|
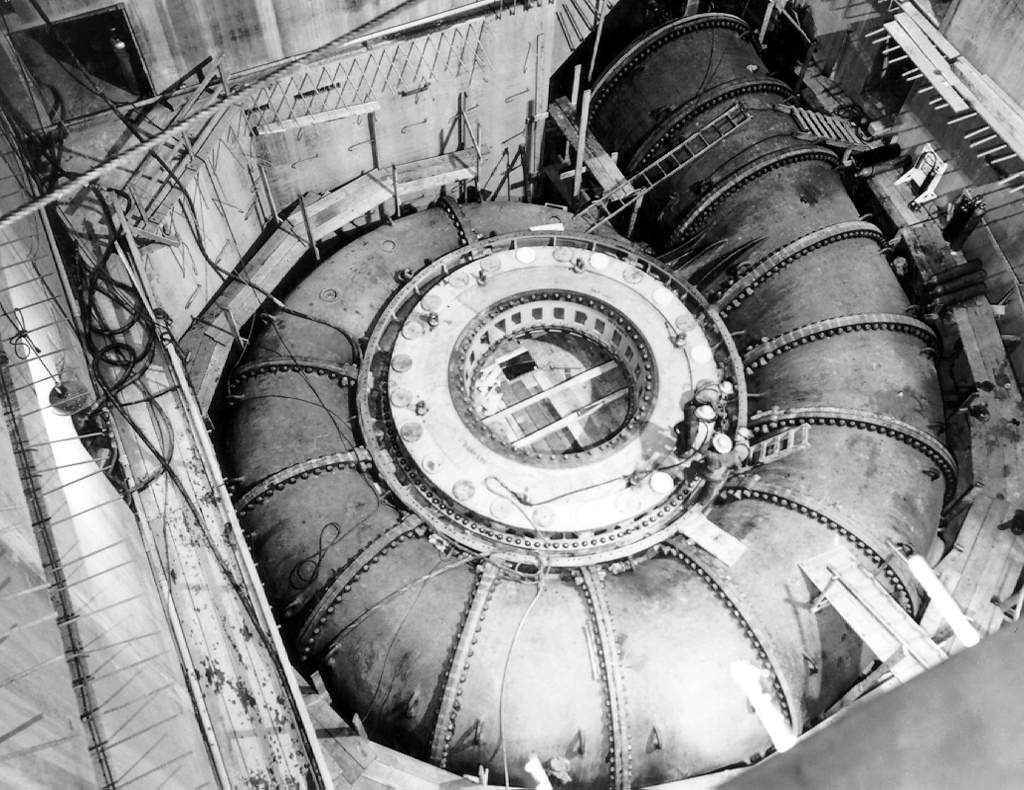
Darbandikhan Dam
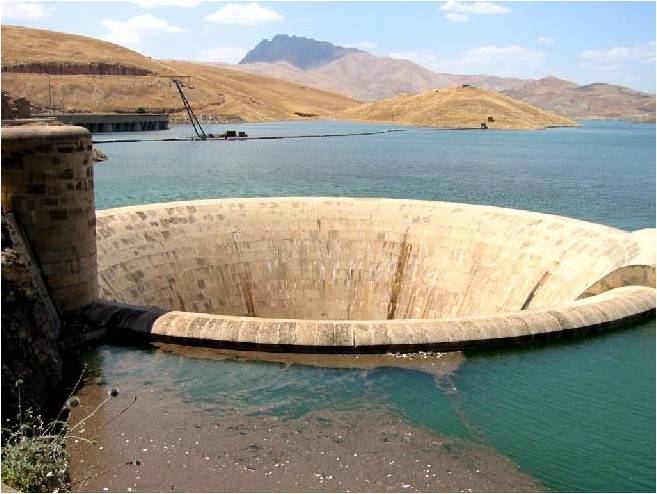
The Darbandikhan Dam ( ku, Bendava Derbendîxanê ,بەنداوی دەربەندیخان) is a multi-purpose embankment dam on the Diyala River in northern Sulaymaniyah Governorate, Iraq. It was constructed between 1956 and 1961. The purpose of the dam is irrigation, flood control, hydroelectric power production and recreation. Due to poor construction and neglect, the dam and its 249 MW power station have undergone several repairs over the years. A rehabilitation of the power station began in 2007 and was completed in 2013. Background After the Harza Engineering Company of USA designed the dam, construction began in 1956. The reservoir began to fill in November 1961 and the dam was complete that same year. After the reservoir filled, several problems occurred. In 1967, there was a major slope failure about upstream of the dam. This and other slope failures are continually under repair. The bedrock beneath the dam has to be re-grouted and the crest of the dam settled too much, r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kurdistan Region
Kurdistan Region ( ku, هەرێمی کوردستان, translit=Herêmî Kurdistan; ar, إقليم كردستان), abbr. KRI, is an autonomous region in Iraq comprising the four Kurdish-majority governorates of Erbil, Sulaymaniyah, Duhok, and Halabja, and bordering Iran, Syria, and Turkey. The Kurdistan Region encompasses most of Iraqi Kurdistan but excludes the disputed territories of Northern Iraq, contested between the Kurdistan Regional Government and the central Iraqi government in Baghdad since 1992 when autonomy was realized. The Kurdistan Region Parliament is situated in Erbil, but the constitution of the Kurdistan Region declares the disputed city of Kirkuk to be the capital of the Kurdistan Region. When the Iraqi Army withdrew from most of the disputed areas in mid-2014 following the Islamic State’s invasion of Iraq, Kurdish Forces entered the areas and held control there until Iraq retook the areas in October 2017. Throughout the 20th century, Kurds in Ira ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Power Stations In Iraq
Below is a list of power stations in Iraq. Non-renewable Thermal Natural gas Yusufiyah Location: Salahuddin 8 X 210 MW construction halted? , -, , , , , Nassiriyah GAS power plant AL nassiriyah 500 MW open cycle Renewable Hydroelectric See also * Energy policy of Iraq * Electricity sector in Iraq *List of largest power stations in the world References {{Power stations, state=expanded Power stations Iraq Iraq,; ku, عێراق, translit=Êraq officially the Republic of Iraq, '; ku, کۆماری عێراق, translit=Komarî Êraq is a country in Western Asia. It is bordered by Turkey to the north, Iran to the east, the Persian Gulf and K ... ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Dams And Reservoirs In Iraq
The following is a list of dams and reservoirs in Iraq. They are sorted according to their location in either the Euphrates or the Tigris river basin. Dams in the Euphrates basin *Duban Regulator, on the Euphrates, regulating the flow of the Euphrates into Lake Habbaniyah *Fallujah Barrage, on the Euphrates *Haditha Dam, on the Euphrates, creating Lake Qadisiyah *Hindiya Barrage, on the Hindiya branch of the Euphrates *Ramadi Barrage, on the Euphrates *Warrar Regulator, on the Euphrates *Three dams in Wadi Hauran (Hussayniyah dam, Rutba dam, and the Hauran dam) Dams in the Tigris basin *Adhaim Dam, on the Adhaim River *Alwand Dam, on the Alwand River *Badush Dam (incomplete), on the Tigris *Bastora Dam (under construction), on the Bastora River *Bawanur Dam (under construction), on the Diyala River *Beduhe Dam, on the Beduhe River *Bekhme Dam (incomplete), on the Great Zab *Darbandikhan Dam, on the Diyala River *Deralok Dam (under construction), on the Great Zab * Dibis Dam, on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydraulic Head
Hydraulic head or piezometric head is a specific measurement of liquid pressure above a vertical datum., 410 pages. See pp. 43–44., 650 pages. See p. 22. It is usually measured as a liquid surface elevation, expressed in units of length, at the entrance (or bottom) of a piezometer. In an aquifer, it can be calculated from the depth to water in a piezometric well (a specialized water well), and given information of the piezometer's elevation and screen depth. Hydraulic head can similarly be measured in a column of water using a standpipe piezometer by measuring the height of the water surface in the tube relative to a common datum. The hydraulic head can be used to determine a ''hydraulic gradient'' between two or more points. "Head" in fluid dynamics In fluid dynamics, ''head'' is a concept that relates the energy in an incompressible fluid to the height of an equivalent static column of that fluid. From Bernoulli's principle, the total energy at a given point in a fluid i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Francis Turbine
The Francis turbine is a type of water turbine. It is an inward-flow reaction turbine that combines radial and axial flow concepts. Francis turbines are the most common water turbine in use today, and can achieve over 95% efficiency. The process of arriving at the modern Francis runner design took from 1848 to approximately 1920. It became known as the Francis turbine around 1920, being named after British-American engineer James B. Francis who in 1848 created a new turbine design. Francis turbines are primarily used for producing electricity. The power output of the electric generators generally ranges from just a few kilowatts up to 1000 MW, though mini-hydro installations may be lower. The best performance is seen when the head height is between . Penstock diameters are between . The speeds of different turbine units range from 70 to 1000 rpm. A wicket gate around the outside of the turbine's rotating runner controls the rate of water flow through the turbine for d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tainter Gate
The Tainter gate is a type of radial arm floodgate used in dams and canal locks to control water flow. It is named for Wisconsin structural engineer Jeremiah Burnham Tainter. A side view of a Tainter gate resembles a slice of pie with the curved part of the piece facing the source or upper pool of water and the tip pointing toward the destination or lower pool. The curved face or skinplate of the gate takes the form of a wedge section of cylinder. The straight sides of the pie shape, the trunnion arms, extend back from each end of the cylinder section and meet at a trunnion which serves as a pivot point when the gate rotates. Pressure forces on a submerged body act perpendicular to the body's surface. The design of the Tainter gate results in every pressure force acting through the centre of the imaginary circle of which the gate is a section, so that all resulting pressure force acts through the pivot point of the gate, making construction and design easier. When a Tain ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
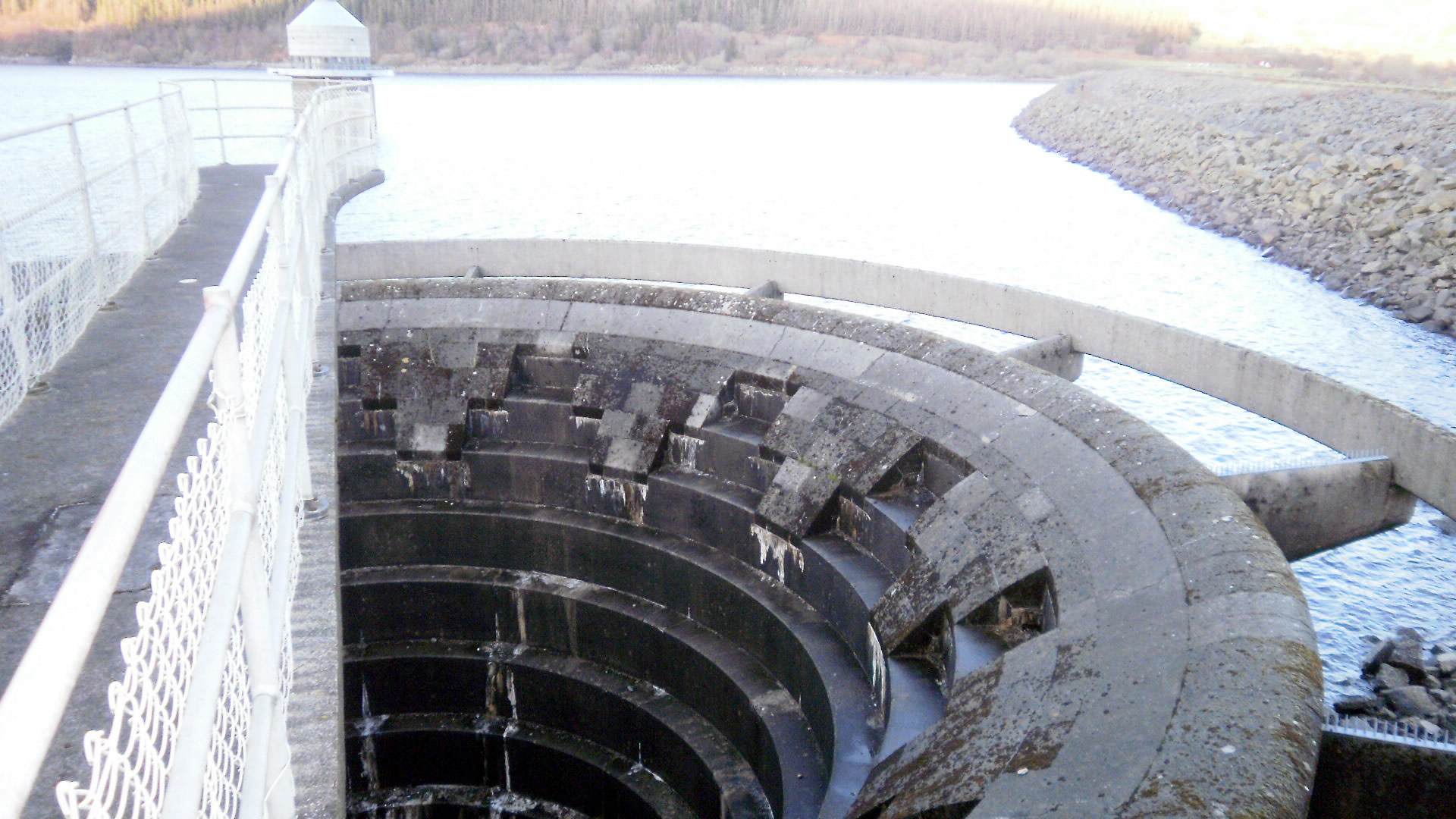
Spillway
A spillway is a structure used to provide the controlled release of water downstream from a dam or levee, typically into the riverbed of the dammed river itself. In the United Kingdom, they may be known as overflow channels. Spillways ensure that water does not damage parts of the structure not designed to convey water. Spillways can include floodgates and fuse plugs to regulate water flow and reservoir level. Such features enable a spillway to regulate downstream flow—by releasing water in a controlled manner before the reservoir is full, operators can prevent an unacceptably large release later. Other uses of the term "spillway" include bypasses of dams and outlets of channels used during high water, and outlet channels carved through natural dams such as moraines. Water normally flows over a spillway only during flood periods, when the reservoir has reached its capacity and water continues entering faster than it can be released. In contrast, an intake tower is a structure ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Drainage Basin
A drainage basin is an area of land where all flowing surface water converges to a single point, such as a river mouth, or flows into another body of water, such as a lake or ocean. A basin is separated from adjacent basins by a perimeter, the '' drainage divide'', made up of a succession of elevated features, such as ridges and hills. A basin may consist of smaller basins that merge at river confluences, forming a hierarchical pattern. Other terms for a drainage basin are catchment area, catchment basin, drainage area, river basin, water basin, and impluvium. In North America, they are commonly called a watershed, though in other English-speaking places, "watershed" is used only in its original sense, that of a drainage divide. In a closed drainage basin, or endorheic basin, the water converges to a single point inside the basin, known as a sink, which may be a permanent lake, a dry lake, or a point where surface water is lost underground. Drainage basins are similar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Darbandikhan Dam Spillway USACE NWD
Darbandikhan ( ku, دەربەندیخان, Derbendîxan) is a town in the governorate of Sulaimaniyah in Kurdistan Region, Iraq. It is situated within the area of autonomy for the Kurdistan region of Iraq, inhabited by the majority of the Kurds. Darbandikhan is located close to Darbandikhan Lake (), and on the border with Diyala Province. It has a population of 45,500 as of 2018. See also *Darbandikhan Dam *Diyala River The Diyala River (Arabic: ; ku, Sîrwan; Farsi: , ) is a river and tributary of the Tigris. It is formed by the confluence of Sirwan river and Tanjaro river in Darbandikhan Dam in the Sulaymaniyah Governorate of Northern Iraq. It covers a total ... References External linksMap and Photos of Darbandikhanat mapcarta.com Populated places in Sulaymaniyah Province Kurdish settlements in Iraq {{Kurdistan-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dokan Dam
The Dukan Dam (Sorani Kurdish: بەنداوی دووکان Arabic: سد دوكان) is a multi-purpose concrete arch dam in As Sulaymaniyah Governorate, Kurdistan Region of Iraq. It impounds the Little Zab, thereby creating Lake Dukan. The Dukan Dam was built between 1954 and 1959 whereas its power station became fully operational in 1979. The dam is long and high and its hydroelectric power station has a maximum capacity of 400 MW. Project history The Dukan Dam was built between 1954 and 1959 as a multi-purpose dam to provide water storage, irrigation and hydroelectricity. The design for the dam was carried out by the British engineering company Binnie & Partners (with Partner and third generation Binnie engineer Geoffrey Binnie the key engineer). Additional structural analysis was done for Binnie by his friends at Imperial College, Professor Pippard and Letitia Chitty, who "developed a stress analysis technique using relaxation methods and a rubber model to verify the des ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
World Bank
The World Bank is an international financial institution that provides loans and grants to the governments of low- and middle-income countries for the purpose of pursuing capital projects. The World Bank is the collective name for the International Bank for Reconstruction and Development (IBRD) and International Development Association (IDA), two of five international organizations owned by the World Bank Group. It was established along with the International Monetary Fund at the 1944 Bretton Woods Conference. After a slow start, its first loan was to France in 1947. In the 1970s, it focused on loans to developing world countries, shifting away from that mission in the 1980s. For the last 30 years, it has included NGOs and environmental groups in its loan portfolio. Its loan strategy is influenced by the Sustainable Development Goals as well as environmental and social safeguards. , the World Bank is run by a president and 25 executive directors, as well as 29 various vice ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |