|
Dance Chimes
The Dance Chimes is a foot-operated chime-like musical instrument that consists of 9 bronze tiles, with mechanical sound elements under each. Description The 9 bronze tiles of the Dance Chimes are arranged in a square formation and usually in-built in the ground. The sound pads are triggered by sensitive hammers activated while hopping, jumping or dancing. The tone is bell-like and the notes are tuned in a pentatonic sequence and can be played note by note to play a melody, or sounded together to play a chord. History Invented and designed by Alfons van Leggelo in the 1970s, last accessed 28 September the Dance Chimes was created to relate the movement of walking directly with sound. The instrument, made of bronze is related to the physical properties of the |
Musical Instrument
A musical instrument is a device created or adapted to make musical sounds. In principle, any object that produces sound can be considered a musical instrument—it is through purpose that the object becomes a musical instrument. A person who plays a musical instrument is known as an instrumentalist. The history of musical instruments dates to the beginnings of human culture. Early musical instruments may have been used for rituals, such as a horn to signal success on the hunt, or a drum in a religious ceremony. Cultures eventually developed composition and performance of melodies for entertainment. Musical instruments evolved in step with changing applications and technologies. The date and origin of the first device considered a musical instrument is disputed. The oldest object that some scholars refer to as a musical instrument, a simple flute, dates back as far as 50,000 - 60,000 years. Some consensus dates early flutes to about 40,000 years ago. However, most historians be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pentatonic
A pentatonic scale is a musical scale with five notes per octave, in contrast to the heptatonic scale, which has seven notes per octave (such as the major scale and minor scale). Pentatonic scales were developed independently by many ancient civilizations and are still used in various musical styles to this day. There are two types of pentatonic scales: those with semitones (hemitonic) and those without (anhemitonic). Types Hemitonic and anhemitonic Musicology commonly classifies pentatonic scales as either ''hemitonic'' or ''anhemitonic''. Hemitonic scales contain one or more semitones and anhemitonic scales do not contain semitones. (For example, in Japanese music the anhemitonic ''yo'' scale is contrasted with the hemitonic ''in'' scale.) Hemitonic pentatonic scales are also called "ditonic scales", because the largest interval in them is the ditone (e.g., in the scale C–E–F–G–B–C, the interval found between C–E and G–B). (This should not be con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carillon
A carillon ( , ) is a pitched percussion instrument that is played with a keyboard and consists of at least 23 cast-bronze bells. The bells are hung in fixed suspension and tuned in chromatic order so that they can be sounded harmoniously together. They are struck with clappers connected to a keyboard of wooden batons played with the hands and pedals played with the feet. Often housed in bell towers, carillons are usually owned by churches, universities, or municipalities. They can include an automatic system through which the time is announced and simple tunes are played throughout the day. Carillons come in many designs, weights, sizes, and sounds. They are among the world's heaviest instruments, and the heaviest carillon weighs over . Most weigh between . To be considered a carillon, a minimum of 23 bells are needed; otherwise, it is called a chime. Standard-sized instruments have about 50, and the world's largest has 77 bells. The appearance of a carillon depends ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battery Park
The Battery, formerly known as Battery Park, is a public park located at the southern tip of Manhattan Island in New York City facing New York Harbor. It is bounded by Battery Place on the north, State Street on the east, New York Harbor to the south, and the Hudson River to the west. The park contains attractions such as an early 19th-century fort named Castle Clinton; multiple monuments; and the SeaGlass Carousel. The surrounding area, known as South Ferry, contains multiple ferry terminals, including the Staten Island Ferry's Whitehall Terminal; a boat launch to the Statue of Liberty National Monument (which includes Ellis Island and Liberty Island); and a boat launch to Governors Island. The park and surrounding area is named for the artillery batteries that were built in the late 17th century to protect the settlement behind them. By the 1820s, the Battery had become an entertainment destination, with the conversion of Castle Clinton into a theater venue. During the m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
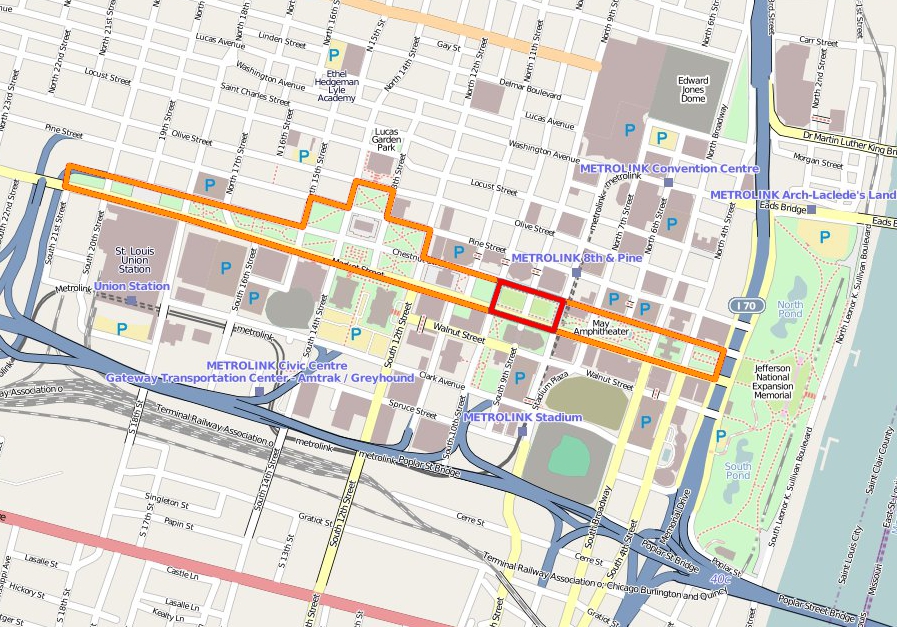
Citygarden
Citygarden is an urban park and sculpture garden in St. Louis, Missouri owned by the City of St. Louis but maintained by the Gateway Foundation. It is located between Eighth, Tenth, Market, and Chestnut streets, in the city's " Gateway Mall" area. Before being converted to a garden and park, the site comprised two empty blocks of grass. Citygarden was dedicated on June 30, 2009, and opened one day later, on July 1, 2009. Citygarden is in size—occupying two square city blocks—and cost US$30 million to develop. St. Louis' Gateway Foundation, a not-for-profit organization supporting public art, funded the design and construction of the garden. While the city owns the land on which Citygarden was developed, the foundation owns the statues and covers all park maintenance costs except water and electricity. The Gateway Foundation is also in charge of providing additional security for the garden. There is no admission fee for visitors of Citygarden, which is located close to St. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diana, Princess Of Wales Memorial Playground
The Diana, Princess of Wales Memorial Playground is a memorial to Diana, Princess of Wales, in Kensington Gardens, in The Royal Borough of Kensington and Chelsea, London. It was erected after her death at a cost of £1.7 million on the site of the existing Peter Pan children's playground which had been founded in the time of JM Barrie (author of ''Peter Pan in Kensington Gardens''), but it is larger and more elaborate than the original. The design, by Land use consultants, was inspired by Barrie's Peter Pan. Its most prominent feature is a full-scale wooden pirate ship which serves as a climbing area for children, and is surrounded by sand in which they can play. Other features include slides, swings, and an area designed for those with disabilities, including fragrant plants and sound features (for those with visual disabilities). The playground is an example of a "natural play" concept, designed to stimulate children's imagination, sense of adventure, and to encourage them to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Museumplein
The Museumplein (; ) is a public space in the Museumkwartier neighbourhood of the Amsterdam-Zuid borough in Amsterdam, Netherlands. Located at the Museumplein are three major museums – the Rijksmuseum, Van Gogh Museum, and Stedelijk Museum – and the concert hall Concertgebouw. The area was originally a wax candle factory and marshy meadows. Construction began following the completion of the Rijksmuseum in 1885, with a street plan based on the design of Pierre Cuypers, the museum's celebrated architect. The area was the location of the International Colonial and Export Exhibition in 1883. The Museumplein was reconstructed after a design by the Swedish/ Danish landscape architect Sven-Ingvar Andersson in 1999. It now includes underground parking spaces and an underground supermarket. In the winter, the pond can be transformed into an artificial ice skating area. The space is also used for (mass) events such as festivals, celebrations, and demonstrations and Armin Van Bu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dance Chimes Details
Dance is a performing art form consisting of sequences of movement, either improvised or purposefully selected. This movement has aesthetic and often symbolic value. Dance can be categorized and described by its choreography, by its repertoire of movements, or by its historical period or place of origin. An important distinction is to be drawn between the contexts of theatrical and participatory dance, although these two categories are not always completely separate; both may have special functions, whether social, ceremonial, competitive, erotic, martial, or sacred/ liturgical. Other forms of human movement are sometimes said to have a dance-like quality, including martial arts, gymnastics, cheerleading, figure skating, synchronized swimming, marching bands, and many other forms of athletics. There are many professional athletes like, professional football players and soccer players, who take dance classes to help with their skills. To be more specific professional athlete ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chime (bell Instrument)
A chime () or set of chimes is a carillon-like instrument, i.e. a pitched percussion idiophone consisting of 22 or fewer cast bronze bells. Chimes are primarily played with a keyboard, but can also be played with an Ellacombe apparatus. Chimes are often automated, in the past with mechanical drums connected to clocks and in the present with electronic action. Bellfounders often did not attempt to tune chime bells to the same precision as carillon bells. Chimes are defined as specifically having fewer than 23 bells to distinguish them from the carillon. American chimes usually have one to one and a half diatonic octaves. According to a recent count, there are over 1,300 existing chimes throughout the world. Almost all are in the Netherlands and the United States, with most of the remainder in Western European countries. Etymology The word ''chime'' dates back to the 14th-century Middle English word , meaning ' cymbal'. It probably originates from the Old French or directly fr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
European Percussion Instruments
European, or Europeans, or Europeneans, may refer to: In general * ''European'', an adjective referring to something of, from, or related to Europe ** Ethnic groups in Europe ** Demographics of Europe ** European cuisine, the cuisines of Europe and other Western countries * ''European'', an adjective referring to something of, from, or related to the European Union ** Citizenship of the European Union ** Demographics of the European Union In publishing * ''The European'' (1953 magazine), a far-right cultural and political magazine published 1953–1959 * ''The European'' (newspaper), a British weekly newspaper published 1990–1998 * ''The European'' (2009 magazine), a German magazine first published in September 2009 *''The European Magazine'', a magazine published in London 1782–1826 *''The New European'', a British weekly pop-up newspaper first published in July 2016 Other uses * * Europeans (band), a British post-punk group, from Bristol See also * * * Europe (disambi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Idiophones
An idiophone is any musical instrument that creates sound primarily by the vibration of the instrument itself, without the use of air flow (as with aerophones), strings (chordophones), membranes (membranophones) or electricity ( electrophones). It is the first of the four main divisions in the original Hornbostel–Sachs system of musical instrument classification (see List of idiophones by Hornbostel–Sachs number). The early classification of Victor-Charles Mahillon called this group of instruments ''autophones''. The most common are struck idiophones, or concussion idiophones, which are made to vibrate by being struck, either directly with a stick or hand (like the wood block, singing bowl, steel tongue drum, triangle or marimba) or indirectly, with scraping or shaking motions (like maracas or flexatone). Various types of bells fall into both categories. A common plucked idiophone is the Jew's harp. According to Sachs, idiophones Etymology The word is from Ancient G ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |