|
Dacian Bracelets
The Dacian bracelets are bracelets associated with the ancient people known as the Dacians, a distinct branch of the Thracians. These bracelets were used as ornaments, currency, high rank insignia and votive offerings * For the various functions of bracelets with Dacians see * For the high rank insignia, see * For the bracelets used as ornaments, see * For the votive offerings see * For the bracelet-currency see * For the North Thracians see Their ornamentations consist of many elaborate regionally distinct styles. Bracelets of various types were worn by Dacians, but the most characteristic piece of their jewelry was the large multi-spiral bracelets; engraved with palmettes towards the ends and terminating in the shape of an animal head, usually that of a snake. Dacians background The Dacians lived in a very large territory, stretching from the Balkans to the northern Carpathians and from the Black Sea and the Tyras River (Nistru) to the Tisa plain, and at times a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dacian Civilization
Dacian, Geto-Dacian, Daco-Getic or Daco-Getian () often refers to something of or relating to: * Dacia (other) * Dacians * Dacian language Dacian may also refer to: * Dacian archaeology * Dacian art * Dacia in art * Dacian culture * Dacian deities * Dacian goddesses * Dacian gods * Dacian mythology * Dacian names * Dacian sites * Dacian bracelets, bracelets associated with the ancient peoples known as the Dacians, a particularly individualized branch of the Thracians * Dacian kings * Dacian towns, settlements and fortified towns * Dacian tribes * Dacian warfare, spans from c. 10th century BC up to the 2nd century AD in the region defined by Ancient Greek and Latin historians as Dacia * Dacian weapons * Domitian's Dacian War, a conflict between the Roman Empire and the Dacian Kingdom * Trajan's Dacian Wars, two military campaigns fought between the Roman Empire and Dacia during Roman Emperor Trajan's rule It may also refer to: * Daco-Roman, the Romanized culture o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
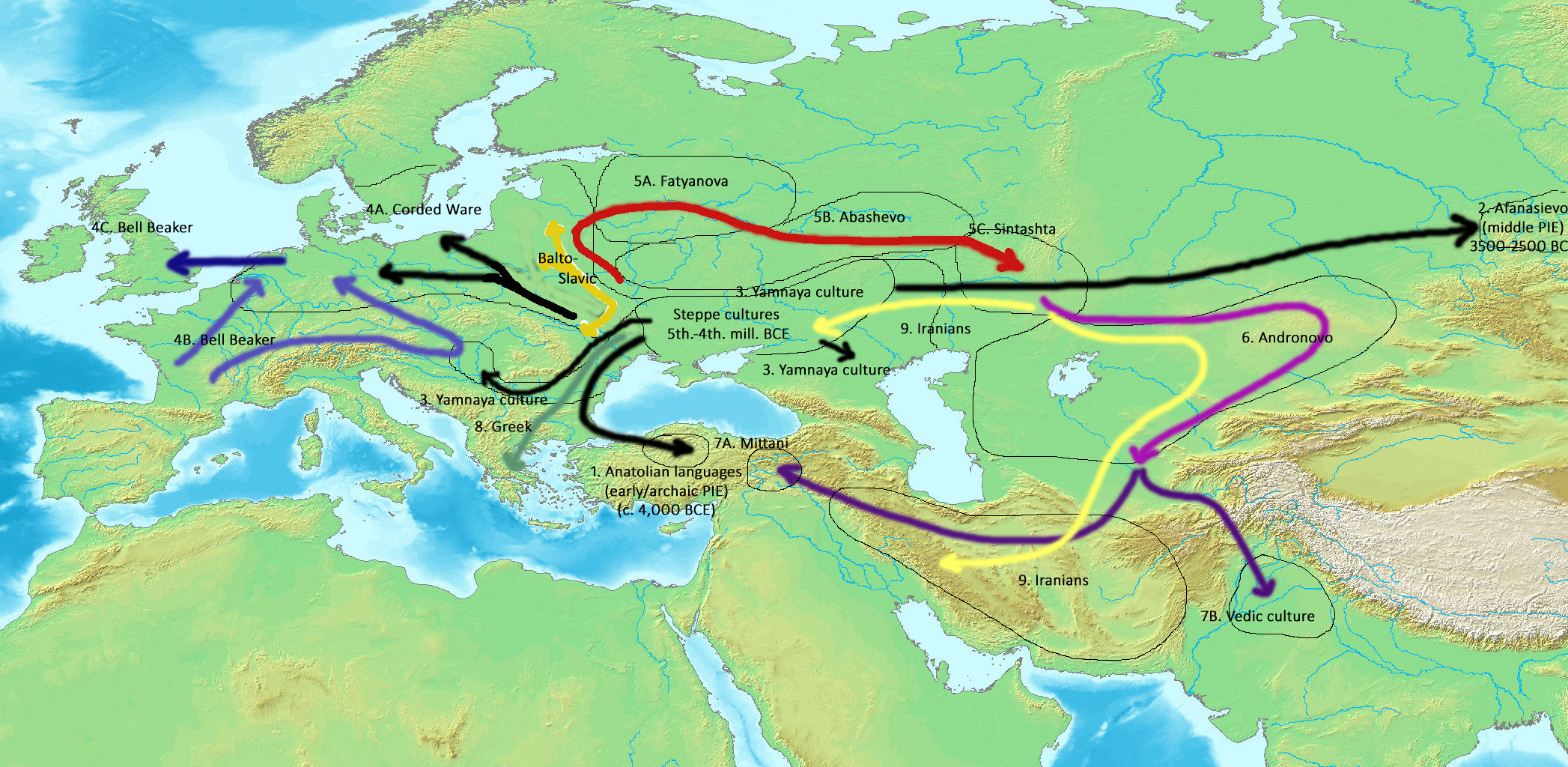
Proto-Indo-Europeans
The Proto-Indo-Europeans are a hypothetical prehistoric population of Eurasia who spoke Proto-Indo-European (PIE), the ancestor of the Indo-European languages according to linguistic reconstruction. Knowledge of them comes chiefly from that linguistic reconstruction, along with material evidence from archaeology and archaeogenetics. The Proto-Indo-Europeans likely lived during the late Neolithic, or roughly the 4th millennium BC. Mainstream scholarship places them in the Pontic–Caspian steppe zone in Eurasia (present-day Ukraine and southern Russia). Some archaeologists would extend the time depth of PIE to the middle Neolithic (5500 to 4500 BC) or even the early Neolithic (7500 to 5500 BC) and suggest alternative location hypotheses. By the early second millennium BC, descendants of the Proto-Indo-Europeans had reached far and wide across Eurasia, including Anatolia (Hittites), the Aegean (the linguistic ancestors of Mycenaean Greece), the north of Europe (Corded War ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Șeica Mare
Șeica Mare (german: Marktschelken; hu, Nagyselyk) is a commune located in Sibiu County, Transylvania, Romania. It is composed of six villages: Boarta, Buia, Mighindoala, Petiș, Șeica Mare and Ștenea. Calvaser (''Kaltwasser''; ''Hidegvíz'') was also a village until the late 20th century, when it was absorbed by Șeica Mare village. At the 2011 census, 88.8% of inhabitants were Romanians, 6% Hungarians, 4.2% Roma and 1% Germans. Villages It is composed of six villages: Buia village was first attested in a document of 1269, under the name of ''poss Bulla''. In 1918, it had 1167 residents, of whom 736 were Romanians and the rest Germans and Hungarians. By 2002, the population was down to 634: 516 Romanians, 104 Hungarians and three Roma. The village is in the southern part of the commune, linked to Șeica Mare by an 11 km stretch of county road. Farkas Bolyai was born there in 1775. Mighindoala (german: Engenthal, meaning "Angels' Valley", hu, Ingodály) is a smal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Șona
Șona (german: Schönau; hu, Szépmező) is a commune located in Alba County, Transylvania, Romania. It is composed of seven villages: Alecuș (''Elekes''), Biia (''Magyarbénye''), Doptău (''Dobtanya''), Lunca Târnavei (until 1964 ''Spini''; ''Kistövis''), Sânmiclăuș (''Betlenszentmiklós''), Șona, and Valea Sasului (''Szászvölgy''). The commune lies on the Transylvanian Plateau, on the banks of the Târnava Mică River. It is located in the northeastern part of the county, from Blaj and from the county seat, Alba Iulia. At the 2011 census, 68.5% of inhabitants were Romanians, 25.2% Hungarians, and 5.8% Roma Roma or ROMA may refer to: Places Australia * Roma, Queensland, a town ** Roma Airport ** Roma Courthouse ** Electoral district of Roma, defunct ** Town of Roma, defunct town, now part of the Maranoa Regional Council *Roma Street, Brisbane, a .... Notable sights include the , dating to the 16th century, and the , dating to the 17th century. Natives * F ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mycenaean Greece
Mycenaean Greece (or the Mycenaean civilization) was the last phase of the Bronze Age The Bronze Age is a historic period, lasting approximately from 3300 BC to 1200 BC, characterized by the use of bronze, the presence of writing in some areas, and other early features of urban civilization. The Bronze Age is the second pri ... in Ancient Greece, spanning the period from approximately 1750 to 1050 BC.. It represents the first advanced and distinctively Greek civilization in mainland Greece with its palatial states, urban organization, works of art, and writing system.Lazaridis, Iosif et al.Genetic origins of the Minoans and Mycenaeans. ''Nature'', 2017Supplementary Information "The Mycenaeans", pp. 2–3).. The Mycenaeans were mainland Greeks, Greek peoples who were likely stimulated by their contact with insular Minoan civilization, Minoan Crete and other Mediterranean Sea, Mediterranean cultures to develop a more sophisticated sociopolitical culture of their own. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Săcueni
Săcueni (; ; ; yi, סעקלהיד ''Seklhid''; ), often spelled ''Săcuieni'', is a town in Bihor County, Romania. It administers five villages: Cadea (''Kágya''), Ciocaia (''Csokaly''), Cubulcut (''Érköbölkút''), Olosig (''Érolaszi'') and Sânnicolau de Munte (''Hegyközszentmiklós''). Geography It is located around 42 km north-east of Oradea, in the proximity of the Hungarian border in Bihor County, Crișana, Romania. History The first written record of the town's name dates back to 1217. Then its name arose in 1278 as ''Zekulhyd'' and in 1325 as ''Zekulhyda'' whose meaning is bridge of Székely in Hungarian, and according to a legend, Székelys were settled down here to guard the bridge of ''Ér'' as early as the 10th century. In 1417, Hungarian king Sigismund gave Székelyhíd the right of organizing a fair. Soon afterwards, it also got the right that the fair to be weekly scheduled. In 1514, it was occupied by György Dózsa's army and then in 1661, it wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Șagu
Șagu ( hu, Németság, german: Segenthau) is a commune in Arad County, Romania Romania ( ; ro, România ) is a country located at the crossroads of Central, Eastern, and Southeastern Europe. It borders Bulgaria to the south, Ukraine to the north, Hungary to the west, Serbia to the southwest, Moldova to the east, and ..., is situated on the Vingăi Plateau and it stretches over 10266 hectares. It is composed of five villages: Cruceni (''Temeskeresztes''; ''Kreuzstätten''), Firiteaz (''Féregyház''), Fiscut (''Temesfűzkút''), Hunedoara Timișană and Șagu (situated at 15 km from Arad). Population According to the last census, the population of the commune counts 3862 inhabitants, out of which 91.5% are Romanians, 3.8% Hungarians, 2.7% Roma, 1.2% Germans and 0.8% are of other or undeclared nationalities. History The first documentary record of Șagu dates back to 1333. Cruceni was attested documentarily in 1772, Firiteaz in 1256, Fiscut in 1493, while Hunedoa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Darova
Darova ( hu, Daruvár; german: Darowa or ''Kranichstätten'') is a commune in Timiș County, Romania. It is composed of three villages: Darova, Hodoș ( hu, Krassóhódos) and Sacoșu Mare (until 1921 Sacoșu Unguresc; hu, Magyarszákos; german: Ungarisch-Sakosch or ''Großsakosch''). Ștefănești ( hu, Istvánfalva) existed as a separate hamlet from 1885 to 1930, when it was merged into Darova, with Darova Nouă ( hu, Újdaruvár) similarly absorbed in 1956. History Darova was founded in 1786 by 57 families of German settlers from Silesia and Württemberg. It happened during the third wave of colonizations in Banat, under the reign of Emperor Joseph II. The name was given in honor of the government commissioner of Temes County, Count Johann Jankovits von Daruwar. Only two years after its founding, in the autumn of 1788, Darova was invaded by the Turks. Most of the younger settlers fled Darova and only a few returned after the Turks were driven out. In 1791, some of the German in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iron Age
The Iron Age is the final epoch of the three-age division of the prehistory and protohistory of humanity. It was preceded by the Stone Age (Paleolithic, Mesolithic, Neolithic) and the Bronze Age (Chalcolithic). The concept has been mostly applied to Iron Age Europe and the Ancient Near East, but also, by analogy, to other parts of the Old World. The duration of the Iron Age varies depending on the region under consideration. It is defined by archaeological convention. The "Iron Age" begins locally when the production of iron or steel has advanced to the point where iron tools and weapons replace their bronze equivalents in common use. In the Ancient Near East, this transition took place in the wake of the Bronze Age collapse, in the 12th century BC. The technology soon spread throughout the Mediterranean Basin region and to South Asia (Iron Age in India) between the 12th and 11th century BC. Its further spread to Central Asia, Eastern Europe, and Central Europe is somewhat dela ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eneolithic
The asterisk ( ), from Late Latin , from Ancient Greek , ''asteriskos'', "little star", is a typographical symbol. It is so called because it resembles a conventional image of a heraldic star. Computer scientists and mathematicians often vocalize it as star (as, for example, in ''the A* search algorithm'' or '' C*-algebra''). In English, an asterisk is usually five- or six-pointed in sans-serif typefaces, six-pointed in serif typefaces, and six- or eight-pointed when handwritten. Its most common use is to call out a footnote. It is also often used to censor offensive words. In computer science, the asterisk is commonly used as a wildcard character, or to denote pointers, repetition, or multiplication. History The asterisk has already been used as a symbol in ice age cave paintings. There is also a two thousand-year-old character used by Aristarchus of Samothrace called the , , which he used when proofreading Homeric poetry to mark lines that were duplicated. Origen is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)

