|
Dance Guru Meenakshi Sundaram Pillai
Meenakshisundaram Pillai (1869–1964) is a classical dance guru considered as the prominent founder of ''Pandanallur style'' of Bharatanatyam, Indian dance. He lived in the village of Pandanallur, in the Thanjavur district in the south Indian state of Tamil Nadu. Background Meenakshisundaram Pillai, whose ancestors were nattuvanars, was a descendant from the Thanjavur Quartet, which comprised four brothers: Chinnaiah, Ponniah, Sivanandam and Vadivel. The works of these four brothers, who were court composers in the early 19th century in Thanjavur, form the main classical masterpieces of Bharatanatyam. Baroda Guru Kubernath Tanjorkar (1916 - 2007), a disciple of Pillai, later established Tanjor Dance Music & Art Research Centre in Baroda, Gujarat. Thiruvallaputhur Swaminatha Pillai, also known as T.K.Swaminatha Pillai, was one of the leading disciples of Pillai. He learned Bharathanatiyam under the Gurukula of Pillai for more than ten years. He also mentored Ram Gopal, who beca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bharatanatyam
Bharatanatyam () is a major form of Indian classical dance that originated in Tamil Nadu. It is one of the eight widely recognized Indian classical dance forms, and expresses South Indian religious themes and spiritual ideas, particularly of Shaivism and in general of Hinduism.Bharata-natyam ''Encyclopædia Britannica''. 2007 A description of Bharatanatyam from the 2nd century CE can be found in the ancient Tamil epic ''Silappatikaram'', while temple sculptures of the 6th to 9th century CE suggest it was a highly refined performance art by the mid-1st millennium CE. Bharatanatyam is the oldest classical dance tradition in India. Bharatanatyam is the state dance form of Tamil Nadu. Bharatanatyam contains different types of ''baanis''. ''Ba ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tara Chaudhri
Tara Chaudhri was an exponent of Indian classical dance. Believed to have hailed from Lahore, she trained under different maestros of dance, and went on to be acclaimed for her versatility and contributions to the dance forms of Kathak, Manipuri, Kathakali and Bharathnatyam. She was described as the " Pavlova of Punjab" and earned acclaim and respect from international contemporaries. Early life She traveled to South India in 1943 to train further in South Indian dance forms of Kathakalli. Her initiation to Bharathnatyam remains a bit of a mystery, as per some accounts she might have learned the dance during her stay in South India, but according to a 1942 pamphlet, she ran a dance school and taught ‘Bharata Natya’ in Lahore, the cultural capital of North India before Independence. She is known to have trained under Guru Meenakshisundaram Pillai, considered as the prominent founder of Pandanallur style of Bharatanatyam, Indian dance. Tours and recognition As the principal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bhairavi (Carnatic)
Bhairavi is a ''janya'' rāgam in Carnatic music (musical scale of South Indian classical music). Though it is a ''sampoorna'' rāgam (scale having all 7 notes), it has two different ''dhaivathams'' in its scale making it a Bhashanga Ragam, and hence is not classified as a '' melakarta'' rāgam (parent scale). This is one of the ancient rāgams, said to have been prevalent about 1500 years ago. There are numerous compositions in this rāgam. Though a Raga called Bhairavi also exists in Hindusthani music, it is very different from the Carnatic version. Hindustani's Bhairavi, in terms of its aroha and avaroha alone, corresponds to Carnatic music's Thodi. It is considered a ''janya'' of the 20th ''melakarta Natabhairavi''. Its ' structure is as follows (see ''swaras'' of Carnatic music for details on below notation and terms): *: *: The other set of ārohaṇa and avarohaṇa used is: *: *: The notes used are ''chathusruthi rishabham, sadharana gandharam, shuddha mad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
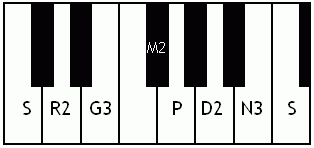
Mechakalyani
Kalyani is a melakarta raga (parent musical scale) in the Carnatic music. It was called Kalyan but is now more popularly called Yaman (raga), Yaman in Hindustani Music. Its Western equivalent is the Lydian mode. Kalyani in Carnatic music In South Indian weddings it is a very prominently played raga. The word ''Kalyani'' means ''she who causes auspicious things''. It is the 65th melakarta raga under the Katapayadi Katapayadi sankhya, sankhya. It is also called ''Mechakalyani''. The notes for Kalyani are S R2 G3 M2 P D2 N3. Kalyani is the first Prathi Madhyama raga that was ever discovered. It was obtained by the process of Graha Bhedam or modal shift of tonic of the ancient Shadja Grama. Specifics on this raga Kalyani has scope for elaborate alapana. One should not remain too long on panchamam (pa) or alternate between shadjamam and panchamam too frequently. Kalyani is prominently known among the public. It is often performed at the beginning of concerts because it is conside ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chakravakam (raga)
Chakravakam or Chakravaham (pronounced chakravākam) is a rāgam in Carnatic music (musical scale in South Indian classical music). It is the 16th ''Melakarta'' rāgam (parent rāgam) in the 72 ''melakarta'' rāgam system. According to the Muthuswami Dikshitar school, this rāgam is called Tōyavēgavāhini.''Ragas in Carnatic music'' by Dr. S. Bhagyalekshmy, Pub. 1990, CBH Publications Chakravakam is similar to Raga ''Ahir bhairav'' in Hindustani music.''Raganidhi'' by P. Subba Rao, Pub. 1964, The Music Academy of Madras ''Chakravakam'' is a raga that is known to incite feelings of devotion, sympathy and compassion in the listeners. Structure and Lakshana It is the 4th ''melakarta'' in the 3rd ''chakra- Agni''. The mnemonic name is ''Agni-Bhu''. The mnemonic phrase is ''sa ra gu ma pa dhi ni''. Its structure (ascending and descending scale) is as follows (see ''Swara#Svaras in Carnatic music, swaras in Carnatic music'' for details on below notation and terms): *Arohana, : * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saveri
Saveri (pronounced sāvēri) is a Carnatic music ragam. This raga is a janya of the 15th Melakarta raga Mayamalavagowla. This raga brings out karuna rasa, i.e. it brings mood of compassion.''Ragas in Carnatic music'' by Dr. S. Bhagyalekshmy, Pub. 1990, CBH Publications Structure and Lakshana This ragam is an ''Audava-Sampurna'' ragam (five notes in the ascending scale and seven notes in the descending scale). * : * : The notes are ''shuddha rishabham, shuddha madhyamam'' and ''shuddha dhaivatam'' in ascending scale and ''kakali nishadam, shuddha dhaivatam, shuddha madhyamam, antara gandharam'' and ''shuddha rishabham'' in descent. The two swaras which give the raga such a characteristic are R (Rishabham) and D (Dhaivatham). Select compositions *''Sarasuda'', a ''varnam'' composed by Kotavasal Venkatarama Iyer, set to ''Adi tala'' *''Sankari Sankuru'', ''Durusuga'' and ''Janani Natajana'' composed by Shyama Sastri *''Bhavayaami Raghuraamam (first raga used in this rag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vasantha (raga)
Vasantha (pronounced vasantā) is a raga in Carnatic music (musical scale of South Indian classical music). It is a ''janya'' raga of '' Suryakantam'', the 17th '' Melakarta'' raga.''Ragas in Carnatic music'' by Dr. S. Bhagyalekshmy, Pub. 1990, CBH Publications According to P, Subba Rao, majority opinion is that the raga is derived from ''Mayamalavagowla'', the 15th ''Melakarta'' raga.''Raganidhi'' by P. Subba Rao, Pub. 1964, The Music Academy of Madras ''Vasantha'' is suitable to be sung in evening and is considered an auspicious raga. Structure ''Vasantha'' is an asymmetric scale that does not contain ''panchamam''. It is called a ''vakra audava-shadava'' raga, malathiga structure is as follows (see ''swaras'' in Carnatic music for details on below notation and terms): * ārohaṇa : * avarohaṇa : This scale uses the notes shadjam, shuddha rishabham, antara gandharam, shuddha madhyamam, chathusruthi dhaivatham and kakali nishadam. Popular compositions ''Vasant ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Meenakshi Chitharanjan
Meenakshi Chitharanjan, an Indian classical dancer, teacher and choreographer, is known as an exponent of the Pandanallur style of the classical dance form of Bharatanatyam. She is the founder of ''Kaladiksha'', an institution promoting Bharatanatyam and striving to preserve the Pandanallur tradition. A disciple of the father-son duo of Chokkalingam Pillai and Subbaraya Pillai, she is a recipient of several honours including Kalaimamani Award of the Government of Tamil Nadu and the ''Natya Kala Sarathi'' of ''Sri Parthasarathy Swami Sabha''. The Government of India awarded her the fourth highest civilian honour of the Padma Shri, in 2008, for her contributions to classical dance. Biography Meenakshi Chitharanjan was born in Chennai, in the south Indian state of Tamil Nadu to Sabanagayam, a government official, as the youngest and only girl child among his five children. Her mother, Savithri, sent the girl to Pandanallur Chockalingam Pillai, a renowned Bharatanatyam guru, when ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alarmel Valli
Alarmel Valli is a leading Indian classical dancer and choreographer and the foremost exponent of the Pandanallur style in the Indian classical dance form, Bharatanatyam. She is widely acclaimed for her ability to turn traditional grammar into deeply internalized, personal dance poetry. She founded The Dipasikha Dance Foundation in Chennai in 1984, where she teaches Bharatanatyam. In 1991, Alarmel Valli was the second youngest dancer to be conferred the Padma Shri from the Government of India, after Vyjayanthimala. She was awarded the Sangeet Natak Akademi Award in 2001 by India's National Academy for Music, Dance and Drama, followed by one of India's highest civilian honours – the Padma Bhushan award from the Government of India in 2004 and Chevalier of Arts and Letters award from the Government of France, also in 2004. Early life Alarmel Valli was born and brought up in Chennai, where she did her schooling at The Sacred Heart Matriculation School, Church Park, Chennai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mrinalini Sarabhai
Mrinalini Vikram Sarabhai (11 May 1918 – 21 January 2016) was an Indian classical dancer, choreographer and instructor. She was the founder and director of the Darpana Academy of Performing Arts, an institute for imparting training in dance, drama, music and puppetry, in the city of Ahmedabad. She received Padma Bhushan in 1992 and Padma Shri in 1965. She also received many other citations in recognition of her contribution to art. Biography Early life and education Mrinalini was born to a Tamil Brahmin father and Malayali Nair mother in present-day Kerala on 11 May 1918. Her parents were Subbarama Swaminathan, a distinguished lawyer with degrees from Harvard and London Universities, practised criminal law at Madras High Court, and A.V. Ammukutty, better known as Ammu Swaminathan, a social worker, an independence activist, and later a parliamentarian. She attended a boarding school in Switzerland for two years, where, she received her first lessons in the Dalcroze school, a W ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deccan Herald
''Deccan Herald'' is an Indian English language daily newspaper published from the Indian state of Karnataka. It was founded by K. N. Guruswamy, a liquor businessman from Ballari and was launched on 17 June 1948. It is published by The Printers Mysore, a privately held company owned by the Nettakallappa family, heirs of Guruswamy. It has seven editions printed from Bengaluru, Hubballi, Davanagere, Hosapete, Mysuru, Mangaluru, and Kalaburagi. History and background ''Deccan Herald'' was launched on 17 June 1948. Its founder, K. N. Guruswamy, in search of a suitable location for a news publishing business, purchased a bar and restaurant called Funnel's, that was owned by an Irish couple, in March 1948. Despite having no experience in the newspaper industry, Guruswamy, along with his close aides and well wishers, decided to launch two newspapers from Bangalore since there was no such title at the time. The Deccan Herald is an Indian English-language daily newspaper published ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)
_savysachi_sarswat_award.jpg)