|
Dalforce
Dalforce, or the Singapore Overseas Chinese Anti-Japanese Volunteer Army (星華義勇軍; ''Xinghua Yi Yong Jun'') was an irregular forces/ guerrilla unit within the British Straits Settlements Volunteer Force during World War II. Its members were recruited among the ethnic Chinese people of Singapore. It was created on 25 December 1941 by Lieutenant Colonel John Dalley of the Federated Malay States Police Force. The unit was known to the British colonial administration as Dalforce, after its chief instructor and commanding officer, John Dalley, whereas the Chinese in Singapore only knew it as the Singapore Overseas Chinese Anti-Japanese Volunteer Army. This formation took part in the Battle of Singapore and some members conducted a guerrilla campaign against Japanese forces during the Japanese occupation. The British noted how ferociously the Chinese volunteers in Dalforce fought, earning them the nickname ''Dalley's Desperadoes''. Origins Dalley had suggested creating a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ee Hoe Hean Club
The Ee Hoe Hean Club (), founded in 1895 and located at Bukit Pasoh Road in Chinatown, was a millionaires' club in Singapore. Besides functioning as a social and business club, members of the club were actively involved in the political development of China in the early 20th century. The club supported the 1911 Xinhai Revolution which overthrew the Qing Dynasty, and later the establishment of the Republic of China. During World War II, it was the headquarters of the anti-Japanese China Salvation Movement in Southeast Asia from 1937 to 1942. On 18 October 1995, the club was gazetted as a Heritage Site by the National Heritage Board of Singapore.Information obtained from on-site plaque installed by the National Heritage Board of Singapore. History Co-founded in 1895 by Lim Nee Soon, Gan Eng Seng and Lim Boon Keng, the three-storey high Ee Hoe Hean Club was originally located on Duxton Hill but moved to 38 Club Street in 1911. It subsequently moved to Bukit Pasoh Road in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Malaya Command
The Malaya Command was a formation of the British Army formed in the 1920s for the coordination of the defences of British Malaya, which comprised the Straits Settlements, the Federated Malay States and the Unfederated Malay States. It consisted mainly of small garrison forces in Kuala Lumpur, Penang, Taiping, Seremban and Singapore. With the outbreak of the Second World War in 1939, the command reinforced its strength in anticipation of an attack. With the bulk of British forces being tied down in Europe and North Africa, the command was mainly augmented by units from India. On 18 November 1940, the command was placed under the command of the British Far East Command and later, on 7 January 1942, under the short-lived South West Pacific Command or ABDACOM, which was tasked to maintain control of the "Malay Barrier" (or "East Indies Barrier"), a notional line running down the Malayan Peninsula, through Singapore and the southernmost islands of the Dutch East Indies. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Resistance During World War II
Resistance movements during World War II occurred in every occupied country by a variety of means, ranging from non-cooperation to propaganda, hiding crashed pilots and even to outright warfare and the recapturing of towns. In many countries, resistance movements were sometimes also referred to as The Underground. The resistance movements in World War II can be broken down into two primary politically polarized camps: the internationalist and usually Communist Party-led anti-fascist resistance that existed in nearly every country in the world; and the various fascist/anti-communist nationalist resistance groups in Nazi- or Soviet-occupied countries that opposed the foreign fascists and the communists, often switching sides depending on the vicissitudes of the war and which side of the ever-moving military front lines they found themselves on. Among the most notable resistance movements were the Polish Resistance (including the Polish Home Army, Leśni, People’s Army, and t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1st Malaya Infantry Brigade
The 1st Malaya Infantry Brigade was a regular infantry brigade formed in 1939 with its headquarters in Singapore immediately after the outbreak of hostilities in Europe. The Brigade participated in the Battle of Singapore against the Japanese until the surrender of the garrison in February 1942. History Formed on 3 September 1939, the formation was initially known as the Malaya Infantry Brigade as part of the wartime expansion and reinforcement of Malaya Command. It was re-designated the 1st Malaya Infantry Brigade when the 2nd Malaya Infantry Brigade was formed on 8 September 1940. Malayan Campaign The 1st Battalion, Mysore Infantry served in airfield security duties during the Battle of Kota Bahru as part of the 8th Indian Infantry Brigade. With the collapse of the defences in Kota Bahru, the Battalion was withdrawn to Singapore and was joined with the Brigade on 18 December 1941. Battle of Singapore All organised Allied forces in Malaya had retreated to Singapore on 31 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
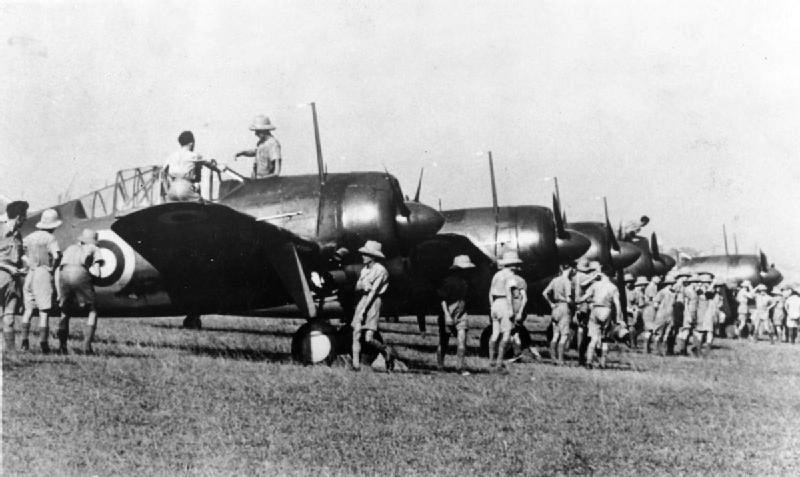
Battle Of Singapore
The Fall of Singapore, also known as the Battle of Singapore,; ta, சிங்கப்பூரின் வீழ்ச்சி; ja, シンガポールの戦い took place in the South–East Asian theatre of the Pacific War. The Empire of Japan captured the British stronghold of Singapore, with fighting lasting from 8 to 15 February 1942. Singapore was the foremost British military base and economic port in South–East Asia and had been of great importance to British interwar defence strategy. The capture of Singapore resulted in the largest British surrender in its history. Prior to the battle, Japanese General Tomoyuki Yamashita had advanced with about 30,000 men down the Malayan Peninsula in the Malayan campaign. The British erroneously considered the jungle terrain impassable, leading to a swift Japanese advance as Allied defences were quickly outflanked. The British Lieutenant-General, Arthur Percival, commanded 85,000 Allied troops at Singapore, although many units ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Straits Settlements Volunteer Force
The Straits Settlements Volunteer Force (SSVF) was a military reserve force in the Straits Settlements, while they were under British rule. While the majority of the personnel were from Singapore, some lived in other parts of the Settlements, including Penang, Province Wellesley, Malacca and Labuan. History The SSVF had its origins in thSingapore Volunteer Rifle Corps(SVRC), formed in 1854. The SVRC was disbanded in 1887 and an artillery corps named, the Singapore Volunteer Artillery Corps (SVA) was formed in 1888. In 1915 it helped suppress the mutiny of Sepoys in Singapore. The SSVF was officially formed in 1922, following the amalgamation of the Singapore Volunteer Corps, Penang and Province Wellesley Volunteer Corps, Malacca Volunteer Corps, and Labuan Volunteer Defence Detachment. In 1928, the SSVF infantry was re-organised into 4 battalions. The 1st and 2nd battalions consisted of members of the Singapore Volunteer Corps (1,250 men), the 3rd battalion consisted of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Friendly Fire
In military terminology, friendly fire or fratricide is an attack by belligerent or neutral forces on friendly troops while attempting to attack enemy/hostile targets. Examples include misidentifying the target as hostile, cross-fire while engaging an enemy, long range ranging errors or inaccuracy. Accidental fire not intended to attack enemy/hostile targets, and deliberate firing on one's own troops for disciplinary reasons, is not called friendly fire,Regan, Geoffrey (2002) ''Backfire: a history of friendly fire from ancient warfare to the present day'', Robson Books and neither is unintentional harm to civilian or neutral targets, which is sometimes referred to as collateral damage. Training accidents and bloodless incidents also do not qualify as friendly fire in terms of casualty reporting. Use of the term "friendly" in a military context for allied personnel started during the First World War, often when shells fell short of the targeted enemy. The term ''friendly fire' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
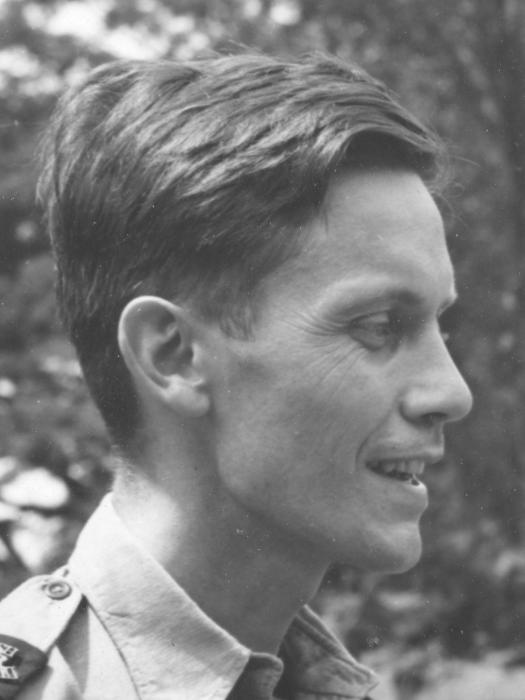
Ian Morrison (journalist)
Ian Ernest McLeavy Morrison (31 May 1913 – 12 August 1950) was an Australian journalist and war correspondent for ''The Times''. He was one of the first journalists to be killed in the Korean War. The Academy Award-nominated film ''Love Is a Many-Splendored Thing (film), Love is a Many-Splendored Thing'' is based on Morrison's love affair with author Han Suyin in Hong Kong. Early career He was born on 31 May 1913 in Beijing, Peking, as the oldest son to Australian adventurer and journalist George Ernest Morrison (1862–1920) and Jennie Wark Robin (1889–1923). His father had been living in Peking on and off since 1897, when he had been stationed there as ''The Times first Peking correspondent. In 1919, the family moved to the United Kingdom, where the father died in 1920. Ian Morrison and his two younger brothers, Alastair Gwynne (1915–2009) and Colin (1917–1990), were all educated at Winchester College before continuing to University of Cambridge, Cambridge University. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Times
''The Times'' is a British daily national newspaper based in London. It began in 1785 under the title ''The Daily Universal Register'', adopting its current name on 1 January 1788. ''The Times'' and its sister paper '' The Sunday Times'' (founded in 1821) are published by Times Newspapers, since 1981 a subsidiary of News UK, in turn wholly owned by News Corp. ''The Times'' and ''The Sunday Times'', which do not share editorial staff, were founded independently and have only had common ownership since 1966. In general, the political position of ''The Times'' is considered to be centre-right. ''The Times'' is the first newspaper to have borne that name, lending it to numerous other papers around the world, such as '' The Times of India'', ''The New York Times'', and more recently, digital-first publications such as TheTimesBlog.com (Since 2017). In countries where these other titles are popular, the newspaper is often referred to as , or as , although the newspaper is of nati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kerchief
A kerchief (from the Old French ''couvrechief'', "cover head"), also known as a bandana, bandanna, or "Wild Rag" (in cowboy culture), is a triangular or square piece of cloth tied around the head, face or neck for protective or decorative purposes. The popularity of ''head kerchiefs'' may vary by culture or religion, often being used as a Christian headcovering by women of the Anabaptist, Eastern Orthodox, and Plymouth Brethren denominations, as well as by some Orthodox Jewish and Muslim women. The '' neckerchief'' and ''handkerchief'' are related items. Types Bandana A bandana or bandanna (from Sanskrit बन्धन or bandhana, "a bond") is a type of large, usually colourful kerchief, originating from the Indian subcontinent, often worn on the head or around the neck of a person. It is considered to be a hat by some. Bandanas are frequently printed in a paisley pattern and are most often used to hold hair back, either as a fashionable head accessory, or for practical pur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Republic Of China (1912–1949)
The Republic of China (ROC), between 1912 and 1949, was a sovereign state recognised as the official designation of China when it was based on Mainland China, prior to the relocation of its central government to Taiwan as a result of the Chinese Civil War. At a population of 541 million in 1949, it was the world's most populous country. Covering , it consisted of 35 provinces, 1 special administrative region, 2 regions, 12 special municipalities, 14 leagues, and 4 special banners. The People's Republic of China (PRC), which rules mainland China today, considers ROC as a country that ceased to exist since 1949; thus, the history of ROC before 1949 is often referred to as Republican Era () of China. The ROC, now based in Taiwan, today considers itself a continuation of the country, thus calling the period of its mainland governance as the Mainland Period () of the Republic of China in Taiwan. The Republic was declared on 1 January 1912 after the Xinhai Revolution, wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |