|
Darayan I
Darayan I (also spelled Darew I, Darev I and Darius I; Aramaic: 𐡃𐡀𐡓𐡉𐡅 ''d’ryw'') was the first king of Persis, most likely invested with kingship of the region by his overlord, the Parthian monarch Phraates II () sometime after 132 BC. Although Darayan I's name was usually read as "Darew" by numismatics, an engraving of his name on a silver bowl has led to his name being read as "Darayan" by most recent studies. The name is derived from Old Persian ''daraya-vahauš'', the name of the prominent Achaemenid King of Kings Darius the Great (). Darayan I, unlike his predecessors—the fratarakas—used the title of shah ("king"), and laid foundations to a new dynasty, which may be labelled the Darayanids. The title for "king" he uses on his coinage is '' malik'', whilst the legend on the reverse is ''d’ryw mlk’'' ("Darius the King"). The reason behind his adoption of the title of Darayan was seemingly because he felt strong enough to do so, and in spite of the d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Persepolis
, native_name_lang = , alternate_name = , image = Gate of All Nations, Persepolis.jpg , image_size = , alt = , caption = Ruins of the Gate of All Nations, Persepolis. , map = , map_type = Iran#West Asia , map_alt = , map_caption = , map_size = , altitude_m = , altitude_ref = , relief = yes , coordinates = , map_dot_label = , location = Marvdasht, Fars Province, Iran , region = , type = Settlement , part_of = , length = , width = , area = , volume = , diameter = , circumference = , height = , builder = , and , material = Limestone, mud-brick, cedar wood , built = 6th century BC , abandoned = , epochs = Achaemenid Empire , cultures = Persian , dependency_of = , occupants = , event = * Battle of the Pe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frataraka
Frataraka (Aramaic: ''Prtkr’'', "governor", or more specifically "sub-satrapal governor") is an ancient Persian title, interpreted variously as “leader, governor, forerunner”. It is an epithet or title of a series of rulers in Persis from 3rd to mid 2nd century BC, or alternatively between 295 and 220 BC, at the time of the Seleucid Empire, prior to the Parthian conquest of West Asia and Iran. Studies of ''frataraka coins'' are important to historians of this period. Rulers and period Several rulers have been identified as belonging to Fratarakā dynasty (from the title ''prtrk' zy alhaya'', or "governor of the gods" on their coins): ''bgdt'' (Baydād), ''rtḥštry'' (Ardaxšīr I), ''whwbrz'' (Vahbarz, who is called Oborzos in Polyenus 7.40), and ''wtprdt'' (Vādfradād I). Traditionally, they used to be considered as independent, anti-Seleucid rulers of Persis in the 3rd century BC. It seems however that they were rather representatives of the Seleucids in the region ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
History Of Fars Province
History (derived ) is the systematic study and the documentation of the human activity. The time period of event before the invention of writing systems is considered prehistory. "History" is an umbrella term comprising past events as well as the memory, discovery, collection, organization, presentation, and interpretation of these events. Historians seek knowledge of the past using historical sources such as written documents, oral accounts, art and material artifacts, and ecological markers. History is not complete and still has debatable mysteries. History is also an academic discipline which uses narrative to describe, examine, question, and analyze past events, and investigate their patterns of cause and effect. Historians often debate which narrative best explains an event, as well as the significance of different causes and effects. Historians also debate the nature of history as an end in itself, as well as its usefulness to give perspective on the problems of the p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
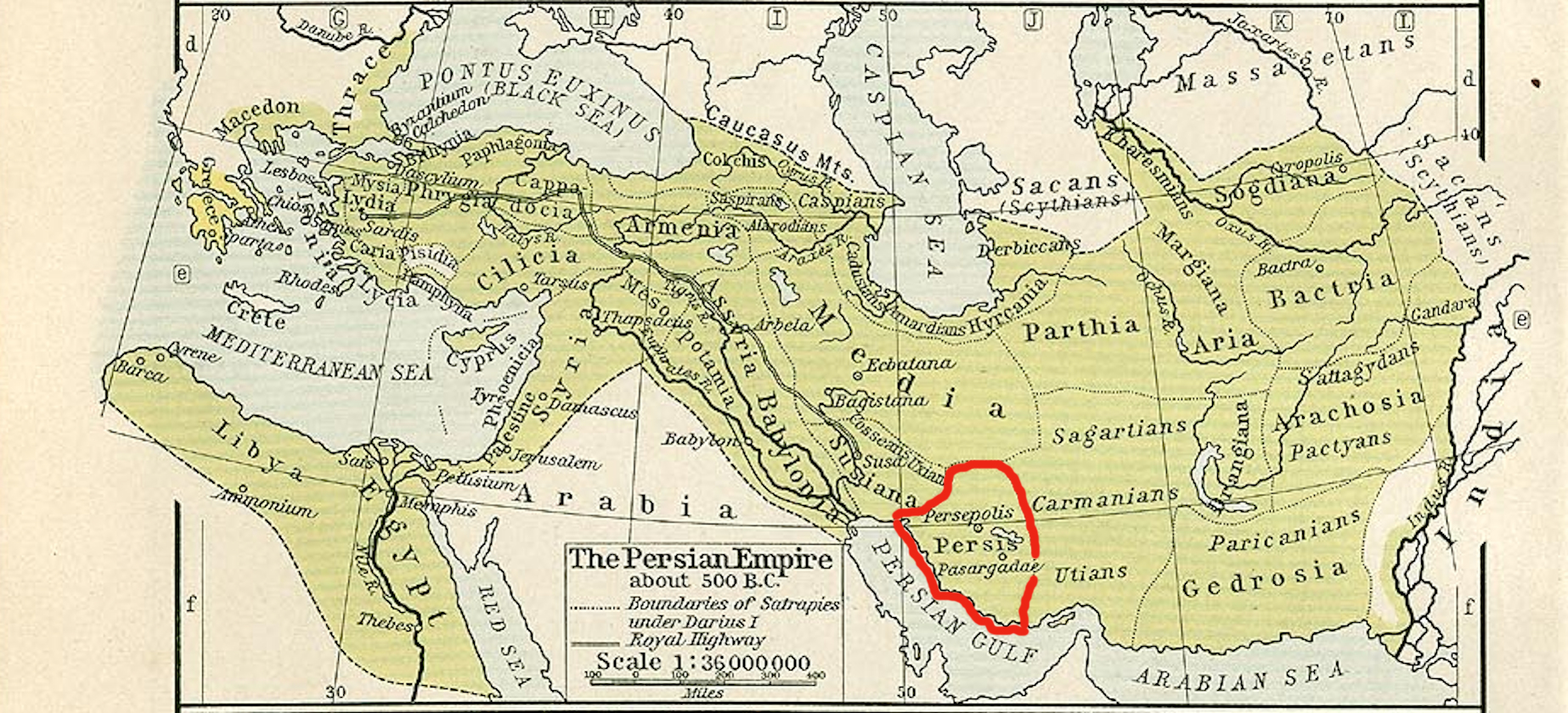
King Of Persis
The Kings of Persis, also known as the Darayanids, were a series of Persian kings, who ruled the region of Persis in southwestern Iran, from the 2nd century BCE to 224 CE. They ruled as sub-kings of the Parthian Empire, until they toppled them and established the Sasanian Empire. They effectively formed some Persian dynastic continuity between the Achaemenid Empire (6th century BCE – 4th century BCE) and the Sasanian Empire (3rd century CE – 7th century CE). History Persis (also known as Pars), a region in the southwestern Iranian plateau, was the homeland of a southwestern branch of the Iranian peoples, the Persians. It was also the birthplace of the first Iranian Empire, the Achaemenids. The region served as the center of the empire until its conquest by the Macedonian king Alexander the Great (). Since the end of the 3rd or the beginning of the 2nd century BCE, Persis was ruled by local dynasts subject to the Hellenistic Seleucid Empire. These dynasts held the ancient Pe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aramaic Script
The Aramaic languages, short Aramaic ( syc, ܐܪܡܝܐ, Arāmāyā; oar, 𐤀𐤓𐤌𐤉𐤀; arc, 𐡀𐡓𐡌𐡉𐡀; tmr, אֲרָמִית), are a language family containing many varieties (languages and dialects) that originated in the ancient region of Syria. For over three thousand years, It is a sub-group of the Semitic languages. Aramaic varieties served as a language of public life and administration of ancient kingdoms and empires and also as a language of divine worship and religious study. Several modern varieties, namely the Neo-Aramaic languages, are still spoken in the present-day. The Aramaic languages belong to the Northwest group of the Semitic language family, which also includes the Canaanite languages such as Hebrew, Edomite, Moabite, and Phoenician, as well as Amorite and Ugaritic. Aramaic languages are written in the Aramaic alphabet, a descendant of the Phoenician alphabet, and the most prominent alphabet variant is the Syriac alphabet. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ahura Mazda
Ahura Mazda (; ae, , translit=Ahura Mazdā; ), also known as Oromasdes, Ohrmazd, Ahuramazda, Hoormazd, Hormazd, Hormaz and Hurmuz, is the creator deity in Zoroastrianism. He is the first and most frequently invoked spirit in the ''Yasna''. The literal meaning of the word ''Ahura'' is "lord", and that of ''Mazda'' is "wisdom". The first notable invocation of Ahura Mazda occurred during the Achaemenid period () with the Behistun Inscription of Darius the Great. Until the reign of Artaxerxes II (), Ahura Mazda was worshipped and invoked alone in all extant royal inscriptions. With Artaxerxes II, Ahura Mazda was gathered in a triad with Mithra and Anahita. In the Achaemenid period, there are no known representations of Ahura Mazda at the royal court other than the custom for every emperor to have an empty chariot drawn by white horses to invite Ahura Mazda to accompany the Military history of Iran#Achaemenid Era, Persian army on battles. Images of Ahura Mazda, however, were pre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zoroastrian
Zoroastrianism is an Iranian religion and one of the world's oldest organized faiths, based on the teachings of the Iranian-speaking prophet Zoroaster. It has a dualistic cosmology of good and evil within the framework of a monotheistic ontology and an eschatology which predicts the ultimate conquest of evil by good. Zoroastrianism exalts an uncreated and benevolent deity of wisdom known as '' Ahura Mazda'' () as its supreme being. Historically, the unique features of Zoroastrianism, such as its monotheism, messianism, belief in free will and judgement after death, conception of heaven, hell, angels, and demons, among other concepts, may have influenced other religious and philosophical systems, including the Abrahamic religions and Gnosticism, Northern Buddhism, and Greek philosophy. With possible roots dating back to the 2nd millennium BCE, Zoroastrianism enters recorded history around the middle of the 6th century BCE. It served as the state religion of the ancient I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fire Temple
A fire temple, Agiary, Atashkadeh ( fa, آتشکده), Atashgah () or Dar-e Mehr () is the place of worship for the followers of Zoroastrianism, the ancient religion of Iran (Persia). In the Zoroastrian religion, fire (see ''atar''), together with clean water (see ''aban''), are agents of ritual purity. Clean, white "ash for the purification ceremonies sregarded as the basis of ritual life", which "are essentially the rites proper to the tending of a domestic fire, for the temple ireis that of the hearth fire raised to a new solemnity". For, one "who sacrifices unto fire with fuel in his hand ..., is given happiness". , there were 167 fire temples in the world, of which 45 were in Mumbai, 105 in the rest of India, and 17 in other countries. Of these only 9 (1 in Iran and 8 in India) are the main temples known as '' atash behrams'' and the remaining are the smaller temples known as ''agiarys''. History and development Concept First evident in the 9th century BCE, the Zoroastr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bashlyk
A bashlyk, also spelled bashlik ( krc, Başlıq, Adyghe: ''Shkharkhon,'' Abkhaz: ''qtarpá'', Chechen: ''Ċukkuiy,'' Ossetic: ''Kaskæ'' crh, Başlıq, Tatar: Başlıq, Turkish: Başlık; "baş" - head, "-lıq" (''Tatar'') / "-lık" (''Turkish'') - derivative suffix)'','' is a traditional Turkic, Caucasian, Iranian, and Cossack cone-shaped headdress hood, usually of leather, felt or wool, an ancient round topped felt bonnet with lappets for wrapping around the neck. Local versions determine the trim, which may consist of decorative cords, embroidery, jewelry, metallized strings, fur balls or tassels. Among dozens of versions are winter bashlyks worn atop regular headdress, cotton bashlyks, homeknitted bashlyks, silk bashlyks, scarf bashlyks, down bashlyks, dress bashlyks, jumpsuit-type bashlyks, etc. Bashlyks are used as traditional folk garment, and as uniform headdress. A variation of bashlyks is a Kalpak (Qalpaq), a cone-shaped headdress without lappets, mostly made of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Drachma
The drachma ( el, δραχμή , ; pl. ''drachmae'' or ''drachmas'') was the currency used in Greece during several periods in its history: # An ancient Greek currency unit issued by many Greek city states during a period of ten centuries, from the Archaic period throughout the Classical period, the Hellenistic period up to the Roman period under Greek Imperial Coinage. # Three modern Greek currencies, the first introduced in 1832 by the Greek King Otto () and the last replaced by the euro in 2001 (at the rate of 340.75 drachmae to the euro). The euro did not begin circulating until 2001 but the exchange rate was fixed on 19 June 2000, with legal introduction of the euro taking place in January 2002. It was also a small unit of weight.. Ancient drachma The name ''drachma'' is derived from the verb (, "(I) grasp"). It is believed that the same word with the meaning of "handful" or "handle" is found in Linear B tablets of the Mycenean Pylos. Initially a drachma was a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Malik
Malik, Mallik, Melik, Malka, Malek, Maleek, Malick, Mallick, or Melekh ( phn, 𐤌𐤋𐤊; ar, ملك; he, מֶלֶךְ) is the Semitic term translating to "king", recorded in East Semitic and Arabic, and as mlk in Northwest Semitic during the Late Bronze Age (e.g. Aramaic, Canaanite, Hebrew). Although the early forms of the name were to be found among the pre-Arab and pre-Islamic Semites of the Levant, Canaan, and Mesopotamia, it has since been adopted in various other, mainly but not exclusively Islamized or Arabized non-Semitic Asian languages for their ruling princes and to render kings elsewhere. It is also sometimes used in derived meanings. The female version of Malik is Malikah ( ar, ملكة; or its various spellings such as Malekeh or Melike), meaning "queen". The name Malik was originally found among various pre-Arab and non-Muslim Semitic peoples such as the indigenous ethnic Assyrians of Iraq, Amorites, Jews, Arameans, Mandeans, Syriacs, and pre-Islami ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)


_p012_BAKU%2C_FIRE_TEMPLE_(cropped).jpg)
%2C_governor%2C_c._mid_3rd_century_BC.jpg)

