|
Dakhla Formation
The Dakhla Formation is a Maastrichtian- Danian geologic formation Formation may refer to: Linguistics * Back-formation, the process of creating a new lexeme by removing or affixes * Word formation, the creation of a new word by adding affixes Mathematics and science * Cave formation or speleothem, a secondar ... in Egypt. Dinosaur remains are among the fossils that have been recovered from the formation, although none have yet been referred to a specific genus.Weishampel, et al. (2004). "Dinosaur distribution." Pp. 517–607. Fossil content Reptiles Dinosaurs Mosasaurs Testudines Fish Invertebrates Bivalves Plants See also * List of dinosaur-bearing rock formations ** List of stratigraphic units with indeterminate dinosaur fossils References Bibliography * Weishampel, David B.; Dodson, Peter; and Osmólska, Halszka (eds.): The Dinosauria, 2nd, Berkeley: University of California Press. 861 pp. . Geologic formations of Egypt Upper Cretac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geological Formation
A geological formation, or simply formation, is a body of rock having a consistent set of physical characteristics ( lithology) that distinguishes it from adjacent bodies of rock, and which occupies a particular position in the layers of rock exposed in a geographical region (the stratigraphic column). It is the fundamental unit of lithostratigraphy, the study of strata or rock layers. A formation must be large enough that it can be mapped at the surface or traced in the subsurface. Formations are otherwise not defined by the thickness of their rock strata, which can vary widely. They are usually, but not universally, tabular in form. They may consist of a single lithology (rock type), or of alternating beds of two or more lithologies, or even a heterogeneous mixture of lithologies, so long as this distinguishes them from adjacent bodies of rock. The concept of a geologic formation goes back to the beginnings of modern scientific geology. The term was used by Abraham Gottlob Wer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Globidens
''Globidens'' ("Globe teeth") is an extinct genus of mosasaur lizard classified as part of the Globidensini tribe in the Mosasaurinae subfamily. ''Globidens alabamaensis'' was the first species of ''Globidens'' described, in a publication by Charles W. Gilmore (1912). It is used as the type specimen for ''Globidens''. ''Globidens'' belongs to the family Mosasauridae, which consists of several genera of predatory marine reptiles prevalent during the Late Cretaceous. Specimens of ''Globidens'' have been discovered in Syria, North America, Morocco, Angola, and Indonesia. Among mosasaurs, ''Globidens'' is probably most well known for its highly rounded, globe-like teeth. Description ''Globidens'' was a relatively medium sized mosasaur, measuring long and weighing . It was similar in appearance to other mosasaurs (streamlined body with flippers, a laterally flattened tail and powerful jaws). The teeth of ''Globidens'' differed from those of other mosasaurs in being globu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taphrosphys
''Taphrosphys'' is an extinct genus of bothremydid pleurodiran turtle that was discovered Angola, Morocco and the United States.E. D. Cope. 1869. The fossil reptiles of New Jersey. American Naturalist 3:84-91 The genus consists of type species ''Platemys sulcatus'' (''combinatio nova'' ''T. sulcatus''), ''T. ippolitoi'', ''T. congolensis'', and the dubious ''T. dares''. Discovery The holotype of ''Taphrosphys'' was discovered in New Jersey New Jersey is a state in the Mid-Atlantic and Northeastern regions of the United States. It is bordered on the north and east by the state of New York; on the east, southeast, and south by the Atlantic Ocean; on the west by the Delaware .... References Bothremydidae Prehistoric turtle genera Late Cretaceous turtles Maastrichtian life Paleocene life Cretaceous–Paleogene boundary Fossils of the United States Fossils of Angola Fossils of Morocco Cretaceous North America Cretaceous Africa Fossil taxa described in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
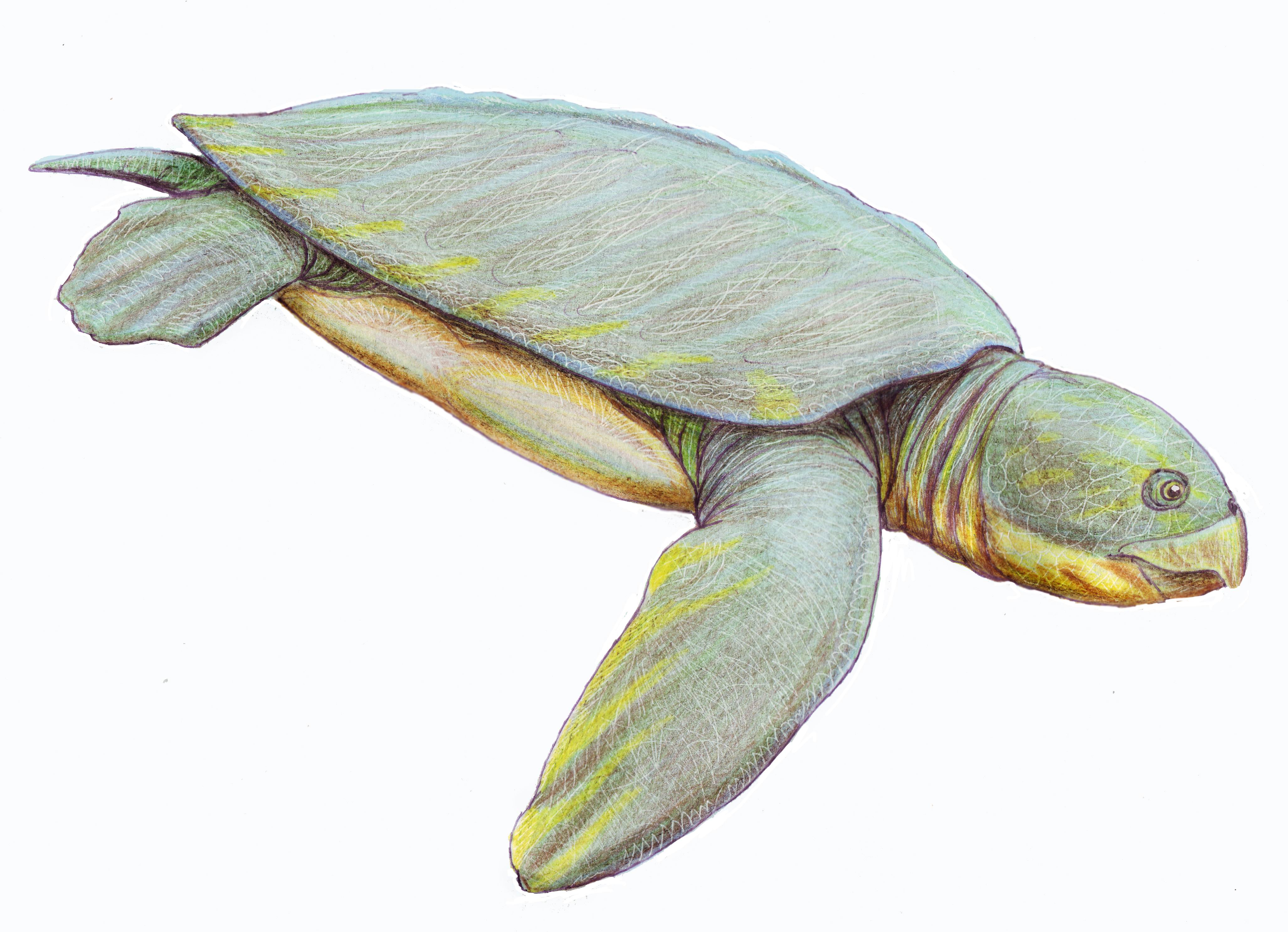
Marine Turtle
Sea turtles (superfamily Chelonioidea), sometimes called marine turtles, are reptiles of the order Testudines and of the suborder Cryptodira. The seven existing species of sea turtles are the flatback, green, hawksbill, leatherback, loggerhead, Kemp's ridley, and olive ridley sea turtles. All six of the sea turtle species present in US waters (all of those listed above except the flatback) are listed as endangered and/or threatened under the Endangered Species Act. The seventh sea turtle species is the flatback, which exists in the waters of Australia, Papua New Guinea and Indonesia. Sea turtles can be separated into the categories of hard-shelled (cheloniid) and leathery-shelled ( dermochelyid).Wyneken, J. 2001. The Anatomy of Sea Turtles. U.S Department of Commerce NOAA Technical Memorandum NMFS-SEFSC-470, 1-172 pp. There is only one dermochelyid species which is the leatherback sea turtle. Description For each of the seven types of sea turtles, females and males are the s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Humerus
The humerus (; ) is a long bone in the arm that runs from the shoulder to the elbow. It connects the scapula and the two bones of the lower arm, the radius and ulna, and consists of three sections. The humeral upper extremity consists of a rounded head, a narrow neck, and two short processes (tubercles, sometimes called tuberosities). The body is cylindrical in its upper portion, and more prismatic below. The lower extremity consists of 2 epicondyles, 2 processes (trochlea & capitulum), and 3 fossae (radial fossa, coronoid fossa, and olecranon fossa). As well as its true anatomical neck, the constriction below the greater and lesser tubercles of the humerus is referred to as its surgical neck due to its tendency to fracture, thus often becoming the focus of surgeons. Etymology The word "humerus" is derived from la, humerus, umerus meaning upper arm, shoulder, and is linguistically related to Gothic ''ams'' shoulder and Greek ''ōmos''. Structure Upper extremity The upper or pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Panchelonioidea
Panchelonioidea is a clade of marine turtles that includes the sea turtle Sea turtles (superfamily Chelonioidea), sometimes called marine turtles, are reptiles of the order Testudines and of the suborder Cryptodira. The seven existing species of sea turtles are the flatback, green, hawksbill, leatherback, loggerhe ...s and related taxa. Phylogeny Evers et al. (2019): References Cryptodira {{Turtle-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nuchal
The nape is the back of the neck. In technical anatomical/medical terminology, the nape is also called the nucha (from the Medieval Latin rendering of the Arabic , "spinal marrow"). The corresponding adjective is ''nuchal'', as in the term ''nuchal rigidity'' for neck stiffness. In many mammals the nape bears a loose, non-sensitive area of skin, known as the scruff, by which a mother carries her young by her teeth, temporarily immobilizing it during transport. In the mating of cats the male will grip the female's scruff with his teeth to help immobilize her during the act, a form of pinch-induced behavioral inhibition Pinch-induced behavioural inhibition (PIBI), also called dorsal immobility, transport immobility or clipnosis, is a partially inert state which results from a gentle squeeze of the skin behind the neck. It is mostly observed among cats and allows .... Cultural connotations In traditional Japanese culture, the was one of the few areas of the body (other than f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pelvis
The pelvis (plural pelves or pelvises) is the lower part of the trunk, between the abdomen and the thighs (sometimes also called pelvic region), together with its embedded skeleton (sometimes also called bony pelvis, or pelvic skeleton). The pelvic region of the trunk includes the bony pelvis, the pelvic cavity (the space enclosed by the bony pelvis), the pelvic floor, below the pelvic cavity, and the perineum, below the pelvic floor. The pelvic skeleton is formed in the area of the back, by the sacrum and the coccyx and anteriorly and to the left and right sides, by a pair of hip bones. The two hip bones connect the spine with the lower limbs. They are attached to the sacrum posteriorly, connected to each other anteriorly, and joined with the two femurs at the hip joints. The gap enclosed by the bony pelvis, called the pelvic cavity, is the section of the body underneath the abdomen and mainly consists of the reproductive organs (sex organs) and the rectum, while the pelvic f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bothremydidae
Bothremydidae is an extinct family of side-necked turtles (Pleurodira) known from the Cretaceous and Cenozoic. They are closely related to Podocnemididae, and are amongst the most widely distributed pleurodire groups, with their fossils having been found in Africa, India, the Middle East, Europe, North America and South America. Bothremydids were aquatic turtles with a high morphological diversity, indicative of generalist, molluscivorous, and piscivorous diets. Unlike modern pleurodires, which are exclusively freshwater, bothremydids inhabited freshwater, marine and coastal settings. Their marine habits allowed bothremydids to disperse across oceanic barriers into Europe and North America during the early Late Cretaceous (Cenomanian). The youngest records of the group are indeterminate remains from Saudi Arabia and Oman, dating to the Miocene. Taxonomy The family is split into two subfamilies and a number of tribes. Bothremydidae *'' Pleurochayah appalachius'' Adrian et al., ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
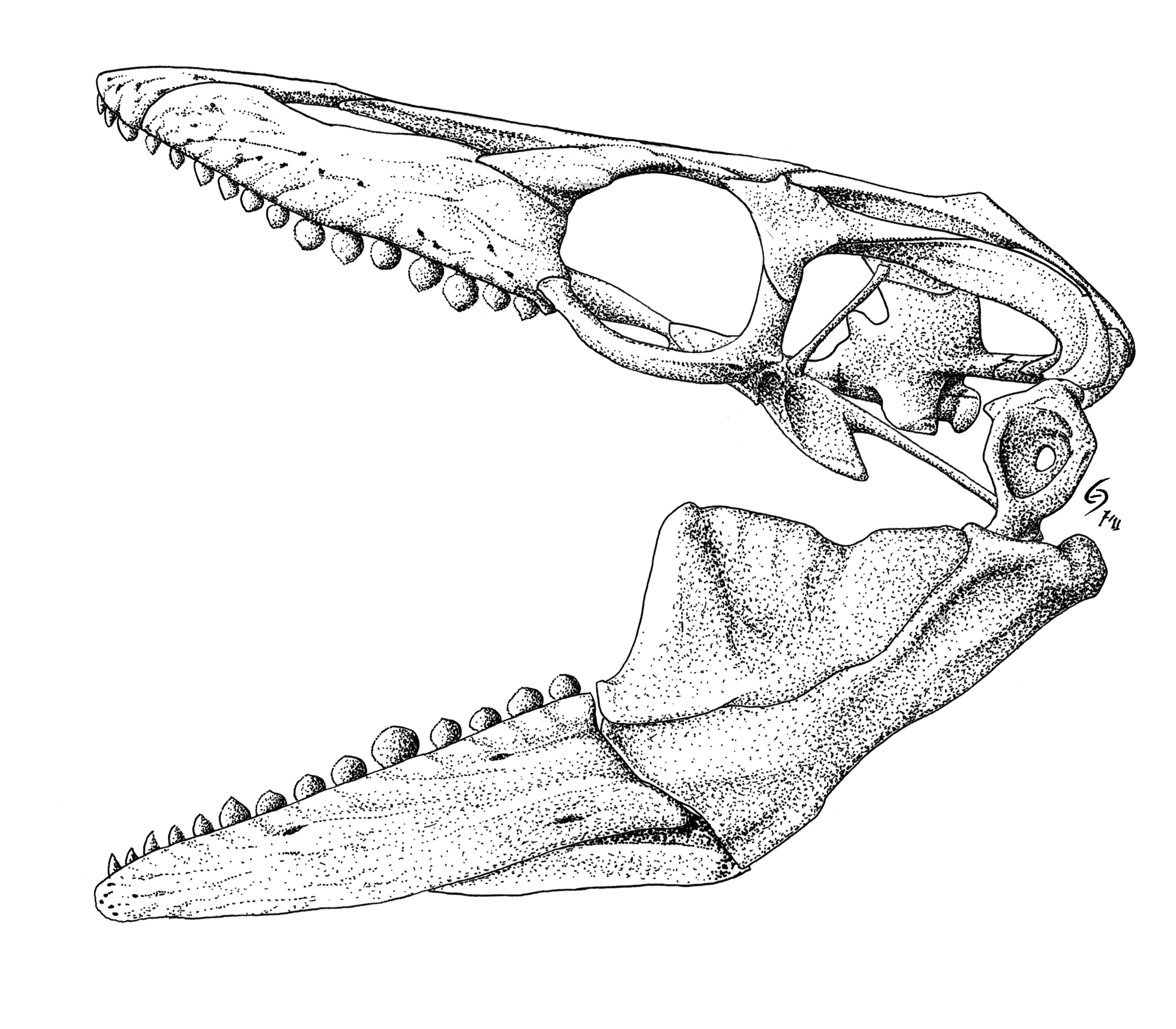
Arenila
''Arenila'' is an extinct genus of bothremydid pleurodiran turtle that was discovered in the Western Desert of Egypt. The genus consists solely of type species ''A. krebsi''.F. Lapparent de Broin and C. Werner. 1998. New Late Cretaceous turtles from the Western Desert, Egypt. Annales de Paléontologie 84(2):131-214 Discovery ''Arenila'' was discovered in the Ammonite Hill Member of the Dakhla Formation The Dakhla Formation is a Maastrichtian- Danian geologic formation Formation may refer to: Linguistics * Back-formation, the process of creating a new lexeme by removing or affixes * Word formation, the creation of a new word by adding affi ..., Egypt, which dates back to the Maastrichtian.E. S. Gaffney, H. Tong, and P. A. Meylan. 2006. Evolution of the side-necked turtles: The families Bothremydidae, Euraxemydidae, and Araripemydidae. Bulletin of the American Museum of Natural History 300:1-318 Description The holotype of ''Arenila'' is a partial skull. Most of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Testudines
Turtles are an order (biology), order of reptiles known as Testudines, characterized by a special turtle shell, shell developed mainly from their ribs. Modern turtles are divided into two major groups, the Pleurodira (side necked turtles) and Cryptodira (hidden necked turtles), which differ in the way the head retracts. There are 360 living and recently extinct species of turtles, including land-dwelling tortoises and freshwater terrapins. They are found on most continents, some islands and, in the case of sea turtles, much of the ocean. Like other Amniote, amniotes (reptiles, birds, and mammals) they breathe air and do not lay eggs underwater, although many species live in or around water. Turtle shells are made mostly of bone; the upper part is the domed Turtle shell#Carapace, carapace, while the underside is the flatter plastron or belly-plate. Its outer surface is covered in scale (anatomy), scales made of keratin, the material of hair, horns, and claws. The carapace bon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |