|
Danan (volcano)
Danan (uncertain derivation) was one of the three volcanic cones (the others being Perboewatan and Rakata) on the island of Krakatoa, in the Sunda Strait, in Indonesia. It stood , lay in the central area of the island, and may have been a twin volcano. Danan was almost entirely destroyed in the 1883 eruption of Krakatoa; only a rocky islet named Bootsmansrots remains of it. Form Not much can be found about Danan; the interior of Krakatoa was little explored or surveyed. There were several peaks, and Verbeek surmised that it formed a "ring-shaped crater wall". In one of the photographs of Perboewatan erupting in May 1883, Danan's irregular shape can be seen in the background, partially obscured by the ash cloud arising from Perboewatan. Eruptions 1680–1681 eruption Danan apparently joined Perboewatan in eruption sometime after May 1680, when Perboewatan started erupting. A returning Dutch traveler saw both cones erupting in February 1681. The 1883 eruption {{main, 1883 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Volcanic Cone
Volcanic cones are among the simplest volcanic landforms. They are built by ejecta from a volcanic vent, piling up around the vent in the shape of a cone with a central crater. Volcanic cones are of different types, depending upon the nature and size of the fragments ejected during the eruption. Types of volcanic cones include stratocones, spatter cones, tuff cones, and cinder cones. Stratocone Stratocones are large cone-shaped volcanoes made up of lava flows, explosively erupted pyroclastic rocks, and igneous intrusives that are typically centered around a cylindrical vent. Unlike shield volcanoes, they are characterized by a steep profile and periodic, often alternating, explosive eruptions and effusive eruptions. Some have collapsed craters called calderas. The central core of a stratocone is commonly dominated by a central core of intrusive rocks that range from around to over several kilometers in diameter. This central core is surrounded by multiple generations of lava ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Perboewatan
Perboewatan (also spelled Perbuatan; apparently a Malay word of uncertain derivation) was one of the three main volcanic cones (the others being Danan and Rakata) on the island of Krakatoa (or Krakatau), in the Sunda Strait, in Indonesia. It was the lowest (400 ft) and northernmost of the cones. Perboewatan was completely destroyed during the 1883 eruption; the caldera is approximately deep at its former location. Form Photographed on May 27, 1883 by visitors to the island, Perboewatan is the only cone on Krakatoa of which quality pre-1883 photographs exist. In the photos, it appears to be a low hill with a flat top. Climbers reported the erupting crater to be about across at the top, narrowing to at the bottom and 500–800 ft deep. Samples were collected, revealing upon analysis a silica (SiO2) content of 65%. Eruptions 1680–81 In February 1681, two individuals traveling through the Straits witnessed the eruption of Krakatoa. Johann Wilhelm Vogel, a mining assayer, was t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rakata
Rakata ( ), also called Greater Krakatau, is a partially collapsed stratovolcano on the Indonesian island of Krakatoa ( id, Krakatau) in the Sunda Strait between the islands of Sumatra and Java. Standing tall, it was the largest and southernmost of three volcanoes that formed the island Krakatoa (the others being Danan (volcano) and Perboewatan) and the only one not totally destroyed in the 1883 eruption. Rakata is the last remnant of the original island prior to its destruction. However, Rakata did lose its northern half in that eruption, leaving just its southern half. The exposed cliff is quite striking visually, partially of a large exposed dike terminating in a large lenticular extrusion at the middle of the almost vertical cliff. The feature has been called "the Eye of Krakatoa." Etymology Because the words ''Rakata'' and ''Krakatau'' are the same in Indonesian, both names are used interchangeably, leading to confusion in languages which distinguish between the two wo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
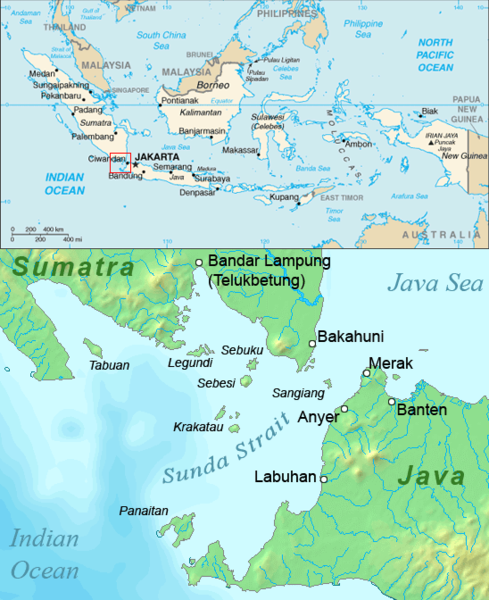
Krakatoa
Krakatoa (), also transcribed (), is a caldera in the Sunda Strait between the islands of Java and Sumatra in the Indonesian province of Lampung. The caldera is part of a volcanic island group ( Krakatoa archipelago) comprising four islands. Two, Lang and Verlaten, are remnants of a previous volcanic edifice destroyed in eruptions long before the famous 1883 eruption; another, Rakata, is the remnant of a much larger island destroyed in the 1883 eruption. In 1927, a fourth island, Anak Krakatoa, or "Child of Krakatoa", emerged from the caldera formed in 1883. There has been new eruptive activity since the late 20th century, with a large collapse causing a deadly tsunami in December 2018. Historical significance The most notable eruptions of Krakatoa culminated in a series of massive explosions over 26–27 August 1883, which were among the most violent volcanic events in recorded history. With an estimated Volcanic Explosivity Index (VEI) of 6, the eruption was equiv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sunda Strait
The Sunda Strait ( id, Selat Sunda) is the strait between the Indonesian islands of Java and Sumatra. It connects the Java Sea with the Indian Ocean. Etymology The strait takes its name from the Sunda Kingdom, which ruled the western portion of Java (an area covering the present day West Java, Jakarta, Banten, and some of western Central Java) from 669 to around 1579."Sunda Islands". Concise Dictionary of World Place-Names. John Everett-Heath. Oxford University Press 2005. Oxford Reference Online. Oxford University Press. The name also alludes to the Sundanese people native to West Java and Banten, as distinct from the Javanese people, who live mostly in Central and East Java. Geography Extending in a roughly southwest/northeast orientation, with a minimum width of at its northeastern end between Cape Tua on Sumatra and Cape Pujat on Java, the strait is part of the Java Sea. It is essentially triangular in shape, with two large bays on its northern side. It is also very b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indonesia
Indonesia, officially the Republic of Indonesia, is a country in Southeast Asia and Oceania between the Indian and Pacific oceans. It consists of over 17,000 islands, including Sumatra, Java, Sulawesi, and parts of Borneo and New Guinea. Indonesia is the world's largest archipelagic state and the 14th-largest country by area, at . With over 275 million people, Indonesia is the world's fourth-most populous country and the most populous Muslim-majority country. Java, the world's most populous island, is home to more than half of the country's population. Indonesia is a presidential republic with an elected legislature. It has 38 provinces, of which nine have special status. The country's capital, Jakarta, is the world's second-most populous urban area. Indonesia shares land borders with Papua New Guinea, East Timor, and the eastern part of Malaysia, as well as maritime borders with Singapore, Vietnam, Thailand, the Philippines, Australia, Palau, and India ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Volcano
A volcano is a rupture in the Crust (geology), crust of a Planet#Planetary-mass objects, planetary-mass object, such as Earth, that allows hot lava, volcanic ash, and volcanic gas, gases to escape from a magma chamber below the surface. On Earth, volcanoes are most often found where list of tectonic plates, tectonic plates are divergent boundary, diverging or convergent boundary, converging, and most are found underwater. For example, a mid-ocean ridge, such as the Mid-Atlantic Ridge, has volcanoes caused by divergent tectonic plates whereas the Pacific Ring of Fire has volcanoes caused by convergent tectonic plates. Volcanoes can also form where there is stretching and thinning of the crust's plates, such as in the East African Rift and the Wells Gray-Clearwater volcanic field and Rio Grande rift in North America. Volcanism away from plate boundaries has been postulated to arise from upwelling diapirs from the core–mantle boundary, deep in the Earth. This results in hotspot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1883 Eruption Of Krakatoa
The 1883 eruption of Krakatoa ( id, Letusan Krakatau 1883) in the Sunda Strait occurred from 20 May until 21 October 1883, peaking in the late morning hours of 27 August when over 70% of the island of Krakatoa and its surrounding archipelago were destroyed as it collapsed into a caldera. The eruption was one of the deadliest and most destructive volcanic events in recorded history. The explosion was heard away in Perth, Western Australia, and Rodrigues near Mauritius, away. The sound wave is recorded to have travelled around the globe seven times. At least 36,417 deaths are attributed to the eruption and the tsunamis it created. Significant additional effects were also felt around the world in the days and weeks after the volcano's eruption. Additional seismic activity was reported until February 1884, but any reports after October 1883 were dismissed by Rogier Verbeek's subsequent investigation into the eruption. Early phase In the years before the 1883 eruption, seis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rogier Verbeek
Rogier Diederik Marius Verbeek (7 April 1845, Doorn – 9 April 1926, The Hague) was a Dutch geologist and natural scientist. His journal ''Krakatau'', which was edited in 1884 and 1885 by order of the Governor-General of the Dutch East Indies, is his most known work. It deals with the eruption of the volcanic island Krakatoa in 1883 and brought volcanology into scientific prominence. Just two years before, Verbeek had done research in the area. Living in Buitenzorg on Java, he was a direct witness to the eruption. In the BBC docudrama '' Krakatoa: The Last Days'', he is the protagonist and was portrayed by Kevin McMonagle. In 1909, he obtained an honorary doctorate of the Delft University of Technology. He was an honorary member of the Koninklijk Nederlands Geologisch Mijnbouwkundig Genootschap and a member of the Maatschappij der Nederlandsche Letterkunde. Works The following are some of Verbeek's other writings: *''Topographische en geologische Beschrijving van een De ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bosun
A boatswain ( , ), bo's'n, bos'n, or bosun, also known as a deck boss, or a qualified member of the deck department, is the most senior rate of the deck department and is responsible for the components of a ship's hull. The boatswain supervises the other members of the ship's deck department, and typically is not a watchstander, except on vessels with small crews. Additional duties vary depending upon ship, crew, and circumstances. History The word ''boatswain'' has been in the English language since approximately 1450. It is derived from late Old English ''batswegen'', from ''bat'' (''boat'') concatenated with Old Norse ''sveinn'' ('' swain''), meaning a young man, apprentice, a follower, retainer or servant. Directly translated to modern Norwegian it would be ''båtsvenn'', while the actual crew title in Norwegian is ''båtsmann'' ("''boats-man''"). While the phonetic spelling ''bosun'' is reported as having been observed since 1868, this latter spelling was used in Sha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parallel (geometry)
In geometry, parallel lines are coplanar straight lines that do not intersect at any point. Parallel planes are planes in the same three-dimensional space that never meet. ''Parallel curves'' are curves that do not touch each other or intersect and keep a fixed minimum distance. In three-dimensional Euclidean space, a line and a plane that do not share a point are also said to be parallel. However, two noncoplanar lines are called '' skew lines''. Parallel lines are the subject of Euclid's parallel postulate. Parallelism is primarily a property of affine geometries and Euclidean geometry is a special instance of this type of geometry. In some other geometries, such as hyperbolic geometry, lines can have analogous properties that are referred to as parallelism. Symbol The parallel symbol is \parallel. For example, AB \parallel CD indicates that line ''AB'' is parallel to line ''CD''. In the Unicode character set, the "parallel" and "not parallel" signs have co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hypersthene
Hypersthene is a common rock-forming inosilicate mineral belonging to the group of orthorhombic pyroxenes. Its chemical formula is . It is found in igneous and some metamorphic rocks as well as in stony and iron meteorites. Many references have formally abandoned this term, preferring to categorise this mineral as enstatite or ferrosilite. It forms a solid solution series with the minerals enstatite and ferrosilite, being a mid-way member between the two. Pure enstatite contains no iron, while pure ferrosilite contains no magnesium; hypersthene is the name given to the mineral when a significant amount of both elements are present. Enstatite is stable at atmospheric pressure, but ferrosilite is stable only at elevated pressure, decomposing into quartz and fayalite at atmospheric pressure unless stabilized by magnesium or other impurities. Distinctly developed crystals are rare, the mineral being usually found as foliated masses embedded in the igneous rocks norite and hypersth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |






.png)