeralda, Rio Grande do Sul, a municipality in Brazil * Esmeralda, a town in Chile * Esmeralda Island, Chile * Esmeralda, Cuba * Esmeralda County, Nevada, United States Arts and entertainment ''The Hunchback of Notre Dame'' * Esmeralda (''The Hunchback of Notre-Dame''), a character in Victor Hugo's novel and its adaptations * ''Esmeralda'' (opera), an 1883 English opera by Arthur Goring Thomas * ''La Esmeralda'' (opera), a 1836 French opera by Louise Bertin * ''La Esmeralda'' (ballet), an 1844 ballet * ''Esmeralda'' (Dargomyzhsky), an 1847 opera by Alexander Dargomyzhsky * ''Esmeralda'' (1905 film), a French short silent film * ''Esmeralda'' (1922 film), a British silent film Television * ''Esmeralda'' (Mexican TV series), a telenovela on El Canal de las Estrellas * ''Esmeralda'' (Venezuelan TV series), a program b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mikhail Glinka
Mikhail Ivanovich Glinka ( rus, link=no, Михаил Иванович Глинка, Mikhail Ivanovich Glinka., mʲɪxɐˈil ɪˈvanəvʲɪdʑ ˈɡlʲinkə, Ru-Mikhail-Ivanovich-Glinka.ogg; ) was the first Russian composer to gain wide recognition within his own country and is often regarded as the fountainhead of Russian classical music. His compositions were an important influence on Russian composers, notably the members of The Five (composers), The Five, who produced a distinctive Russian style of music. Early life and education Glinka was born in the village of Novospasskoye, not far from the Desna River in the Smolensk Governorate of the Russian Empire (now in the Yelninsky District of the Smolensk Oblast). His wealthy father had retired as an army captain, and the family had a strong tradition of loyalty and service to the tsars, and several members of his extended family had lively cultural interests. His great-great-grandfather was a Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Hunchback Of Notre Dame
''The Hunchback of Notre-Dame'' (french: Notre-Dame de Paris, translation=''Our Lady of Paris'', originally titled ''Notre-Dame de Paris. 1482'') is a French Gothic novel by Victor Hugo, published in 1831. It focuses on the unfortunate story of Quasimodo, the Gypsy street dancer Esmeralda and Quasimodo's guardian the Archdeacon Claude Frollo in 15th-century Paris. All its elements—Renaissance setting, impossible love affairs, marginalized characters—make the work a model of the literary themes of Romanticism. The novel has been described as a key text in French literature and has been adapted for film over a dozen times, in addition to numerous television and stage adaptations, such as a 1923 silent film with Lon Chaney, a 1939 sound film with Charles Laughton, and a 1996 Disney animated film with Tom Hulce. The novel sought to preserve values of French culture in a time period of great change, which resulted in the destruction of many French Gothic structures. The nov ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
César Cui
César Antonovich Cui ( rus, Це́зарь Анто́нович Кюи́, , ˈt͡sjezərʲ ɐnˈtonəvʲɪt͡ɕ kʲʊˈi, links=no, Ru-Tsezar-Antonovich-Kyui.ogg; french: Cesarius Benjaminus Cui, links=no, italic=no; 13 March 1918) was a Russian composer and music critic, member of the Belyayev circle and The Five – a group of composers combined by the idea of creating a specifically Russian type of music. As an officer of the Imperial Russian Army he rose to the rank of Engineer-General (equivalent to full General), taught fortifications in Russian military academies and wrote a number of monographs on the subject. Biography Upbringing and career Cesarius-Benjaminus Cui was born in Wilno, Vilna Governorate of the Russian Empire (now Vilnius, Lithuania) into a Roman Catholic family of French and Polish– Lithuanian descent, the youngest of five children. The original French spelling of his surname was "Queuille". His French father, Antoine (Anton Leonardovic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Male Opera Composers
Male ( symbol: ♂) is the sex of an organism that produces the gamete (sex cell) known as sperm, which fuses with the larger female gamete, or ovum, in the process of fertilization. A male organism cannot reproduce sexually without access to at least one ovum from a female, but some organisms can reproduce both sexually and asexually. Most male mammals, including male humans, have a Y chromosome, which codes for the production of larger amounts of testosterone to develop male reproductive organs. Not all species share a common sex-determination system. In most animals, including humans, sex is determined genetically; however, species such as ''Cymothoa exigua'' change sex depending on the number of females present in the vicinity. In humans, the word ''male'' can also be used to refer to gender in the social sense of gender role or gender identity. Overview The existence of separate sexes has evolved independently at different times and in different lineages, an example ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Burials At Tikhvin Cemetery
Burial, also known as interment or inhumation, is a method of final disposition whereby a dead body is placed into the ground, sometimes with objects. This is usually accomplished by excavating a pit or trench, placing the deceased and objects in it, and covering it over. A funeral is a ceremony that accompanies the final disposition. Humans have been burying their dead since shortly after the origin of the species. Burial is often seen as indicating respect for the dead. It has been used to prevent the odor of decay, to give family members closure and prevent them from witnessing the decomposition of their loved ones, and in many cultures it has been seen as a necessary step for the deceased to enter the afterlife or to give back to the cycle of life. Methods of burial may be heavily ritualized and can include natural burial (sometimes called "green burial"); embalming or mummification; and the use of containers for the dead, such as shrouds, coffins, grave liners, and bu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
19th-century Male Musicians
The 19th (nineteenth) century began on 1 January 1801 ( MDCCCI), and ended on 31 December 1900 ( MCM). The 19th century was the ninth century of the 2nd millennium. The 19th century was characterized by vast social upheaval. Slavery was abolished in much of Europe and the Americas. The First Industrial Revolution, though it began in the late 18th century, expanding beyond its British homeland for the first time during this century, particularly remaking the economies and societies of the Low Countries, the Rhineland, Northern Italy, and the Northeastern United States. A few decades later, the Second Industrial Revolution led to ever more massive urbanization and much higher levels of productivity, profit, and prosperity, a pattern that continued into the 20th century. The Islamic gunpowder empires fell into decline and European imperialism brought much of South Asia, Southeast Asia, and almost all of Africa under colonial rule. It was also marked by the collapse of the large S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |